本文主要介绍了java中LinkedList使用迭代器优化移除批量元素原理,分享给大家,具体如下:
public interface Iterator<E> {
/**
*是否还有下一个元素
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
*下一个元素
*/
E next();
/**
* 从集合中删除最后一个返回的元素
*/
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
/**
* 传入一个Consumer对剩余的每个元素执行指定的操作,直到所有元素已处理或操作引发异常
*/
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
//requireNonNull 静态方法将会在参数为null时主动抛出NullPointerException 异常。
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
}
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
/**
* 是否有后继
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* 后继节点
*/
E next();
/**
* 是否有前驱
*/
boolean hasPrevious();
/**
* 前驱节点
*/
E previous();
/**
* 下一个节点的下标
*/
int nextIndex();
/**
* 前驱节点的下标
*/
int previousIndex();
/**
* 移除元素
*/
void remove();
/**
* 替换最后返回的元素
*/
void set(E e);
/**
* 插入一个结点到最后返回的元素之后
*/
void add(E e);
}
普通版 ArrayListdie迭代器
调用方法:list.iterator();
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // 当前下标
int lastRet = -1; // 最后一个元素的索引,没有返回1
int expectedModCount = modCount;//创建迭代器时列表被修改的次数,防止多线程操作。快速失败
/**
* 先检查一下是否列表已经被修改过
* 做一些简单的越界检查
* 返回元素,并且记录下返回元素的下标给lastRet,当前下标+1,
*/
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
/**
* 调用ArrayListdie自身的remove方法移除元素
* ArrayListdie自身的remove 会修改modCount的值所以需要更新迭代器的expectedModCount
* expectedModCount = modCount;
*/
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//把剩下为next遍历的所有元素做一个遍历消费
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
//检查是否列表已经被修改了
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
增强版本 ArrayListdie迭代器
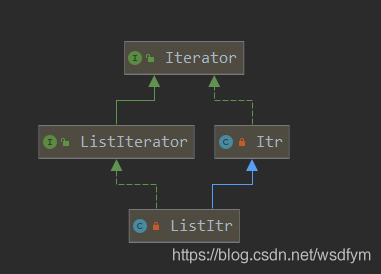
实现了ListIterator接口,ListIterator接口继承Iterator接口。并且ListItr extends Itr。Itr有的方法其都有。并且增加了
- hasPrevious 是否有前驱
- nextIndex 下一个索引位置
- previousIndex 前驱的索引位置
- previous 前驱元素
