机器学习过程中经常需要可视化,有助于加强对模型和参数的理解。 下面对梯度下降过程进行动图演示,可以修改不同的学习率,观看效果。 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfro
机器学习过程中经常需要可视化,有助于加强对模型和参数的理解。
下面对梯度下降过程进行动图演示,可以修改不同的学习率,观看效果。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython import display
X = 2*np.random.rand(100,1)
y = 4+3*X+np.random.randn(100,1) # randn正态分布
X_b = np.c_[np.ones((100,1)),X] # c_行数相等,左右拼接
eta = 0.1 # 学习率
n_iter = 1000 # 迭代次数
m = 100 # 样本点个数
theta = np.random.randn(2,1) # 参数初始值
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
mngr = plt.get_current_fig_manager() # 获取当前figure manager
mngr.window.wm_geometry("+520+520") # 调整窗口在屏幕上弹出的位置,注意写在打开交互模式之前
# 上面固定窗口,方便screentogif定位录制,只会这种弱弱的方法
plt.ion()# 打开交互模式
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = "SimHei"# 消除中文乱码
for iter in range(n_iter):
plt.cla() # 清除原图像
gradients = 2/m*X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-y)
theta = theta - eta*gradients
X_new = np.array([[0],[2]])
X_new_b = np.c_[np.ones((2,1)),X_new]
y_pred = X_new_b.dot(theta)
plt.axis([0,2,0,15])
plt.plot(X,y,"b.")
plt.plot(X_new,y_pred,"r-")
plt.title("学习率:{:.2f}".format(eta))
plt.pause(0.3) # 暂停一会
display.clear_output(wait=True)# 刷新图像
plt.ioff()# 关闭交互模式
