一、WebSocket介绍
网站上的即时通讯是很常见的,比如网页的QQ,聊天系统等。按照以往的技术能力通常是采用轮询、Comet技术解决。
HTTP协议是非持久化的,单向的网络协议,在建立连接后只允许浏览器向服务器发出请求后,服务器才能返回相应的数据。当需要即时通讯时,通过轮询在特定的时间间隔(如1秒),由浏览器向服务器发送Request请求,然后将最新的数据返回给浏览器。这样的方法最明显的缺点就是需要不断的发送请求,而且通常HTTP request的Header是非常长的,为了传输一个很小的数据 需要付出巨大的代价,是很不合算的,占用了很多的宽带。
缺点:会导致过多不必要的请求,浪费流量和服务器资源,每一次请求、应答,都浪费了一定流量在相同的头部信息上
然而WebSocket的出现可以弥补这一缺点。在WebSocket中,只需要服务器和浏览器通过HTTP协议进行一个握手的动作,然后单独建立一条TCP的通信通道进行数据的传送。
二、WebSocket运行机制
WebSocket 是 HTML5 一种新的协议,也是一个典型的应用层协议。它实现了浏览器与服务器全双工通信,能更好的节省服务器资源和带宽并达到实时通讯,它建立在 TCP 之上,同 HTTP 一样通过 TCP 来传输数据,但是它和 HTTP 最大不同是:
WebSocket 是一种双向通信协议,在建立连接后,WebSocket 服务器和 Browser/Client Agent 都能主动的向对方发送或接收数据,就像 Socket 一样;
WebSocket 需要类似 TCP 的客户端和服务器端通过握手连接,连接成功后才能相互通信。
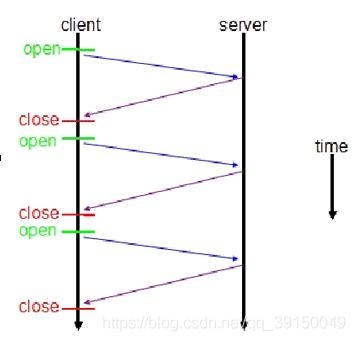
非 WebSocket 模式传统 HTTP 客户端与服务器的交互如下图所示:
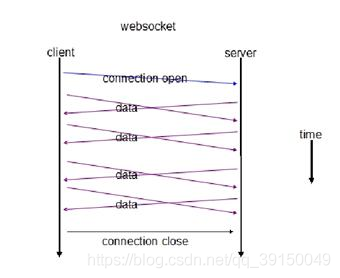
使用 WebSocket 模式客户端与服务器的交互如下图:
三、WebSocket实现
这里通过一个简单的聊天例程,实现spring boot +websocket代码的演示。
引入maven
<!-- websocket -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
配置类WebConfig
package org.antry.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
/**
* @ClassName WebSocketConfig
* @Description TODO
* @Autor TT
* @Date 2020/10/9 23:00
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
WebSocket类
在这个类里,有一个集合,用来存放所有连接。
当有新的连接进来时,在onOpen()方法中,我们每个连接都会存下对应id作为标识。假设这个id已经存过,则会关闭此连接,防止同一个id多处登录。
连接断开时,在onClose()方法中,将此连接移出集合。
当有新的消息发送过来时,会去遍历连接,找到对应接收人id的连接,然后把消息推送给接收人。
package org.antry.websocket;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.websocket.OnClose;
import javax.websocket.OnMessage;
import javax.websocket.OnOpen;
import javax.websocket.Session;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @ClassName MyWebsocket
* @Description TODO
* @Autor TT
* @Date 2020/10/10 11:02
* @Version 1.0
*/
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocket/{user}")
@Component
public class MyWebsocket {
// 通过类似GET请求方式传递参数的方法(服务端采用第二种方法"WebSocketHandler"实现)
// websocket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:18080/testWebsocket?id=23&name=Lebron");
/**
* 在线人数
*/
public static AtomicInteger onlineNumber = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 所有的对象,每次连接建立,都会将我们自己定义的MyWebsocket存放到List中,
*/
public static List<MyWebsocket> webSockets = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<MyWebsocket>();
/**
* 会话,与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据
*/
private Session session;
