目录 单神经元引论 参考 多神经元 单神经元引论 对于如花,大美,小明三个因素是如何影响小强这个因素的。 这里用到的是多元的线性回归,比较基础 from numpy import array,exp,dot,random
目录
- 单神经元引论
- 参考
- 多神经元
单神经元引论
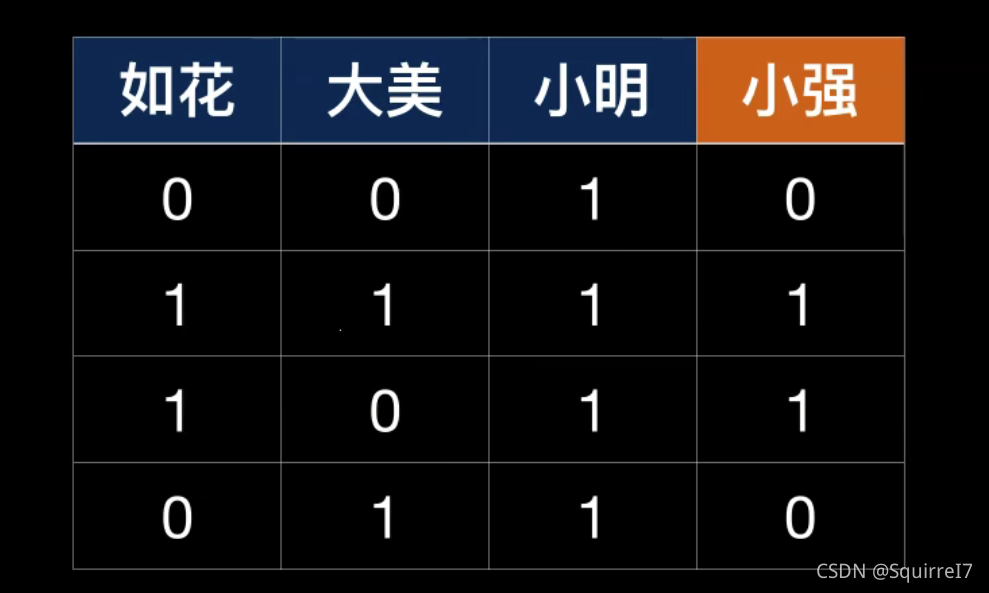
对于如花,大美,小明三个因素是如何影响小强这个因素的。
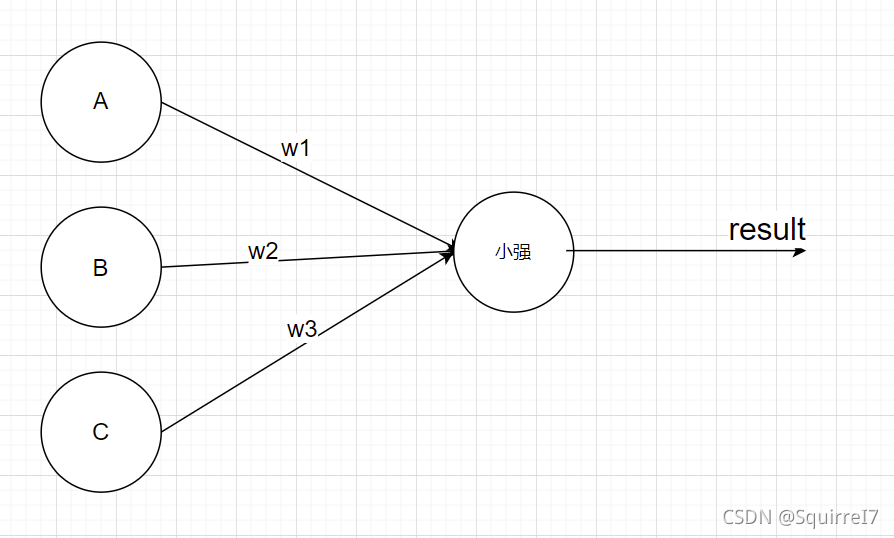
这里用到的是多元的线性回归,比较基础
from numpy import array,exp,dot,random
其中dot是点乘
导入关系矩阵:
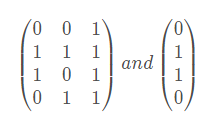
X= array ( [ [0,0,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[0,1,1]]) y = array( [ [0,1,1,0]]).T ## T means "transposition"
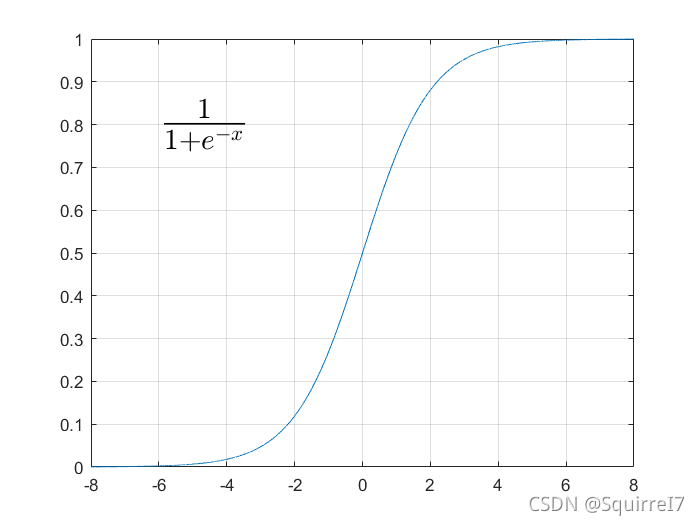
为了满足0到1的可能性,我们采用激活函数
matlab作图
x=[-8:0.001:8]
y=1./(1+exp(-x))
plot(x,y)
grid on
text(-6,0.8,['$\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}$'],'interpreter','latex','fontsize',25)
然后
for it in range(10000):
z=dot(X,weights)
output=1/(1+exp(-z))##'dot' play role of "dot product"
error=y-output
delta=error*output*(1-output)
weights+=dot(X.T,delta)
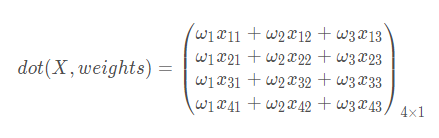
其中