plt.show()
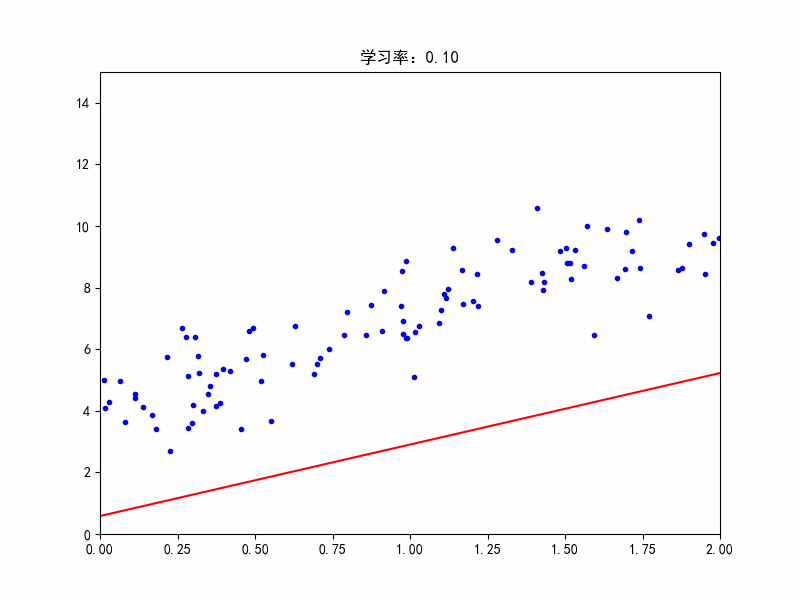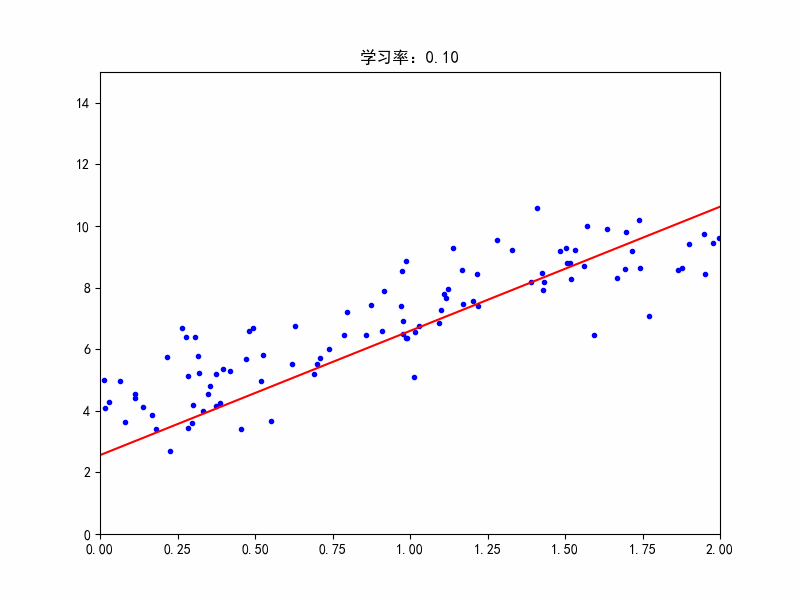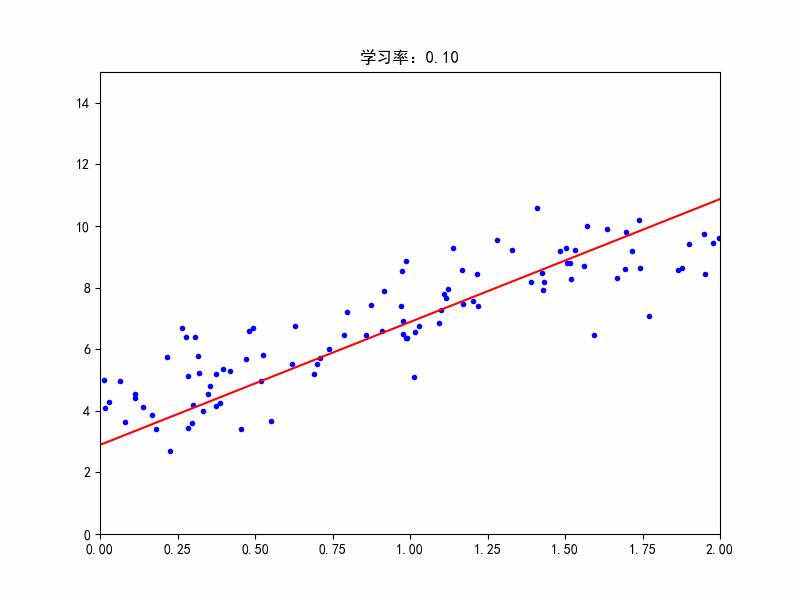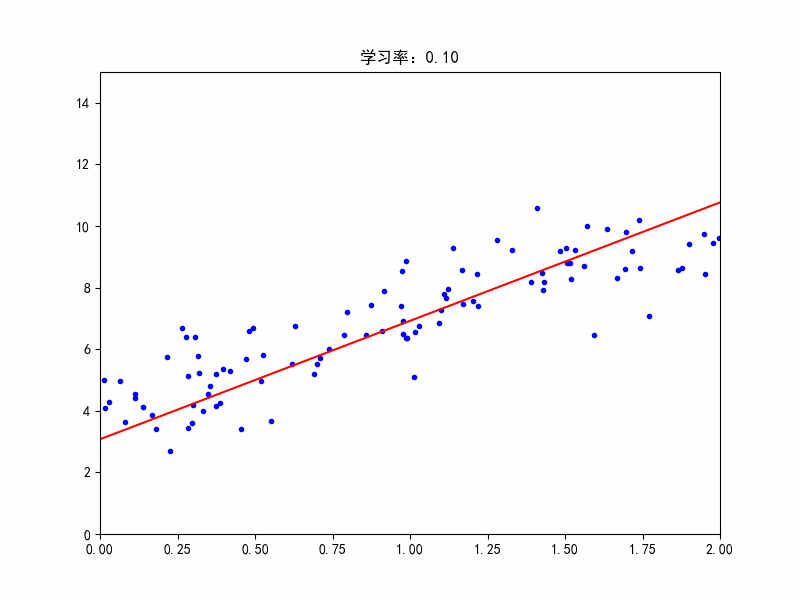
学习率:0.1,较合适
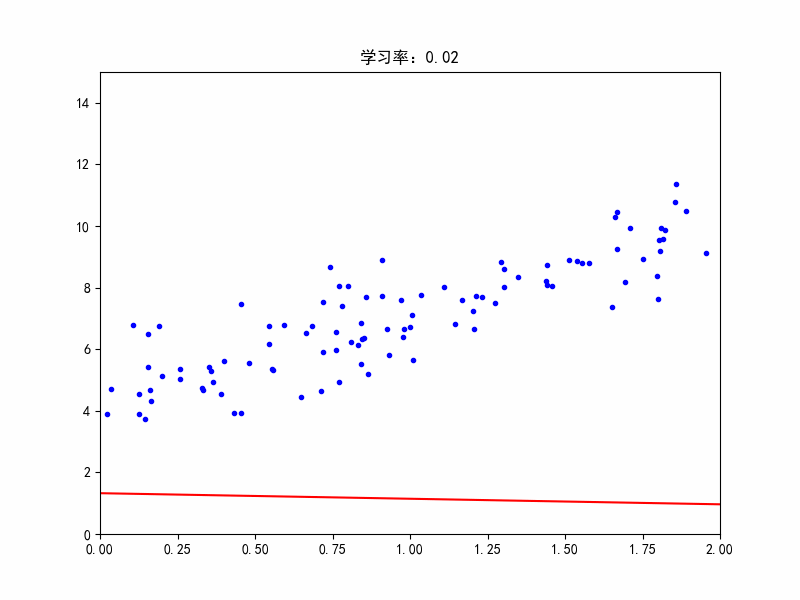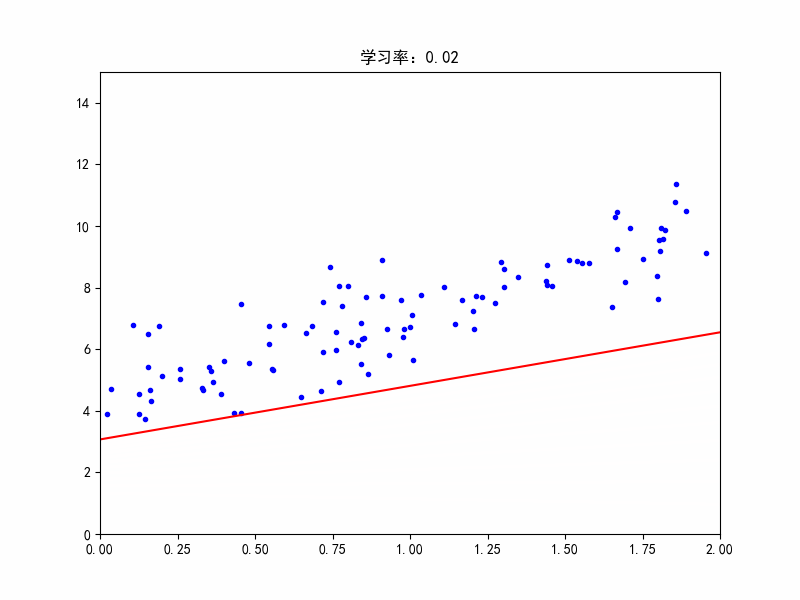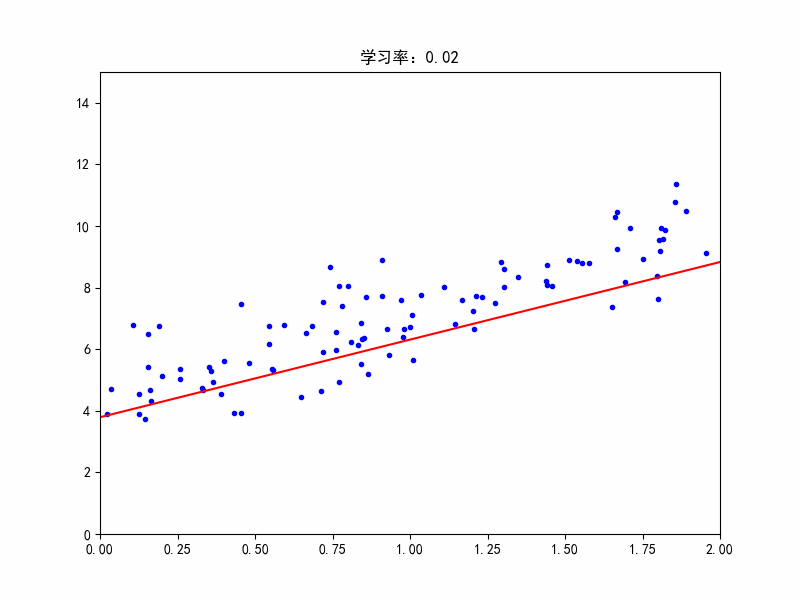