fwrite函数的一般调用形式是“fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp);”;其中,buffer是准备输出的数据块的起始地址,size是每个数据块的字节数,count用来指定每写一次或输出的数据块,fp为文件指针。
fwrite函数的一般调用形式是“fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp);”;其中,buffer是准备输出的数据块的起始地址,size是每个数据块的字节数,count用来指定每写一次或输出的数据块,fp为文件指针。

fwrite() 是C 语言标准库中的一个文件处理函数,功能是向指定的文件中写入若干数据块,如成功执行则返回实际写入的数据块数目。该函数以二进制形式对文件进行操作,不局限于文本文件。
语法:
fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp)
参数:
buffer是准备输出的数据块的起始地址
size是每个数据块的字节数
count用来指定每写一次或输出的数据块
fp为文件指针。
函数返回写入数据的个数。
注意
(1)写操作fwrite()后必须关闭流fclose()。
(2)不关闭流的情况下,每次读或写数据后,文件指针都会指向下一个待写或者读数据位置的指针。
读写常用类型
(1)写int数据到文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ()
{
FILE * pFile;
int buffer[] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
if((pFile = fopen ("myfile.txt", "wb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
//可以写多个连续的数据(这里一次写4个)
fwrite (buffer , sizeof(int), 4, pFile);
fclose (pFile);
return 0;
}(2)读取int数据
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main () {
FILE * fp;
int buffer[4];
if((fp=fopen("myfile.txt","rb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
if(fread(buffer,sizeof(int),4,fp)!=4) //可以一次读取
{
printf("file read error\n");
exit(0);
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
printf("%d\n",buffer[i]);
return 0;
}执行结果:
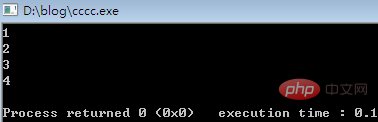
5.读写结构体数据
(1)写结构体数据到文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
int age;
char name[30];
}people;
int main ()
{
FILE * pFile;
int i;
people per[3];
per[0].age=20;strcpy(per[0].name,"li");
per[1].age=18;strcpy(per[1].name,"wang");
per[2].age=21;strcpy(per[2].name,"zhang");
if((pFile = fopen ("myfile.txt", "wb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(fwrite(&per[i],sizeof(people),1,pFile)!=1)
printf("file write error\n");
}
fclose (pFile);
return 0;
}(2)读结构体数据
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
int age;
char name[30];
}people;
int main () {
FILE * fp;
people per;
if((fp=fopen("myfile.txt","rb"))==NULL)
{
printf("cant open the file");
exit(0);
}
while(fread(&per,sizeof(people),1,fp)==1) //如果读到数据,就显示;否则退出
{
printf("%d %s\n",per.age,per.name);
}
return 0;
}执行结果:
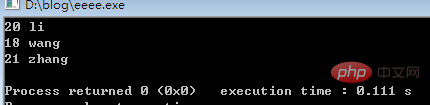
相关