delta=error*output*(1-output)
是求导的结果和误差相乘,表示梯度
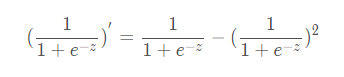
具体数学流程
所以具体流程如下,X具体化了一下
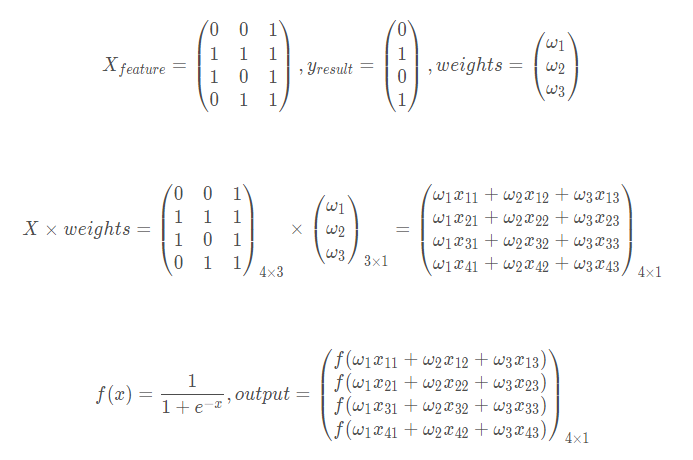
error即为每个带权参数经过激活函数映射后到y结果的量化距离

最终代码:(PS:默认lr取1,可修改)
from numpy import array,exp,dot,random
"""
Created on vscode 10/22/2021
@author Squirre17
"""
X=array([[0,0,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[0,1,1]])
y=array([[0,1,1,0]]).T ## T means "transposition"
random.seed(1)
epochs=10000
weights=2*random.random((3,1))-1## 3 row 1 line, range[-1,1)
for it in range(epochs):
output=1/(1+exp(-dot(X,weights)))##'dot' play role of "dot product"
error=y-output
slope=output*(1-output)
delta=error*slope
weights+=dot(X.T,delta)
print(weights)
print(1/(1+exp( -dot([[1,0,0]], weights))))
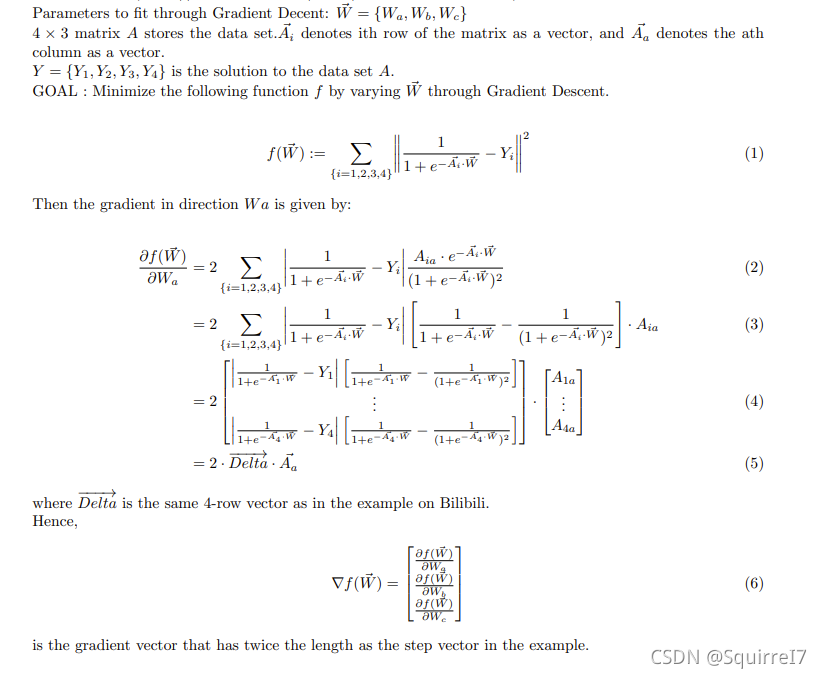
参考
多神经元
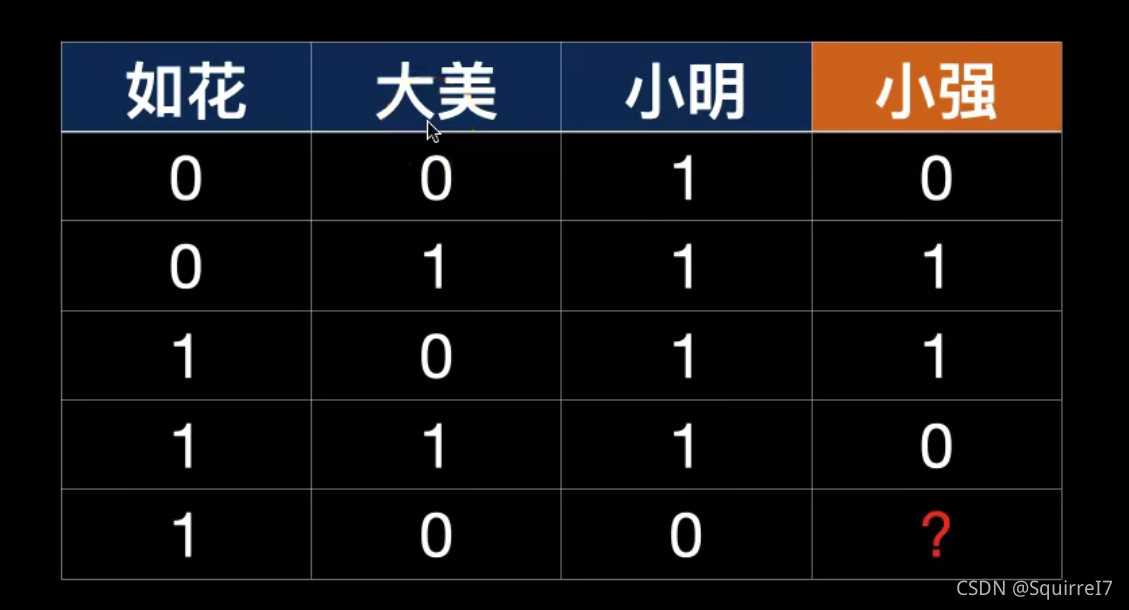
这个意思就是两个美女XOR
单神经元没法解决,只能解决单一线性关系
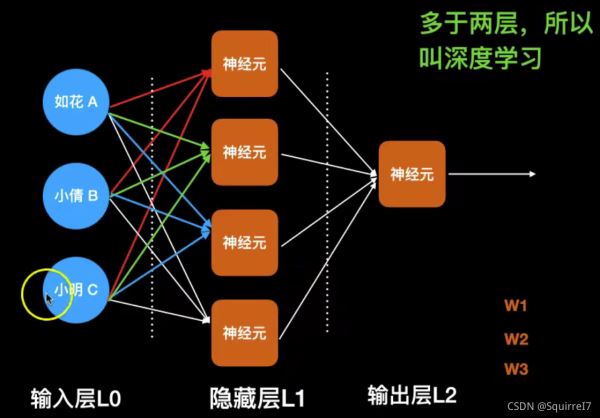

代码如下,可自行调整epoches和lr
