目录
- 什么是SPI
- 与 接口类-实现类 提供的RPC 方式有什么区别?
- 假设我们需要实现RPC,是怎么做的?
- 那RPC究竟跟SPI什么关系?
- SPI的应用场景
- 怎么实现一个SPI?
- 中间件是怎么实现SPI的?
- Apollo-Client中的实现
- JDBC中的实现
什么是SPI
SPI ,全称为 Service Provider Interface,是一种服务发现机制。其为框架提供了一个对外可扩展的能力。
与 接口类-实现类 提供的RPC 方式有什么区别?
- 传统的接口类实现形式为如下
public interface AdOpFromApolloService {}
public class AdOpFromDbServiceImpl implements AdOpFromDbService {}
假设我们需要实现RPC,是怎么做的?
RPC会在对应的接口类AdOpFromApolloService新增一个注解用于标注是RPC类,然后将当前类放在依赖包提供给其他项目来通过接口类进行调用
简而言之:RPC调用中只提供接口类,然后让第三方调用(第三方只调,不写实现)
那RPC究竟跟SPI什么关系?
- SPI:提供接口,第三方引用包之后可重写或用默认的SPI接口的实现。
- RPC:提供接口,但是实现是私有的,不对外开放重写能力。
SPI的应用场景
框架实现案例:
- Spring扩展插件实现。如JDCB
- 中间件扩展插件实现。如Dubbo、Apollo
- 开发过程中举例:实现一个拦截器,并用SPI机制来扩展其拦截方式(比如全量拦截、每分钟拦截多少、拦截比例多少、拦截的日志是log打印还是落库、落es)
怎么实现一个SPI?
接下来用两个项目模块来讲解SPI的用法,先看项目结构图如下
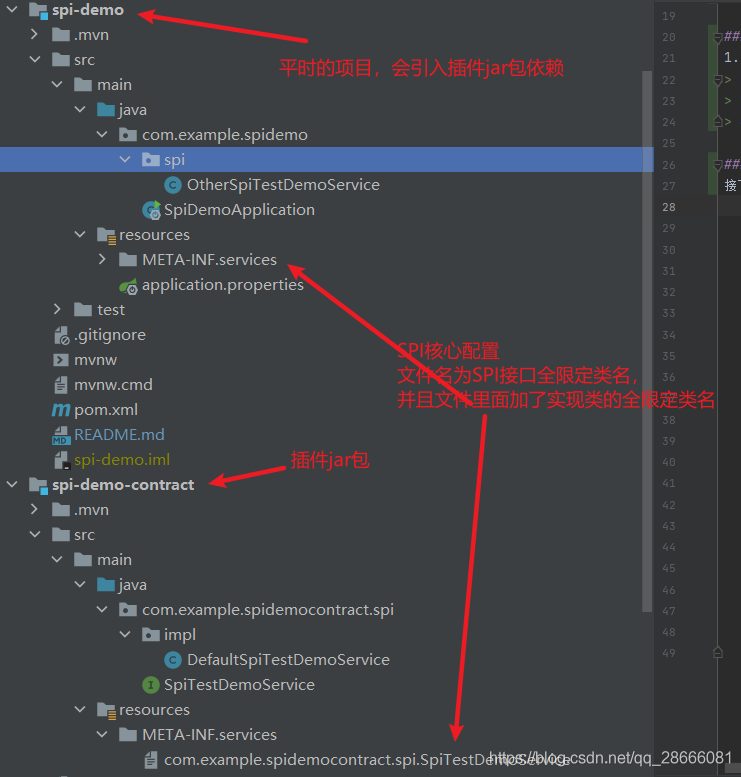
接下来是实现的过程
第一步:创建spi-demo-contract项目,在resources目录下新建如下目录(MATE-INF/services)和文件(com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService)
- 修改com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService文件
- 新增第二步一样位置的接口类,以及对应的实现类
第二步:创建spi-demo项目,然后引入spi-demo-contract依赖
- 在resources目录下新建如下目录(MATE-INF/services)和文件(com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService),文件名跟spi-demo-contract的完全一致
- 修改com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService(与依赖包的文件名称完全一致,但内容指向了当前项目自定义的实现类)文件
- 实现SPI接口,自定义spi-demo项目的实现类(这里可以把优先级调到最高)
第三步:在spi-demo项目中用ServiceLoader进行加载SPI接口补充说明:我们可以重写声明类的优先级,来判断需要用哪个实现类来处理。比如重写一个优先级=0最高优先级,然后加载的时候默认只取第一个优先级最高的,那我们重写的自定义实现类就能覆盖掉默认SPI实现类
详细步骤拆分如下
- 第一步:创建spi-demo-contract项目,在resources目录下新建如下目录(MATE-INF/services)和文件(com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService)
-- resources ---- META-INF -------- services ------------ com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService
- 修改com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService文件如下
com.example.spidemocontract.spi.impl.DefaultSpiTestDemoService
- 新增第二步一样位置的接口类,以及对应的实现类
/**
* 这个接口类完全对应resources/META-INF/services/com.example.spidemocontract.spi.impl.DefaultSpiTestDemoService
**/
public interface SpiTestDemoService {
void printLog();
int getOrder();
}
/**
* 将默认的设置为优先级最低,这是默认的SPI接口的实现类
*/
public class DefaultSpiTestDemoService implements SpiTestDemoService {
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
@Override
public void printLog() {
System.out.println("输出 DefaultSpiTestDemoService log");
}
}
- 第二步:创建spi-demo项目,然后引入spi-demo-contract依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spi-demo-contract</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
- 在resources目录下新建如下目录(MATE-INF/services)和文件(com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService),文件名跟spi-demo-contract的完全一致
-- resources ---- META-INF -------- services ------------ com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService
- 修改com.example.spidemocontract.spi.SpiTestDemoService(与依赖包的文件名称完全一致,但内容指向了当前项目自定义的实现类)文件如下
com.example.spidemo.spi.OtherSpiTestDemoService
- 实现SPI接口,自定义spi-demo项目的实现类
/**
* 其他,把他优先级设置的比较高
*/
public class OtherSpiTestDemoService implements SpiTestDemoService {
// 后面我们用SPI类加载器获取时,会根据order排序,越小优先级越高
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void printLog() {
System.out.println("输出 OtherSpiTestDemoService log");
}
}
- 第三步:在spi-demo项目中用ServiceLoader进行加载SPI接口
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载SPI
