下面由Laravel教程栏目给大家介绍Laravel 5.8 中如何正确地应用 Repository 设计模式,希望对需要的朋友有所帮助!

在本文中,我会向你展示如何在 Laravel 中从头开始实现 repository 设计模式。我将使用 Laravel 5.8.3 版,但 Laravel 版本不是最重要的。在开始写代码之前,你需要了解一些关于 repository 设计模式的相关信息。
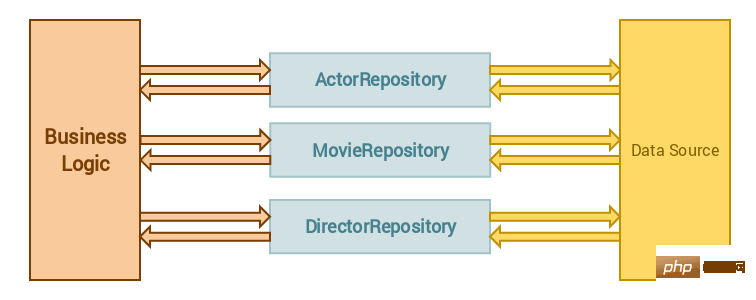
repository 设计模式允许你使用对象,而不需要了解这些对象是如何持久化的。本质上,它是数据层的抽象。
这意味着你的业务逻辑不需要了解如何检索数据或数据源是什么,业务逻辑依赖于 repository 来检索正确的数据。
关于这个模式,我看到有人将它误解为 repository 被用来创建或更新数据。 这不是 repository 应该做的,repository 不应该创建或更新数据,仅仅用于检索数据。
理解透了吧?接下来一起写代码
既然我们从头开始,那么我们先创建一个新的 Laravel 项目吧:
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel repository
对于本教程,我们将构建一个小型的博客应用。现在我们已经创建好了一个新的 Laravel 项目,接下来应该为它创建一个控制器和模型。
php artisan make:controller BlogController
这将在 app/Http/Controllers 目录中创建 BlogController 。
php artisan make:model Models/Blog -m
提示:-m 选项会创建一个对应的数据库迁移,你可以在 *database/migrations 目录中找到所生成的迁移。*
现在你应该能在 app/Models 目录中找到刚生成的模型 Blog 了吧。这只是一种我喜欢的存放模型的方式。
现在我们有了控制器和模型,是时候看看我们创建的迁移文件了。除了默认的 Laravel 时间戳字段外,我们的博客只需要 标题、内容 和 用户ID 字段。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;class CreateBlogsTable extends Migration{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('blogs', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->string('title');
$table->text('content');
$table->integer('user_id');
$table->timestamps();
$table->foreign('user_id')
->references('id')
->on('users');
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('blogs');
}}提示:
如果你使用的是 Laravel 5.8 以下的旧版本,请将
$table->bigIncrements('id');替换为:
$table->increments('id');设置数据库
我将使用 MySQL 数据库作为示例,第一步就是创建一个新的数据库。
mysql -u root -p create database laravel_repository;
以上命令将会创建一个叫 laravel_repository 的新数据库。接下来我们需要添加数据库信息到 Laravel 根目录的 .env 文件中。
DB_DATABASE=laravel_repositoryDB_USERNAME=rootDB_PASSWORD=secret
当你更新了 .env 文件后我们需要清空缓存:
php artisan config:clear
运行迁移
现在我们已经设置好了数据库,可以开始运行迁移了:
php artisan migrate
这将会创建 blogs 表,包含了我们在迁移中声明的 title , content 和 user_id 字段。
实现 repository 设计模式
一切就绪,我们现在可以开始实现 repository 设计风格了。我们将会在 app 目录中创建 Repositories 目录。我们将要创建的第二个目录是 Interfaces 目录,这个目录位于 Repositories 目录中。
在 Interfaces 文件中我们将创建一个包含两个方法的 BlogRepositoryInterface 接口。
- 返回所有博客文章的 all 方法
- 返回特定用户所有博客文章的 getByUser 方法
<?php
namespace App\Repositories\Interfaces;use App\User;interface BlogRepositoryInterface{
public function all();
public function getByUser(User $user);}我们需要创建的最后一个类是将要实现 BlogRepositoryInterface 的 BlogRepository ,我们会写一个最简单的实现方式。
<?php
namespace App\Repositories;use App\Models\Blog;use App\User;use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;class BlogRepository implements BlogRepositoryInterface{
public function all()
{