- set 替换最后返回的元素
- add 插入一个结点到最后返回的元素之后
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
//根据lastRet设置元素
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
重点看一下LinkedList的迭代器
调用方法:list.iterator();
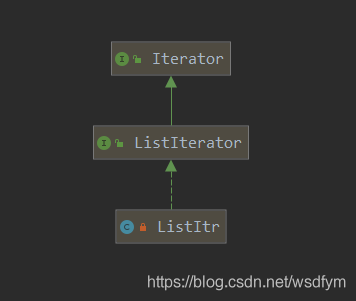
重点看下remove方法
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
//返回的节点
private Node<E> lastReturned;
//下一个节点
private Node<E> next;
//下一个节点索引
private int nextIndex;
//修改次数
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
//根据传进来的数字设置next等属性,默认传0
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
//直接调用节点的后继指针
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
//返回节点的前驱
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
/**
* 最重要的方法,在LinkedList中按一定规则移除大量元素时用这个方法
* 为什么会比list.remove效率高呢;
*/
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
}
LinkedList 源码的remove(int index)的过程是
先逐一移动指针,再找到要移除的Node,最后再修改这个Node前驱后继等移除Node。如果有批量元素要按规则移除的话这么做时间复杂度O(n²)。但是使用迭代器是O(n)。
先看看list.remove(idnex)是怎么处理的
LinkedList是双向链表,这里示意图简单画个单链表
比如要移除链表中偶数元素,先循环调用get方法,指针逐渐后移获得元素,比如获得index = 1;指针后移两次才能获得元素。
当发现元素值为偶数是。使用idnex移除元素,如list.remove(1);链表先Node node(int index)返回该index下的元素,与get方法一样。然后再做前驱后继的修改。所以在remove之前相当于做了两次get请求。导致时间复杂度是O(n)。
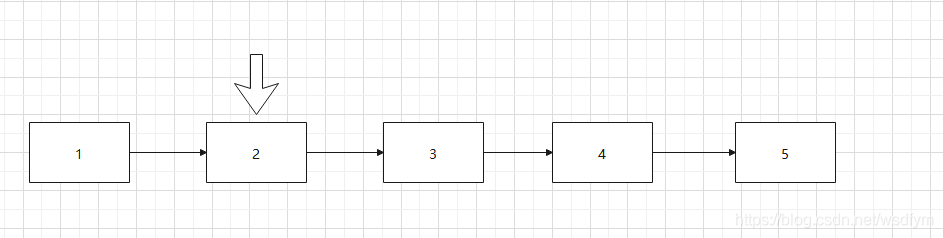
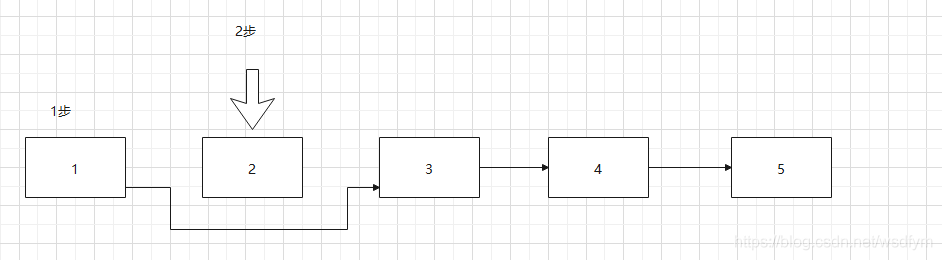
继续移除下一个元素需要重新再走一遍链表(步骤忽略当index大于半数,链表倒序查找)
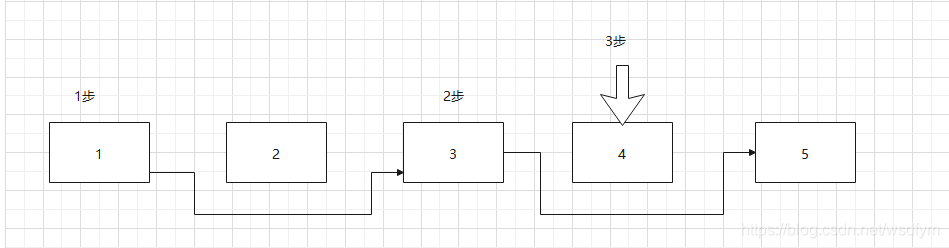
以上如果移除偶数指针做了6次移动。
删除2节点
get请求移动1次,remove(1)移动1次。
删除4节点
get请求移动2次,remove(2)移动2次。
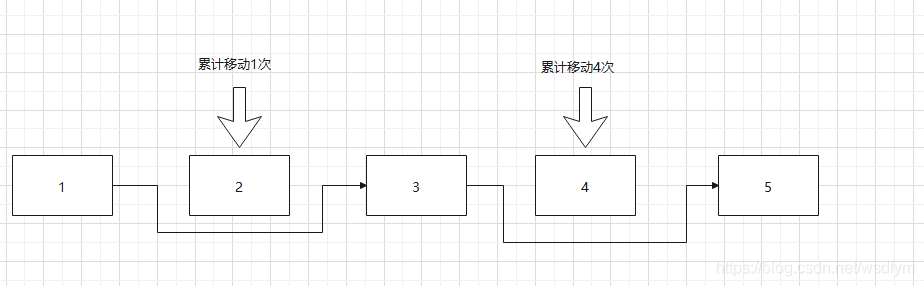
迭代器的处理
迭代器的next指针执行一次一直向后移动的操作。一共只需要移动4次。当元素越多时这个差距会越明显。整体上移除批量元素是O(n),而使用list.remove(index)移除批量元素是O(n²)
到此这篇关于java中LinkedList使用迭代器优化移除批量元素原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关LinkedList 迭代器批量移除内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