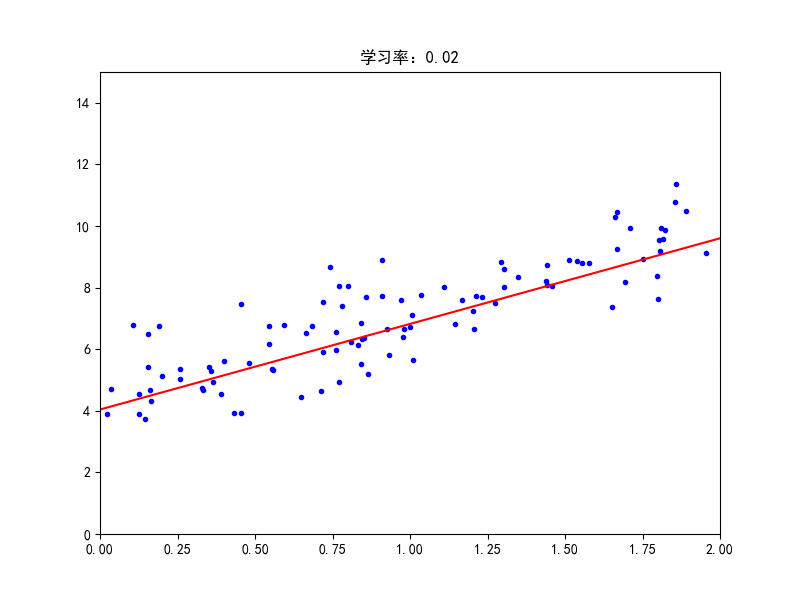
学习率:0.02,收敛变慢了
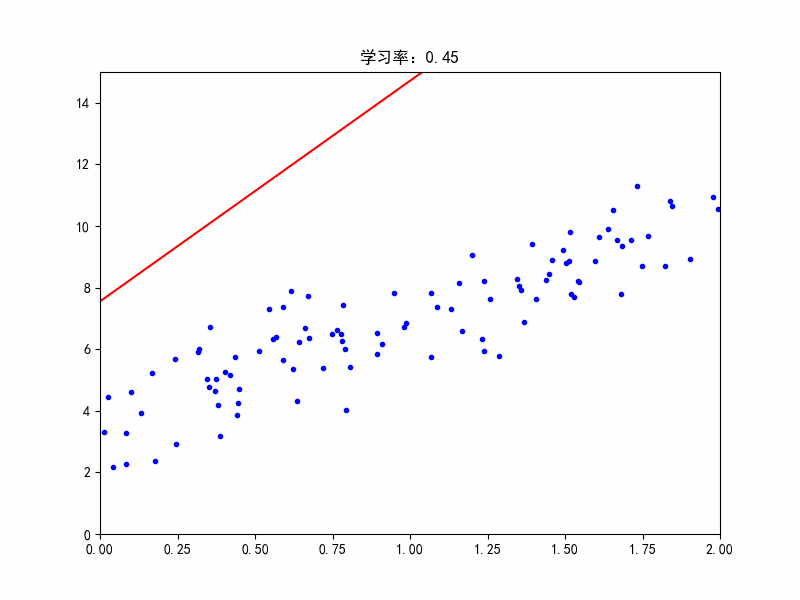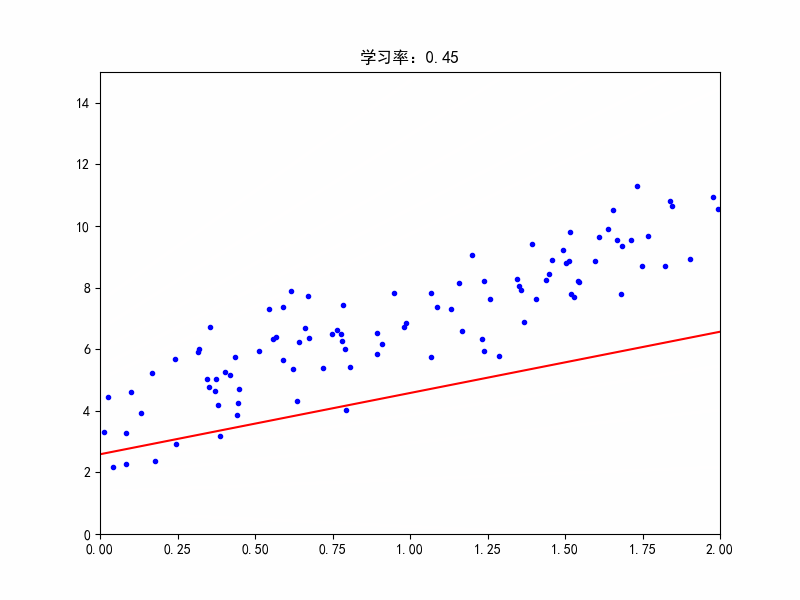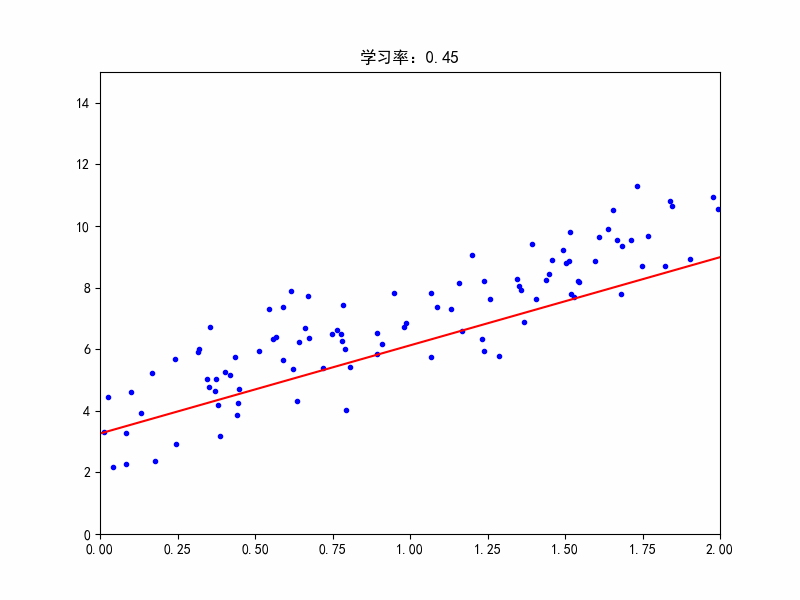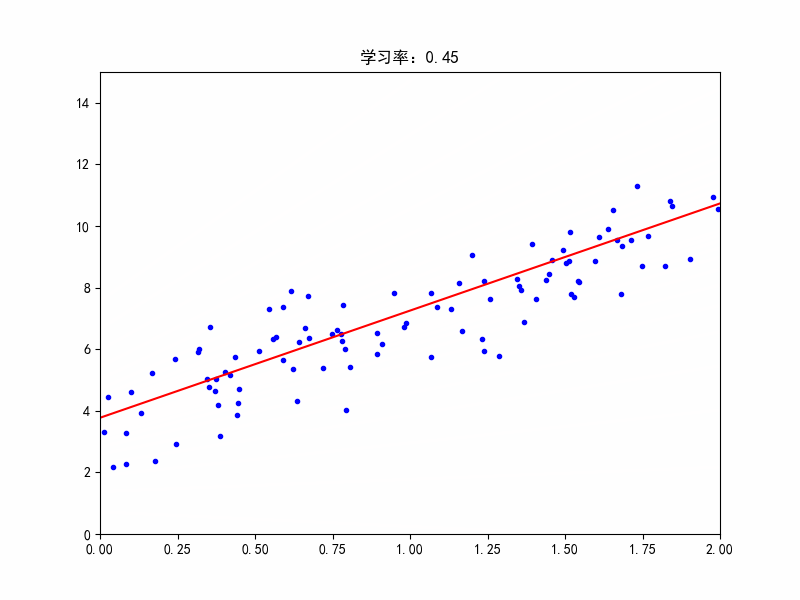
学习率:0.45,在最佳参数附近震荡
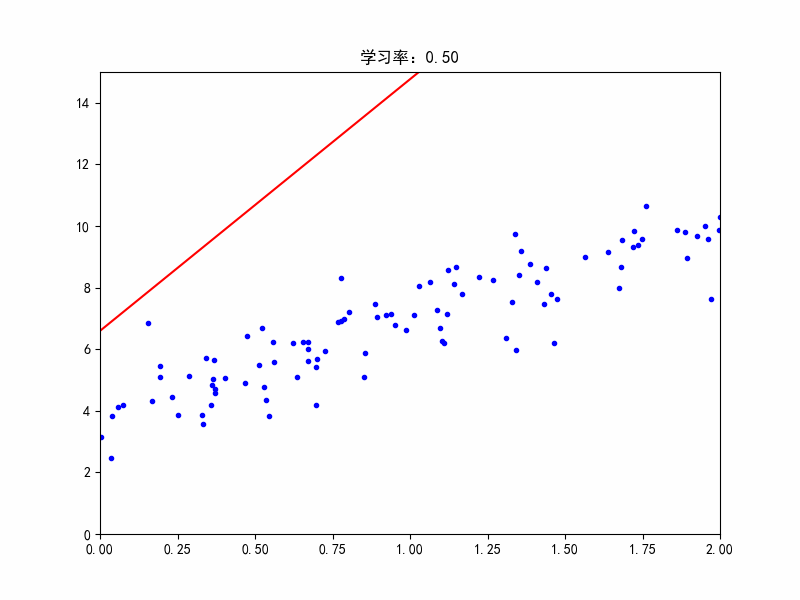