小程序开发教程 栏目介绍loader设计实现。 配置文件中的loader配置 可以根据配置文件匹配到到规则,去执行相应的loader。 // analyze.config.js// 引入loaderconst jsLoader = require(./lib/jsLoader)const
小程序开发教程栏目介绍loader设计实现。

配置文件中的loader配置
可以根据配置文件匹配到到规则,去执行相应的loader。
// analyze.config.js
// 引入loader
const jsLoader = require('./lib/jsLoader')
const jsonLoader = require('./lib/jsonLoader')
const cssLoader = require('./lib/cssLoader')
const htmlLoader = require('./lib/htmlLoader')
const signLoader = require('./lib/signLoader')
const config = {
entry: './',
output: {
name: 'dist',
src: './'
},
module: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: [signLoader, jsLoader],
},
{
test: /\.wxss$/,
loader: [cssLoader],
outputPath: (outputPath) => outputPath.replace('.wxss', '.acss')
},
{
test: /\.wxml$/,
loader: [htmlLoader],
outputPath: (outputPath) => outputPath.replace('.wxml', '.axml')
},
{
test: /\.json$/,
loader: [jsonLoader],
},
]
}
module.exports = config具体loader实现
以jsLoader为例子,接收源码作为参数,返回编译后获得的新的源码
// 前几篇中封装的js转换器
const JsParser = require('./JsParser')
function loader(source) {
const jsParser = new JsParser()
let ast = jsParser.parse(source)
ast = jsParser.astConverter(ast)
return jsParser.astToCode(ast)
}
module.exports = loader不同文件选择对应loader
// 重写Analyze函数中的analyzeFileToLoard文件分析部分
function Analyze(filePath, outputPath){
if (fs.statSync(filePath).isDirectory()) {
const files = fs.readdirSync(filePath)
files.forEach(file => {
const currentFilePath = filePath+'/'+file
const currentOutputPath = outputPath+'/'+file
if(fs.statSync(currentFilePath).isDirectory()) {
fs.mkdirSync(currentOutputPath)
Analyze(currentFilePath, currentOutputPath)
} else analyzeFileToLoard(currentFilePath, currentOutputPath)
})
} else analyzeFileToLoard(filePath, outputPath)
}function analyzeFileToLoard(inputPath, outputPath) {
let source = readFile(inputPath) // 读取源码
const loaders = config.module
loaders.forEach(loader => { // 遍历配置文件,看是否有匹配文件的loader规则
if (loader.test.test(inputPath)) {
// 使用loader
source = useLoader(source, loader.loader, outputPath)
// 输出路径处理函数
if (loader.outputPath) outputPath = loader.outputPath(outputPath)
}
})
writeFile(outputAppPath(outputPath), source) // 将处理过后的源码写入文件
}loader过滤和执行
loader执行是个逆序的执行,从右边向左依次执行。在这里我们先用同步的loader来做讨论。
loader执行前还有个pitch阶段,感觉pitch这个起名方式并不是特别合适,我更愿意叫它过滤筛选阶段。先去顺序执行loader上的pitch方法,要是pitch有返回值,就不再执行在该loader之前执行的loader。
function useLoader(source, loaders = []) {
// 执行loader存储列表
const loaderList = []
// 递归去筛选需要执行的loader
function loaderFilter(loaders) {
const [firstLoader, ...ortherLoader] = loaders
if (loaders.length === 0) return
// 执行pitch,并将剩余的loader传入作为参数
if (firstLoader.pitch && firstLoader.pitch(ortherLoader)) return ortherLoader
else {
// 将可用loader加入待执行列表
loaderList.push(firstLoader)
// 剩余loader作为参数 递归调用
loaderFilter(ortherLoader)
}
}
// 大概,暂时用不到。。。
const remainLoader = loaderFilter(loaders)
// 同步loader逆序执行
function runLoader(source, loaderList) {
const loader = loaderList.pop()
let newSource = loader(source)
if (loaderList.length > 0) return runLoader(newSource, loaderList)
else return newSource
}
source = runLoader(source, loaderList)
return source
}实验
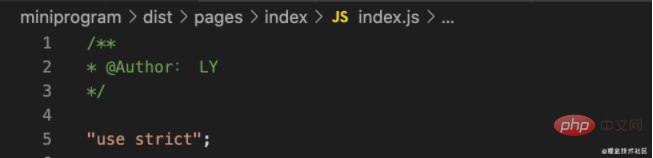
写个signLoader,看看loader能不能像我们想的那样逆序执行
function loader(source) {
let sign = `/**
* @Author: LY
*/
`
source = sign + source
return source
}
module.exports = loader结果:
这样简易的loader部分算是完成了,但这么写只能执行一些同步的loader,异步的loader无法等待执行完成后再写入。
相关学习推荐:小程序开发教程
以上就是微信小程序转换器之 loader设计实现的详细内容,更多请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