/**
* 每个会话的用户
*/
private String user;
/**
* 建立连接
*
* @param session
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("user") String user) {
System.err.println(user);
if (user == null || "".equals(user)) {
try {
session.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
onlineNumber.incrementAndGet();
for (MyWebsocket MyWebsocket : webSockets) {
if (user.equals(MyWebsocket.user)) {
try {
session.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
}
this.session = session;
this.user = user;
webSockets.add(this);
}
/**
* 连接关闭
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
onlineNumber.decrementAndGet();
webSockets.remove(this);
}
/**
* 收到客户端的消息
*
* @param message 消息
* @param session 会话
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session, @PathParam("user") String user) {
System.err.println(message);
String[] strArr = message.split("~");
pushMessage(user,strArr[0],strArr[1]);
}
/**
* 发送消息
*
* @param message 消息
*/
public void sendMessage(String message) {
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 消息推送
*
* @param message
* @param uuid uuid为空则推送全部人员
*/
public static void pushMessage(String user, String message, String uuid) {
if (uuid == null || "".equals(uuid)) {
for (MyWebsocket MyWebsocket : webSockets) {
MyWebsocket.sendMessage(user + ":" + message);
}
} else {
for (MyWebsocket MyWebsocket : webSockets) {
if (uuid.equals(MyWebsocket.user)) {
MyWebsocket.sendMessage(message);
}
}
}
}
}
两个简单的前端页面,他们的不同是,接收id和发送id不同。
testOne.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>聊天窗口1</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link href="public/dist/lib/uploader/zui.uploader.min.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="input-group">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="msg">
<span class="input-group-btn">
<button class="btn btn-default" type="button" onclick="send()">发送</button>
</span>
</div>
</div>
<script src="public/dist/lib/jquery/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="public/dist/js/zui.min.js"></script>
<script src="public/layer/layer.js"></script>
<script src="public/js/function.js"></script>
<script src="public/js/testOne.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
testOne.js
var websocket = null;
var sendId = 0;
var receiveId = 1;
//---------------------------
/**
* 初始化websocket
* @param id
*/
doInit(sendId)