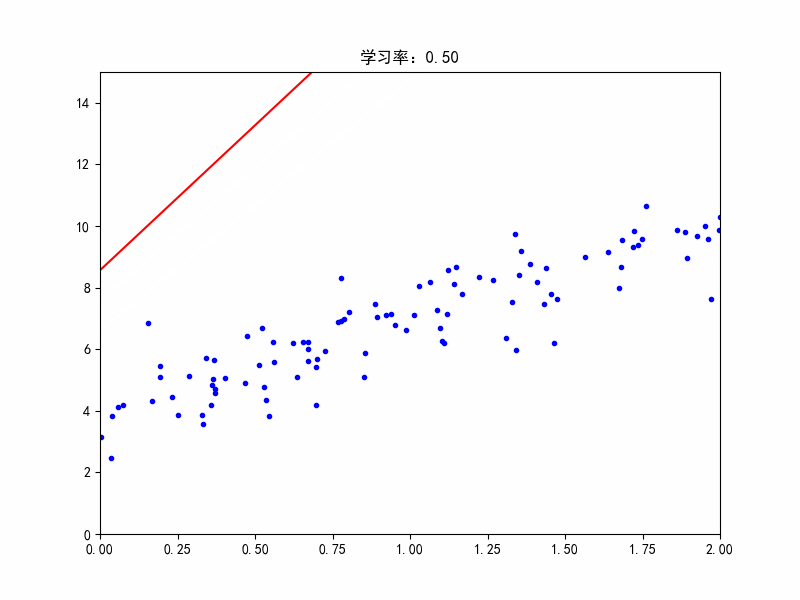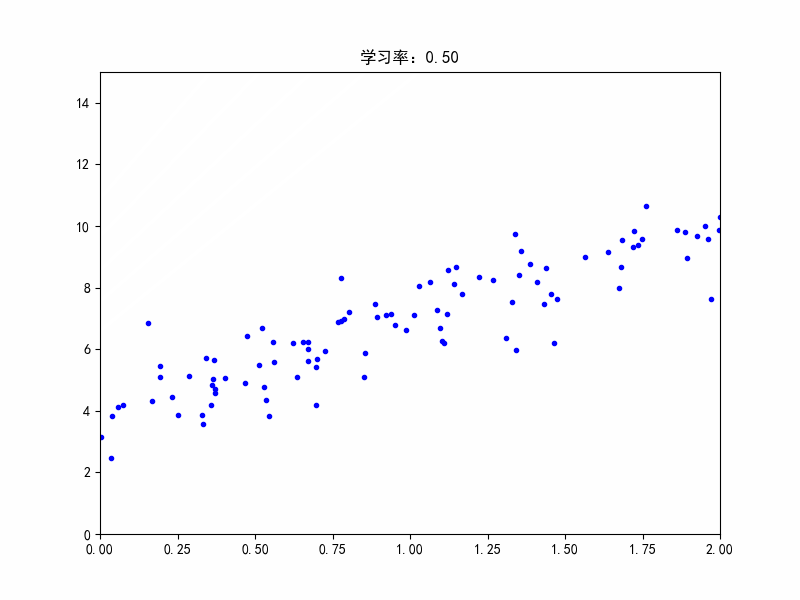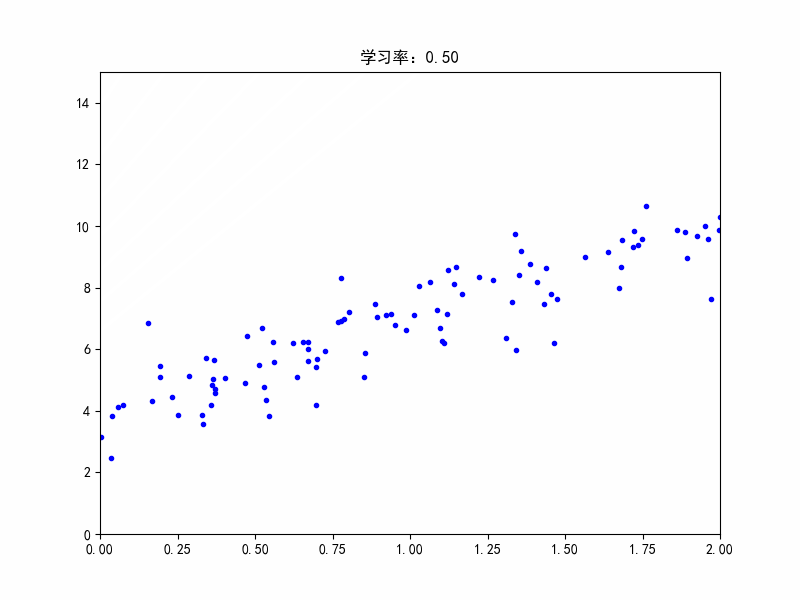
学习率:0.5,不收敛
到此这篇关于浅谈matplotlib 绘制梯度下降求解过程的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关matplotlib 梯度下降内容请搜索易盾网络以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持易盾网络!
