python里面的matplotlib.pylot是大家比较常用的,功能也还不错的一个包。基本框架比较简单,但是做一个功能完善且比较好看整洁的图,免不了要网上查找一些函数。于是,为了节省时间,
python里面的matplotlib.pylot是大家比较常用的,功能也还不错的一个包。基本框架比较简单,但是做一个功能完善且比较好看整洁的图,免不了要网上查找一些函数。于是,为了节省时间,可以一劳永逸。我把常用函数作了一个总结,最后写了一个例子,以后基本不用怎么改了。
一、作图流程:
1.准备数据, , 3作图, 4定制, 5保存, 6显示
1.数据可以是numpy数组,也可以是list
2创建画布:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #figure(num=None, figsize=None, dpi=None, facecolor=None, edgecolor=None, frameon=True) #num:图像编号或名称,数字为编号 ,字符串为名称 #figsize:指定figure的宽和高,单位为英寸; #dpi参数指定绘图对象的分辨率,即每英寸多少个像素,缺省值为80 ,1英寸等于2.5cm,A4纸是 21*30cm的纸张 #facecolor:背景颜色 #edgecolor:边框颜色 #frameon:是否显示边 fig = plt.figure() fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6), dpi=80) fig.add_axes() fig, axes = plt.subplos(nrows = 2, ncols = 2) #axes是长度为4的列表
3、作图路线
一维数据:
axes[0, 0].plot(x, y) axes[0,1].bar([1,2,3], [2,4,8]) axes[0,2].barh([1,2,3], [2,4,8]) axes[1,0].axhline(0.45) axes[1, 1].scatter(x, y) axes[1,2].axvline(0.65) axes[2,0].fill(x,y, color = 'blue') axes[2,1].fill_between(x,y, color = 'blue') axes[2,2].violinplot(y) axes[0,3].arrow(0,0,0.5,0.5) axes[1,3].quiver(x,y)
4, 定制
plt.plot(x,y, alpha=0.4, c = 'blue', maker = 'o')
#颜色,标记,透明度
# 显示数学文本
t = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
s = np.sin(2*np.pi*t)
plt.plot(t,s)
plt.title(r'$\alpha_i > \beta_i$', fontsize=20)
plt.text(1, -0.6, r'$\sum_{i=0}^\infty x_i$', fontsize=20)
plt.text(0.6, 0.6, r'$\mathcal{A}\mathrm{sin}(2 \omega t)$',
fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('volts (mV)')
fig = plt.figure()
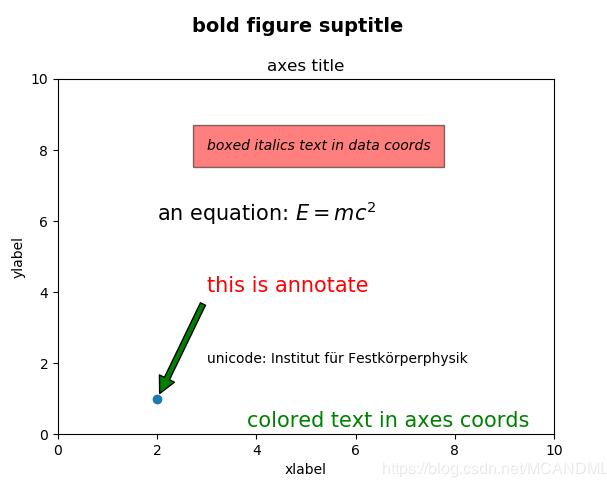
fig.suptitle('bold figure suptitle', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
ax.set_title('axes title')
ax.set_xlabel('xlabel')
ax.set_ylabel('ylabel')
ax.text(3, 8, 'boxed italics text in data coords', style='italic',
bbox={'facecolor':'red', 'alpha':0.5, 'pad':10})
ax.text(2, 6, r'an equation: $E=mc^2$', fontsize=15)
ax.text(3, 2, u'unicode: Institut f\374r Festk\366rperphysik')
ax.text(0.95, 0.01, 'colored text in axes coords',
verticalalignment='bottom', horizontalalignment='right',
transform=ax.transAxes,
color='green', fontsize=15)
ax.plot([2], [1], 'o')
# 注释
ax.annotate('我是注释啦', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 4),color='r',size=15,
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='g', shrink=0.05))
ax.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
5, 保存显示
plt.savefig("1.png")
plt.savefig("1.png", trainsparent =True)
plt.show()
二、部分函数使用详解:
1, fig.add_subplot(numrows, numcols, fignum) ####三个参数,分别代表子图的行数,列数,图索引号。 eg: ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 1) (or ,ax = fig.add_subplot(231))
2, plt.subplots()使用
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi,400)
y = np.sin(x**2)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_title('Simple plot')
# Creates two subplots and unpacks the output array immediately
#fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharey=True)
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax1.set_title('Sharing Y axis')
ax2.scatter(x, y)
# Creates four polar axes, and accesses them through the returned array
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, subplot_kw=dict(polar=True))
axes[0, 0].plot(x, y)
axes[1, 1].scatter(x, y)
# Share a X axis with each column of subplots
plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex='col')
# Share a Y axis with each row of subplots
plt.subplots(2, 2, sharey='row')
# Share both X and Y axes with all subplots
plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex='all', sharey='all')
# Note that this is the same as
plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
# Creates figure number 10 with a single subplot
# and clears it if it already exists.
fig, ax=plt.subplots(num=10, clear=True)
3.plt.legend()
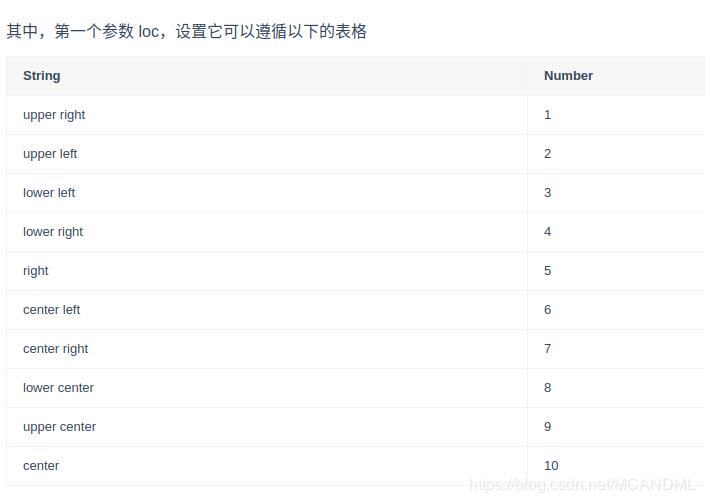
plt.legend(loc='String or Number', bbox_to_anchor=(num1, num2)) plt.legend(loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor (0.6,0.95),ncol=3,fancybox=True,shadow=True) #bbox_to_anchor被赋予的二元组中,第一个数值用于控制legend的左右移动,值越大越向右边移动,第二个数值用于控制legend的上下移动,值越大,越向上移动
以上这篇python matplotlib中的subplot函数使用详解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。