from numpy import array,exp,dot,random
"""
Created on vscode 10/22/2021
@author Squirre17
"""
X=array([[0,0,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]])
y=array([[0,1,1,0]]).T # T means "transposition"
random.seed(1)
epochs=100000
w0=2*random.random((3,4))-1 # input layer neure
w1=2*random.random((4,1))-1 # hidden layer neure
lr=1
def fp(input):
l1=1/(1+exp(-dot(input,w0))) # 4×4
l2=1/(1+exp(-dot(l1,w1))) # 4×1
return l1,l2
def bp(l1,l2,y):
l2_error=y-l2
l2_slope=l2*(1-l2)
l1_delta=l2_error*l2_slope*lr # 4×1
l1_error=l1_delta.dot(w1.T)
l1_slope=l1*(1-l1)
l0_delta=l1_error*l1_slope*lr
return l0_delta,l1_delta
for it in range(epochs):
l0=X
l1,l2=fp(l0)
l0_delta,l1_delta=bp(l1,l2,y)
w1+=dot(l1.T,l1_delta) # 4×4 4×1 # adjust w1 according to loss
w0+=dot(l0.T,l0_delta)
print(fp([[1,0,0]])[1])
其中关于l1_error=l1_delta.dot(w1.T),就是第三层的误差反向加权传播给第二层
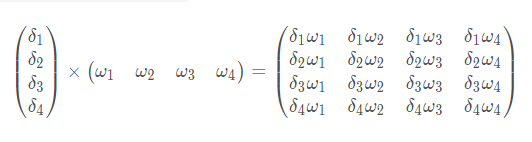
以上就是python机器学习实现神经网络示例解析的详细内容,更多关于python机器学习实现神经网络的资料请关注易盾网络其它相关文章!
