目录
- 一、概述
- Java集合体系结构:
- 二、collection
- 1、List
- 1)ArrayList
- 2)LinkedList
- 2、set
- 1)HashSet
- 2)TreeSet
- 1.实体类
- 2.测试类:
- 3.实体类
- 4.测试类
- 三、Map
- 1、HashMap
- 2、TreeMap
- 3.ConcurrentHashMap
- 总结
一、概述
集合是一种长度可变,存储数据的数据结构多样,存储对象多样的一种数据容器。Java中集合可分为:List集合、Set集合、HashMap集合,等。
Java集合体系结构:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-abSCHb0c-1623645339249)(C:\Users\52425\Desktop\1.png)]](http://img.558idc.com/uploadfile/allimg/java/2021070515460465.png)
二、collection
collection是Java中所有值存储集合的顶级接口,因此它的所有直接或者间接实现类都有它的非私有方法,我们可以从它的方法开始了解这个体系的功能实现。
boolean add(E e)
确保此 collection 包含指定的元素。
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中。
void clear()
移除此 collection 中的所有元素。
boolean contains(Object o)
如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。
boolean equals(Object o)
比较此 collection 与指定对象是否相等。
int hashCode()
返回此 collection 的哈希码值。
boolean isEmpty()
如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true。
Iterator<E> iterator()
返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
boolean remove(Object o)
从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话)。
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素。
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素。
int size()
返回此 collection 中的元素数。
Object[] toArray()
返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。
<T> T[]
toArray(T[] a)
返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同。
1、List
List,是单列集合,存储的是一组插入有序的数据,并且数据可以重复。
List集合
- LinkedList
- ArrayList
1)ArrayList
示例:
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//添加元素,boolean add(E e) 确保此 collection 包含指定的元素
list.add("张三");
list.add(1);
list.add('A');
System.out.println(list);//[张三, 1, A]
//boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
// 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list.add("java");
list.add("MySQL");
list.addAll(list1);
System.out.println(list);//[张三, 1, A, java, MySQL]
//boolean contains(Object o)
// 如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
System.out.println(list.contains("java"));//true
//boolean remove(Object o)
// 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话)。
System.out.println(list.remove("java"));//true
// int size()
// 返回此 collection 中的元素数。
System.out.println(list.size());//4
//set(int index, E element)
// 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。
//并返回被修改的值
System.out.println(list.set(1, "李四"));
//get(int index)
// 返回此列表中指定位置上的元素。
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// Iterator<E> iterator()
// 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
//集合的遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
说明:ArrayList底层是使用数组的形式创建集合的,因此基于数组的特性,此集合对数据的查找很快速,但是在删除或移动大量数据操作上会显得缓慢。它适合用于快速查找,但不适合做删除多的操作。
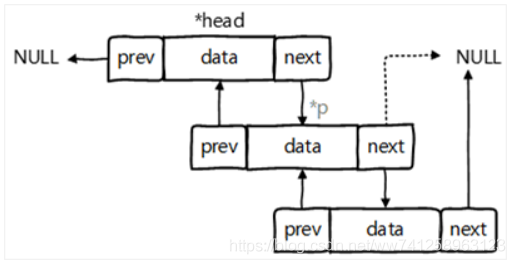
2)LinkedList
LinkedList:双向链表,内部没有声明数组,而是定义了Node类型的first 和last,用于记录首末元素。同时,定义内部类Node,作为LinkedList中 保存数据的基本结构。Node除了保存数据,还定义了两个变量:
- prev变量记录前一个元素的位置
- next变量记录下一个元素的位置
特点:
- 数据有序
- 底层结构为链表
ArrayList比较:
- LinkedList的添加元素速度比ArrayList快;
- LinkedList的查询速度比ArrayList慢;
- 底层数据结构不同:LinkedList用的是链表结构,而ArrayList底层使用 的是数组结构;
说明:LinkedList一般用于添加频繁的操作,ArrayList一般用于频繁查询 的操作。
示例:
public class Stack {
private LinkedList data = null;
public Stack(){
data = new LinkedList();
}
// 添加元素
public boolean push(Object element) {
data.addFirst(element);
return true;
}
// 获取元素
public Object pop() {
return data.pollFirst();
}
// 判断集合是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return data.isEmpty();
}
// 迭代元素
public void list() {
Iterator it = data.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push("张三");
stack.push("李四");
stack.push("王五");
stack.list();
System.out.println("-------------");
Object pop = stack.pop();
System.out.println(pop);
}
}
2、set
1)HashSet
HashSet 是 Set 接口的典型实现,大多数时候使用 Set 集合时都使用 这个实现类。
- HashSet 按 Hash 算法来存储集合中的元素,因此具有很好的存取、 查找、删除性能。
- HashSet 具有以下特点:不能保证元素的排列顺序
- HashSet 不是线程安全的
- 集合元素可以是 null
- 不能添加重复元素
- HashSet 集合判断两个元素相等的标准:两个对象通过 hashCode() 方法比较相等,并且两个对象的 equals() 方法返回值也相等。
- 对于存放在Set容器中的对象,对应的类一定要重写equals()和 hashCode(Object obj)方法,以实现对象相等规则。即:“相等的对象必须具有相等的散列码”。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
// 添加
// boolean add(E e) :把指定的元素添加到集合中
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("world");