return Blog::all();
}
public function getByUser(User $user)
{
return Blog::where('user_id',$user->id)->get();
}}你的 Repositories 目录应该像这样:
app/└── Repositories/
├── BlogRepository.php
└── Interfaces/
└── BlogRepositoryInterface.php你现在已经成功创建了一个 repository 了。但是我们还没有完成,是时候开始使用我们的 repository 了。
在控制器中使用 Repository
要开始使用 BlogRepository ,我们首先需要将其注入到 BlogController 。由于 Laravel 的依赖注入,我们很容易用另一个来替换它。这就是我们控制器的样子:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;use App\User;class BlogController extends Controller{
private $blogRepository;
public function __construct(BlogRepositoryInterface $blogRepository)
{
$this->blogRepository = $blogRepository;
}
public function index()
{
$blogs = $this->blogRepository->all();
return view('blog')->withBlogs($blogs);
}
public function detail($id)
{
$user = User::find($id);
$blogs = $this->blogRepository->getByUser($user);
return view('blog')->withBlogs($blogs);
}}如你所见,控制器中的代码很简短,可读性非常的高。不需要十行代码就可以获取到所需的数据,多亏了 repository ,所有这些逻辑都可以在一行代码中完成。这对单元测试也很好,因为 repository 的方法很容易复用。
repository 设计模式也使更改数据源变得更加容易。在这个例子中,我们使用 MySQL 数据库来检索我们的博客内容。我们使用 Eloquent 来完成查询数据库操作。但是假设我们在某个网站上看到了一个很棒的博客 API,我们想使用这个 API 作为数据源,我们所要做的就是重写 BlogRepository 来调用这个 API 替换 Eloquent 。
RepositoryServiceProvider
我们将注入 BlogController 中的 BlogRepository ,而不是注入 BlogController 中的 BlogRepositoryInterface ,然后让服务容器决定将使用哪个存储库。这将在 AppServiceProvider 的 boot 方法中实现,但我更喜欢为此创建一个新的 provider 来保持整洁。
php artisan make:provider RepositoryServiceProvider
我们为此创建一个新的 provider 的原因是,当您的项目开始发展为大型项目时,结构会变得非常凌乱。设想一下,一个拥有 10 个以上模型的项目,每个模型都有自己的 repository ,你的 AppServiceProvider 可读性将会大大降低。
我们的 RepositoryServiceProvider 会像下面这样:
<?php
namespace App\Providers;use App\Repositories\BlogRepository;use App\Repositories\Interfaces\BlogRepositoryInterface;use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;class RepositoryServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider{
public function register()
{
$this->app->bind(
BlogRepositoryInterface::class,
BlogRepository::class
);
}}留意用另一个 repository 替代 BlogRepository 是多么容易!
不要忘记添加 RepositoryServiceProvider 到 config/app.php 文件的 providers 列表中。完成了这些后我们需要清空缓存:
'providers' => [
//测试¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥¥
\App\Providers\RepositoryServiceProvider::class],php artisan config:clear
就是这样
现在你已经成功实现了 repository 设计模式,不是很难吧?
你可以选择增加一些路由和视图来拓展代码,但本文将在这里结束,因为本文主要是介绍 repository 设计模式的。
如果你喜欢这篇文章,或者它帮助你实现了 repository 设计模式,请确保你也查看了我的其他文章。如果你有任何反馈、疑问,或希望我撰写另一个有关 Laravel 的主题,请随时发表评论。
以上就是教你在Laravel5.8中应用Repository设计模式的详细内容,更多请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
