chcon 命令格式如下:
[root@localhost ~]# chcon [选项] 文件或目录
选项:- -R: 递归,当前目录和目录下的所有子文件同时设置;
- -t: 修改安全上下文的类型字段,最常用;
- -u: 修改安全上下文的身份字段;
- -r: 修改安全上下文的角色字段;
举个例子:
[root@localhost ~]# echo'test page!!!' >> /var/www/html/index.html
#建立一个网页文件,并写入“test page!!!”
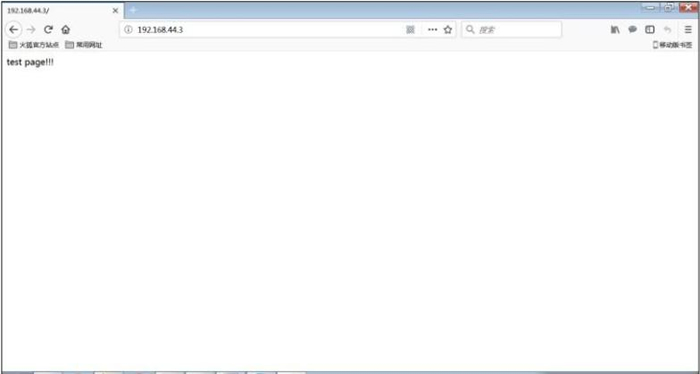
图 1 访问 apache 测试页
[root@localhost ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
#这个网页文件的模式类别是httpd_sys_content_t
[root@localhost ~]# seinfo -t I grep var_t
#查询SELinun中所有的类型、发现有一个类型叫var_t
[root@localhost ~]# chcon -t var_t /var/www/html/index.html
#把网页文件的类型修改为var_t类型
[root@localhost ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. toot root unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
#这个网页的类型已经被修改了
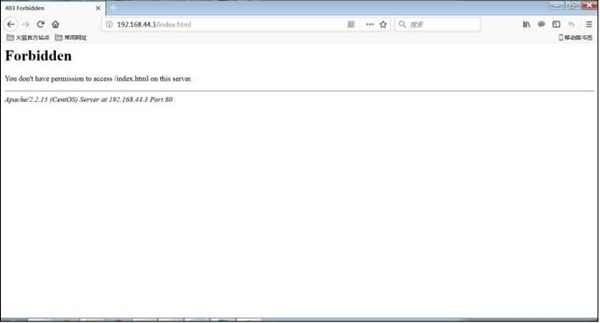
图 2 拒绝访问
这时网页就会提示权限拒绝,这里我们已经知道是安全上下文不匹配惹的祸!当然,我们可以通过 chcon 命令修改回来就可以修复。不过,我们还有一个命令 restorecon,这个命令的作用就是把文件的安全上下文恢复成默认的安全上下文。SELinux 的安全上下文设定非常完善,所以使用 restorecon 命令就可以修复安全上下文不匹配所引起的问题。
restorecon 命令格式如下:
[root@localhost ~] # restorecon [选项】 文件或目录
选项:- -R:递归.当前目录和目录下所有的子文件同时恢复;
- -V:把恢复过程显示到屏幕上;
例如:
[root@1ocalhost ~]# restorecon -Rv /var/www/html/index.html
restorecon reset /var/www/html/index.html context
unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0->unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
#这里已经提示了安全上下文从var_t恢复成了httpd_sys_content_t
[root@1ocalhost ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
#查看一下,安全上下文已经恢复正常了.网页的访问也已经恢复正常了