set.add(null);
System.out.println(set);
// 注:Set集合中元素是无序,并且不能重复
// boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) :把指定的集合添加到集合中
Set set1 = new HashSet();
set1.add("aaa");
set1.add("linux");
;
set.addAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
// boolean remove(Object o) :从集合中删除指定元素
set.remove("hello");
System.out.println(set);
// boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) :从集合中删除指定集合中的所有元素
set1.add("aaa");
set1.add("linux");
set.removeAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
// void clear() :清空集合中所有元素
set.clear();
System.out.println(set);
// int size() :获取集合的元素个数
int size = set.size();
System.out.println(size);
// boolean contains(Object o) :判断集合中是否包含指定元素,包含为true,否则为false;
System.out.println(set.contains("aaa"));
// boolean isEmpty() :判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
}
说明:在HashSet添加元素时,会首先比较两个元素的hashCode值是不相等,如 果不相等则直接添加;如果相等再判断两个元素的equals的值是否相等, 如果相等则不添加,如果不相等则添加。
2)TreeSet
- TreeSet和TreeMap采用红黑树的存储结构
- 特点:有序,查询速度比List快
使用TreeSet集合是,对象必须具有可比较性。而要让对象具有可比较性有 两种方式:
第一种:实现Comparable接口,并重写compareTo()方法:
第二种:写一个比较器类,让该类去实现Comparator接口,并重写 comare()方法。
示例:
1.实体类
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
private int height;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, String sex, int height) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age &&
height == student.height &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name) &&
Objects.equals(sex, student.sex);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, sex, height);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student stu) {
if (stu.getAge() > this.getAge()){
return 1;
}
if (stu.getAge() < this.getAge()){
return -1;
}
return stu.getName().compareTo(this.getName());
}
}
2.测试类:
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
Student student1 = new Student("张三", 20, "男", 165);
Student student2 = new Student("李四", 21, "男", 170);
Student student3 = new Student("王五", 19, "女", 160);
Student student4 = new Student("赵六", 18, "女", 165);
Student student5 = new Student("田七", 20, "男", 175);
treeSet.add(student1);
treeSet.add(student2);
treeSet.add(student3);
treeSet.add(student4);
treeSet.add(student5);
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}
3.实体类
public class Teacher {
private String name;
public Teacher(){}
public Teacher(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Teacher{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4.测试类
public class TreeSetTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher("11");
Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher("12");
Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher("13");
Teacher teacher4 = new Teacher("14");
Teacher teacher5 = new Teacher("15");
TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return o1.hashCode() - o2.hashCode();
}
});
treeSet1.add(teacher1);
treeSet1.add(teacher2);
treeSet1.add(teacher3);
treeSet1.add(teacher4);
treeSet1.add(teacher5);
System.out.println(treeSet1);
}
}
说明:HashSet去重是依靠hashCode和equals()方法,而TreeSet去重则 依靠的是比较器。
三、Map
存储的双列元素,Key是无序的,不可重复,而Value是无序,可重复的。
1、HashMap
public class HashMapDemo {
private Map map = null;
public void init() {
map = new HashMap();
map.put("a", "aaa");
map.put("b", "bbb");
map.put("c", "ccc");
System.out.println(map);
}
// 添加元素
public void testPut() {
// V put(K key, V value) :把指定的key和value添加到集合中
map.put("a1", "aaa");
map.put("b1", "bbb");
map.put("c1", "ccc");
System.out.println(map);
// void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V>m) :把指定集合添加集合中
Map map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put("e", "eee");
map1.put("f", "fff");
map.putAll(map1);
System.out.println(map);
// default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) :如果key不存在就添加
map.putIfAbsent("a", "hello");
System.out.println(map);
map.putIfAbsent("g", "ggg");
System.out.println(map);
}
// 修改元素
public void testModify() {
// V put(K key, V value) :把集合中指定key的值修改为指定的值
map.put("a", "hello");
map.put("a", "world");
System.out.println(map);
// 说明,当key相同时,后面的值会覆盖前面的值。
// default V replace(K key, V value) :根据key来替换值,而不做增加操作
Object replace = map.replace("b1", "java");
System.out.println(replace);
System.out.println(map);