function doInit(sendId){
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
websocket = new WebSocket("ws:localhost:10086/websocket/" + sendId);
} else {
alert("浏览器不支持");
}
websocket.onopen = function () {
addMessage("webscoket已经连接成功");
};
websocket.onclose = function () {
addMessage("webscoket连接失败");
};
websocket.onmessage = function (event) {
alert("收到消息:"+event.data);
};
websocket.onerror = function () {
addMessage("webscoket连接失败");
};
}
/**
* 发送一条消息
*/
function send(){
websocket.send(value('msg')+"~"+receiveId);
}
/**
* 测试打印调试信息用
* @param msg
*/
function addMessage(msg) {
console.log(msg)
}
testTwo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>聊天窗口2</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link href="public/dist/lib/uploader/zui.uploader.min.css" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="input-group">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="msg">
<span class="input-group-btn">
<button class="btn btn-default" type="button" onclick="send()">发送</button>
</span>
</div>
</div>
<script src="public/dist/lib/jquery/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="public/dist/js/zui.min.js"></script>
<script src="public/layer/layer.js"></script>
<script src="public/js/function.js"></script>
<script src="public/js/testTwo.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
testTwo.js
var websocket = null;
var sendId = 1;
var receiveId = 0;
//---------------------------
/**
* 初始化websocket
* @param id
*/
doInit(sendId)
function doInit(receiveId){
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
websocket = new WebSocket("ws:localhost:10086/websocket/" + sendId);
} else {
alert("浏览器不支持");
}
websocket.onopen = function () {
addMessage("webscoket已经连接成功");
};
websocket.onclose = function () {
addMessage("webscoket连接失败");
};
websocket.onmessage = function (event) {
alert("收到消息:"+event.data);
};
websocket.onerror = function () {
addMessage("webscoket连接失败");
};
}
/**
* 发送一条消息
*/
function send(){
websocket.send(value('msg')+"~"+receiveId);
}
/**
* 测试打印调试信息用
* @param msg
*/
function addMessage(msg) {
console.log(msg)
}
分别用两个浏览器,打开这两个页面进行访问。结果如下
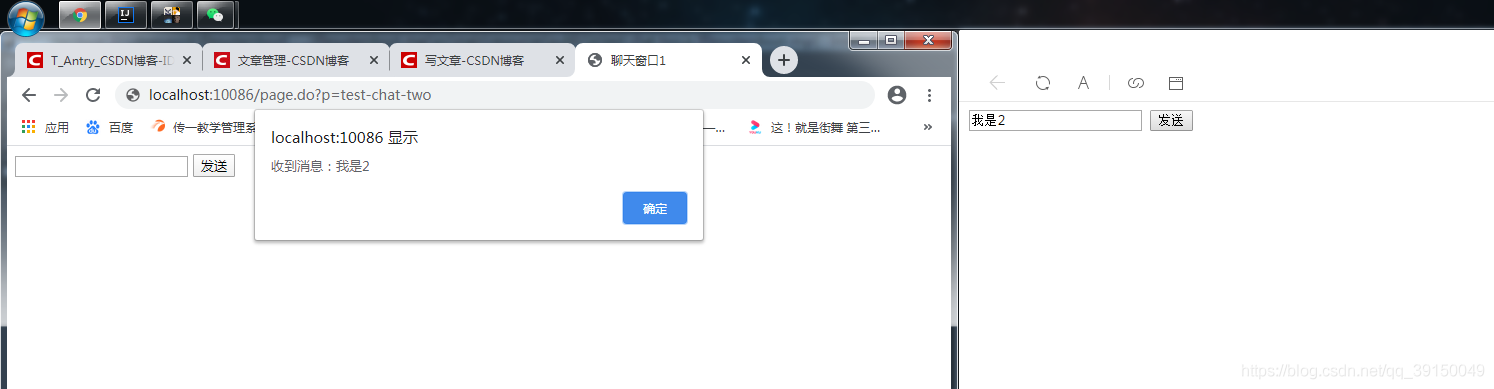
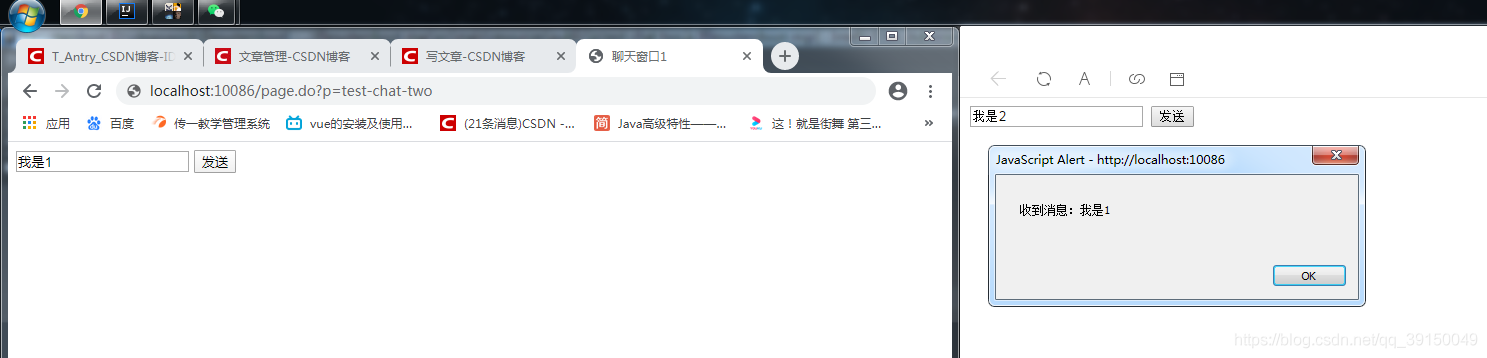
到此这篇关于SpringBoot如何添加WebSocket的方法示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot添加WebSocket内容请搜索易盾网络以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持易盾网络!