Iterator<SpiTestDemoService> iterator = ServiceLoader.load(SpiTestDemoService.class).iterator();
// 实现了ordered,会根据ordered返回值排序,优先级越高,越先取出来
List<SpiTestDemoService> list = Lists.newArrayList(iterator)
.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(SpiTestDemoService::getOrder))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (SpiTestDemoService item : list) {
item.printLog();
}
}
中间件是怎么实现SPI的?
Apollo-Client中的实现
- Apollo-Client初始化过程中,有一个SPI接口ConfigPropertySourcesProcessorHelper
// 当前接口会在resource/META-INF/services目录下对应文件com.ctrip.framework.apollo.spring.spi.ConfigPropertySourcesProcessorHelper
public interface ConfigPropertySourcesProcessorHelper extends Ordered {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
- 当前SPI中的默认实现为
public class DefaultConfigPropertySourcesProcessorHelper implements ConfigPropertySourcesProcessorHelper {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
// .....各种注册bean,初始化的流程
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
// 优先级排序置为最低。方便其他自定义spi实现类能够覆盖
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
- 怎么选择加载出自定义的SPI实现类
通过ServiceLoader.load(Xxxx.class)加载出所有实例,然后根据order来进行排序优先级,order最小的那个优先级最高,只取第一个数据candidates.get(0)并返回。
因为自定义SPI实现优先级可以设置得很高,所以就可以达到覆盖默认实现的目的
public static <S extends Ordered> S loadPrimary(Class<S> clazz) {
List<S> candidates = loadAllOrdered(clazz);
return candidates.get(0);
}
public static <S extends Ordered> List<S> loadAllOrdered(Class<S> clazz) {
Iterator<S> iterator = loadAll(clazz);
if (!iterator.hasNext()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"No implementation defined in /META-INF/services/%s, please check whether the file exists and has the right implementation class!",
clazz.getName()));
}
// 获取迭代中的所有SPI实现实例,然后进行排序,取优先级最高的那个
List<S> candidates = Lists.newArrayList(iterator);
Collections.sort(candidates, new Comparator<S>() {
@Override
public int compare(S o1, S o2) {
// the smaller order has higher priority
return Integer.compare(o1.getOrder(), o2.getOrder());
}
});
return candidates;
}
JDBC中的实现
- JDBC SPI中配置文件resources/META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver,并设置参数如下
com.example.app.driver.MyDriver
- 继承SPI接口java.sql.Driver,实现MyDriver
public class MyDriver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements Driver {
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new MyDriver());
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!", e);
}
}
public MyDriver() throws SQLException {}
@Override
public Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("MyDriver - 准备创建数据库连接.url:" + url);
System.out.println("JDBC配置信息:" + info);
info.setProperty("user", "root");
Connection connection = super.connect(url, info);
System.out.println("MyDriver - 数据库连接创建完成!" + connection.toString());
return connection;
}
}
- 写main方法调用执行刚实现的自定义SPI实现
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Class.forName("com.example.app.driver.MyDriver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
- JDBC如何使用SPI简单分析如下
获取所有注册的驱动(每个驱动的都遍历一下,其实就是最晚注册那个就用那个了,如果失败就往下一个找)
// 获取所有注册的驱动(每个驱动的都遍历一下,其实就是最晚注册那个就用那个了,如果失败就往下一个找)
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
到此这篇关于Java插件扩展机制之SPI案例讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java插件扩展机制之SPI内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