//default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue,V newValue)
}
// 删除元素
public void testRemove() {
// V remove(Object key) :根据指定key删除集合中对应的值
Object c = map.remove("c");
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(map);
// default boolean remove(Object key, Objectvalue) :根据key和value进行删除
map.remove("b", "bbb1");
System.out.println(map);
// void clear() :清空集合中所有元素
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
}
// 判断元素
public void testJudge() {
// boolean isEmpty() :判断集合是否为空,如果是返回true,否则返回false
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
// boolean containsKey(Object key) :判断集合中是否包含指定的key,包含返回true,否则返回false
boolean flag = map.containsKey("a");
System.out.println(flag); // true
flag = map.containsKey("a1");
System.out.println(flag); // false
// boolean containsValue(Object value) :判断集合中是否包含指定的value,包含返回true,否则返回false
flag = map.containsValue("aaa");
System.out.println(flag); // true
flag = map.containsValue("aaa1");
System.out.println(flag); // false
}
// 获取元素
public void testGet() {
// int size() :返回集合的元素个数
int size = map.size();
System.out.println(size);
// V get(Object key) :根据Key获取值,如果找到就返回对应的值,否则返回null
Object val = map.get("a");
System.out.println(val);
val = map.get("a1");
System.out.println(val); // null
// default V getOrDefault(Object key, VdefaultValue) :根据Key获取值,如果key不存在,则返回默认值
val = map.getOrDefault("a1", "hello");
System.out.println(val);
// Collection<V> values() :返回集合中所有的Value
Collection values = map.values();
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// Set<K> keySet() :返回集合中所有的Key
Set set = map.keySet();
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
// 迭代元素
public void testIterator() {
// 第一种:通过key获取值的方式
Set keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator it = keySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object key = it.next();
Object val = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + val);
}
System.out.println("------------------------ ");
// 第二种:使用for循环
for (Object key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" +
map.get(key));
}
System.out.println("------------------------ ");
// 第三种:使用Map接口中的内部类来完成,在框架中大量使用
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Object obj : entrySet) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" +
entry.getValue());
}
}
}
说明:在HashMap中键-值允许为空,但键唯一,值可重复。hashMap不是线程安全的。
2、TreeMap
是一个有序的集合,默认使用的是自然排序方式。
public class Person implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Person) {
Person p = (Person) o;
return this.age - p.age;
}
return 0;
}
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试
public class TeeMapDemo {
@Test
public void testInteger() {
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap();
tm.put(3, 333);
tm.put(2, 222);
tm.put(11, 111);
tm.put(2, 222);
System.out.println(tm);
}
@Test
public void testString() {
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap();
tm.put("hello", "hello");
tm.put("world", "world");
tm.put("about", "");
tm.put("abstract", "");
System.out.println(tm);
}
@Test
public void testPerson() {
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap(new Comparator(){
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if (o1 instanceof Person && o2
instanceof Person) {
Person p1 = (Person) o1;
Person p2 = (Person) o2;
return p1.getAge() - p2.getAge();
}
return 0;
}
});
tm.put(new Person("张三",18), null);
tm.put(new Person("李四",17), null);
System.out.println(tm);
}
}
说明:从上面的代码可以发现,TreeMap的使用和TreeSet的使用非常相似,观察HashSet集合的源代码可以看出,当创建 HashSet集合时,其实是底层使用的是HashMap。
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
HashSet实际上存的是HashMap的Key。
3.ConcurrentHashMap
在Map集合中我们介绍了HashMap,TreeMap,在多线程的情况下这些集合都不是线程安全的,因此可能出现线程安全的问题。
在Java中Hashtable是一种线程安全的HashMap,Hashtable在方法上与HashMap并无区别,仅仅只是在方法使用了synchronized以此来达到线程安全的目的,我们观察Hashtable的源码。
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
以上是Hashtable的get源码,可以看出它仅仅只是在方法上添加了锁,这大大降低了线程的执行效率,以牺牲效率的形式来达到目的,这显然不是我们在实际中想要的,因此我们需要一种既能在线程安全方面有保障,在效率上还可以的方法。
ConcurrentHashMap采用的是分段锁的原理,我们观察源码。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
从源码中可以看出ConcurrentHashMap仅仅是在当有线程去操作当前数据的时候添加了锁,因此效率大大提高了。
在线程安全的情况下提高了效率。
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能对你有所帮助,也希望您能够多多关注自由互联的更多内容!
