单向链表在遍历时只能从头到尾或者从尾遍历到头;所以单向链表可以轻松到达下一节点,但是回到上一个节点是很困难的 而双向链表既可以从头遍历到尾, 又可以从尾遍历到头,链表
单向链表在遍历时只能从头到尾或者从尾遍历到头;所以单向链表可以轻松到达下一节点,但是回到上一个节点是很困难的
而双向链表既可以从头遍历到尾, 又可以从尾遍历到头,链表的相联是双向的,一个节点既有向前连接的引用,也有向后连接的引用
但是正因如此,双向链表在插入或者删除某个节点时,需要处理四个节点的引用,并且所占用内存空间也更大一些
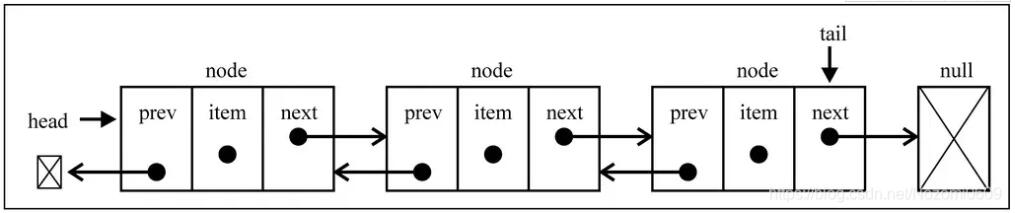
双向链表实现
JavaScript 代码实现双向链表
// 创建双向链表的构造函数
function DoublyLinkedList() {
// 创建节点构造函数
function Node(element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
this.prev = null // 新添加的
}
// 定义属性
this.length = 0
this.head = null
this.tail = null // 新添加的
// 定义相关操作方法
// 在尾部追加数据
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.append = function (element) {
// 1.根据元素创建节点
var newNode = new Node(element)
// 2.判断列表是否为空列表
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = newNode
}
// 3.length+1
this.length++
}
// 在任意位置插入数据
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, element) {
// 1.判断越界的问题
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false
// 2.创建新的节点
var newNode = new Node(element)
// 3.判断插入的位置
if (position === 0) { // 在第一个位置插入数据
// 判断链表是否为空
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.head.prev = newNode
newNode.next = this.head
this.head = newNode
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 插入到最后的情况
// 思考: 这种情况是否需要判断链表为空的情况呢? 答案是不需要, 为什么?
this.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = newNode
} else { // 在中间位置插入数据
// 定义属性
var index = 0
var current = this.head
var previous = null
// 查找正确的位置
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 交换节点的指向顺序
newNode.next = current
newNode.prev = previous
current.prev = newNode
previous.next = newNode
}
// 4.length+1
this.length++
return true
}
// 根据位置删除对应的元素
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.判断越界的问题
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.判断移除的位置
var current = this.head
if (position === 0) {
if (this.length == 1) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head = this.head.next
this.head.prev = null
}
} else if (position === this.length -1) {
current = this.tail
this.tail = this.tail.prev
this.tail.next = null
} else {
var index = 0
var previous = null
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
}
// 3.length-1
this.length--
return current.element
}
// 根据元素获取在链表中的位置
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (element) {
// 1.定义变量保存信息
var current = this.head
var index = 0
// 2.查找正确的信息
while (current) {
if (current.element === element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
// 3.来到这个位置, 说明没有找到, 则返回-1
return -1
}
// 根据元素删除
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.remove = function (element) {
var index = this.indexOf(element)
return this.removeAt(index)
}
// 判断是否为空
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.length === 0
}
// 获取链表长度
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length
}
// 获取第一个元素
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.getHead = function () {
return this.head.element
}
// 获取最后一个元素
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.getTail = function () {
return this.tail.element
}
// 遍历方法的实现
// 正向遍历的方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.forwardString = function () {
var current = this.head
var forwardStr = ""
while (current) {
forwardStr += "," + current.element
current = current.next
}
return forwardStr.slice(1)
}
// 反向遍历的方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.reverseString = function () {
var current = this.tail
var reverseStr = ""
while (current) {
reverseStr += "," + current.element
current = current.prev
}
return reverseStr.slice(1)
}
// 实现toString方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.forwardString()
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
