在javascript中,元素的位置可以分为两种:一种是相对于浏览器视窗的绝对位置;另一种是相对于父节点或 body 元素的偏移位置。下面我们就来了解一下获取两种元素位置的方法。
1、js计算相对于浏览器视窗的元素绝对位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>获取元素的绝对位置</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#div1{width:100px;height:100px;border:3px solid red;}
#div2{width:70px;height:70px;border:3px solid blue;position:relative;}
#div3{width:50px;height:50px;border:3px solid green;position:absolute;
left:20px;top:10px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<div id="div2">
<div id="div3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var div3 = document.getElementById('div3');
div3.getBoundingClientRect().bottom+"px";
console.log("div3元素左外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:");
console.log(div3.getBoundingClientRect().left);
console.log("div3元素右外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:");
console.log(div3.getBoundingClientRect().right);
console.log("div3元素上外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:");
console.log(div3.getBoundingClientRect().top);
console.log(" div3元素下外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为");
console.log(div3.getBoundingClientRect().bottom);
</script>
</body>
</html>分析:(前提,将body 节点的默认内外边距去掉了)
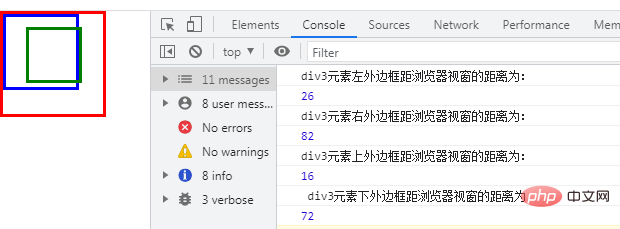
div3元素左外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:div3 的 left(20)+div2 的左边框宽度(3)+div1 的左边框宽度(3)=26
div3元素右外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:div3元素左外边框距浏览器视窗的距离(26)+div3的左边框宽度(3)+div3的内容宽度(50)+div3的右边框宽度(3)=26+3+50+3=82
div3元素上外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:div1和div2的左边框宽度(3+3)+div3的top值(10)=6+10=16
div3元素下外边框距浏览器视窗的距离为:div3元素上外边框距浏览器视窗的距离(16)+div3的上边框宽度(3)+div3的内容宽度(50)+div3的下边框宽度(3)=16+3+50+3=72
我们看看输出结果是不是这样的:
在这段代码中,要介绍2个重要的方法:getElementById()和getBoundingClientRect()。
getElementById()方法可以根据指定id值来获取到元素对象(该方法可返回对拥有指定 ID 的第一个对象的引用)
而元素对象的getBoundingClientRect()方法可以获取元素相对于浏览器视窗的位置,它会返回一个 Object 对象,该对象有 6 个属性:top、left、right、bottom、width、height:
元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().top可返回元素上外边框到浏览器视窗上边框的距离;元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().left可返回元素左外边框到浏览器视窗左边框的距离;元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().right可返回元素右外边框到浏览器视窗左边框的距离;元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().bottom可返回元素下外边框到浏览器视窗上边框的距离;元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().width可返回元素的宽度,其中包括左、右边框宽度;元素对象.getBoundingClientRect().height可返回元素的高度,其中包括上、下边框宽度。
2、计算相对于父节点或 body 元素的偏移位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>获取元素的偏移位置</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#div1{width:100px;height:100px;border:3px solid red;}
#div2{width:70px;height:70px;border:3px solid blue;position:relative;}
#div3{width:50px;height:50px;border:3px solid green;position:absolute;left:20px;
top:10px;}
#div4{width:30px;height:30px;border:3px solid olive;position:absolute;left:20px;
top:10px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<div id="div2">
<div id="div3">
<div id="div4"><div>
</div>
</div>
</div><br /><br /><br /><br />
<div id="content"></div>
<script>
var div2 = document.getElementById('div2');
var div4 = document.getElementById('div4');
console.log("div2的水平偏移位置为:");
console.log(div2.offsetLeft);
console.log("div4的水平偏移位置为:");
console.log(div4.offsetLeft);
console.log("div2的垂直偏移位置为:");
console.log(div2.offsetTop);
console.log("div4的垂直偏移位置为:");
console.log(div4.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>
</html>分析:(前提,将body 节点的默认内外边距去掉了)
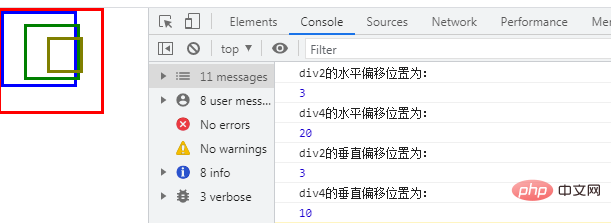
div2因为没有定位父节点,所以其偏移是相对于 body 节点的,则水平和垂直偏移位置都为div1的边框宽度(3px)等于3px。
div4最近的定位父节点为div3,水平偏移位置就是div3的left 属性值(20px),垂直偏移位置就是div3的top 属性值(10px)。
我们看看输出结果是不是这样的:
通过上面示例,我们来了解两个属性:offsetLeft 和 offsetTop。
offsetLeft 和 offsetTop属性可以分别获取元素相对定位父元素或 body 元素的水平和垂直偏移位置。
【推荐学习:javascript高级教程】
以上就是使用js要如何计算元素的位置的详细内容,更多请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
