背景
想必大家在项目中都有遇到把一个列表的多个字段累加求和的情况,也就是一个列表的总计。有的童鞋问,这个不是给前端做的吗?后端不是只需要把列表返回就行了嘛。。。没错,我也是这样想的,但是在一场和前端的撕逼大战中败下阵来之后,这个东西就落在我身上了。当时由于工期原因,时间比较紧,也就不考虑效率和易用性了,只是满足当时的需求,就随便写了个方法统计求和。目前稍微闲下来了,就把原来的代码优化下。我们先来看一下原来的代码...
原代码
工具类
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* * @ClassName CalculationUtil
* * @Description TODO(计算工具类)
* * @Author 我恰芙蓉王
* * @Date 2020年04月21日 11:37
* * @Version 1.0.0
*
**/
public class CalculationUtil {
//拼接get set方法的常量
public static final String GET = "get";
public static final String SET = "set";
/**
* 功能描述: 公用统计小计方法
*
* @param list 原数据列表集合
* @param fields 运算的属性数组
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09
* @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回统计好的对象
**/
public static <T> T totalCalculationForBigDecimal(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return null;
}
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();
//返回值
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
list.stream().forEach(v ->
Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> {
try {
String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t);
//获取get方法
Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, BigDecimal.class);
Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object);
setMethod.invoke(object, (objectValue == null ? BigDecimal.ZERO : (BigDecimal) objectValue).add((BigDecimal) getMethod.invoke(v)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
})
);
return (T) object;
}
/**
* 功能描述: 公用统计小计方法
*
* @param list 原数据列表集合
* @param fields 运算的属性数组
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09
* @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回统计好的对象
**/
public static <T> T totalCalculationForDouble(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return null;
}
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();
//返回值
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
list.stream().forEach(v ->
Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> {
try {
String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t);
//获取get方法
Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, Double.class);
Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object);
setMethod.invoke(object, add((objectValue == null ? new Double(0) : (Double) objectValue), (Double) getMethod.invoke(v)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
})
);
return (T) object;
}
/**
* 功能描述: 公用统计小计方法
*
* @param list 原数据列表集合
* @param fields 运算的属性数组
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09
* @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回统计好的对象
**/
public static <T> T totalCalculationForFloat(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return null;
}
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();
//返回值
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
list.stream().forEach(v ->
Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> {
try {
String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t);
//获取get方法
Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field);
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, Float.class);
Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object);
setMethod.invoke(object, add((objectValue == null ? new Float(0) : (Float) objectValue), (Float) getMethod.invoke(v)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
})
);
return (T) object;
}
/**
* 提供精确的加法运算。
*
* @param v1 被加数
* @param v2 加数
* @return 两个参数的和
*/
public static Double add(Double v1, Double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString());
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString());
return b1.add(b2).doubleValue();
}
/**
* 提供精确的加法运算。
*
* @param v1 被加数
* @param v2 加数
* @return 两个参数的和
*/
public static Float add(Float v1, Float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString());
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString());
return b1.add(b2).floatValue();
}
}
实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Order {
//订单号
private String orderNo;
//订单金额
private Double money;
//折扣
private Double discount;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Phone {
//手机名
private String name;
//成本
private BigDecimal cost;
//售价
private BigDecimal price;
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<Order> orderList = new ArrayList<Order>() {
{
add(new Order("D20111111", 256.45, 11.11));
add(new Order("D20111112", 123.85, 1.11));
add(new Order("D20111113", 546.13, 2.14));
add(new Order("D20111114", 636.44, 0.88));
}
};
List<Phone> phoneList = new ArrayList<Phone>() {
{
add(new Phone("苹果", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22")));
add(new Phone("三星", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22")));
add(new Phone("华为", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22")));
add(new Phone("小米", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22")));
}
};
Order orderTotal = totalCalculationForDouble(orderList, "money", "discount");
System.out.println("总计数据为 :" + orderTotal);
Phone phoneTotal = totalCalculationForBigDecimal(phoneList, "cost", "price");
System.out.println("总计数据为 :" + phoneTotal);
}
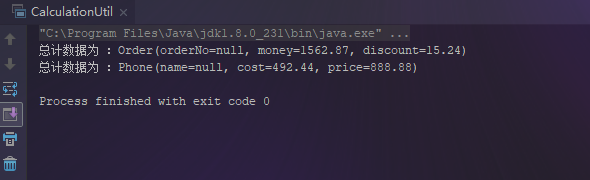
通过以上代码可以看出,效果是实现了,但是缺点也是很明显的:
1.太过冗余,相同代码太多,多个方法只有少数代码不相同(工具类中黄色标注的地方);
2.效率低,列表中每个元素的每个属性都要用到反射赋值;
3.灵活性不够,要求实体类中需要参加运算的属性都为同一类型,即必须都为Double,或必须都为BigDecimal;
4.硬编码,直接在方法调用时把实体类中的字段写死,既不符合JAVA编码规范也容易出错,而且当该实体类中的属性名变更的时候,IDE无法提示我们相应的传参的变更,极容易踩坑。
因为项目中用的JDK版本是1.8,当时在写的时候就想通过方法引用规避掉这种硬编码的方式,因为在Mybatis-Plus中也有用到方法引用赋值条件参数的情况,但还是因为时间紧急,就没去研究了。
今天就顺着这个方向去找了一下实现的方法,把代码优化了部分,如下:
优化后
首先,我是想通过传参为方法引用的方式来获取Getter方法对应的属性名,通过了解,JDK8中已经给我们提供了实现方式,首先声明一个自定义函数式接口(需要实现Serializable)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface SerializableFunction<T, R> extends Function<T, R>, Serializable {
}
然后定义一个反射工具类去解析这个自定义函数式接口,在此工具类中有对方法引用解析的具体实现,在此类中规避掉缺点4
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import java.lang.invoke.SerializedLambda;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @ClassName ReflectionUtil
* @Description TODO(反射工具类)
* @Author 我恰芙蓉王
* @Date 2020年09月08日 15:10
* @Version 2.0.0
**/
public class ReflectionUtil {
public static final String GET = "get";
public static final String SET = "set";
/**
* 功能描述: 通过get方法的方法引用返回对应的Field
*
* @param function
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年09月08日 16:20:56
* @return: java.lang.reflect.Field
**/
public static <T> Field getField(SerializableFunction<T, ?> function) {
try {
/**
* 1.获取SerializedLambda
*/
Method method = function.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace");
method.setAccessible(Boolean.TRUE);
/**
* 2.利用jdk的SerializedLambda,解析方法引用,implMethodName 即为Field对应的Getter方法名
*/
SerializedLambda serializedLambda = (SerializedLambda) method.invoke(function);
//获取get方法的方法名
String getter = serializedLambda.getImplMethodName();
//获取属性名
String fieldName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(getter.replace(GET, ""));
/**
* 3.获取的Class是字符串,并且包名是“/”分割,需要替换成“.”,才能获取到对应的Class对象
*/
String declaredClass = serializedLambda.getImplClass().replace("/", ".");
Class clazz = Class.forName(declaredClass, false, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
/**
* 4.通过Spring中的反射工具类获取Class中定义的Field
*/
return ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, fieldName);
} catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
接着改写原来计算工具类中的代码,在此类中将原缺点的1,2,3点都规避了,将原来冗余的多个方法精简成一个 totalCalculation ,通过 methodMap 对象将get,set方法缓存(但此缓存还有优化的空间,可以将方法中的缓存对象提到tomcat内存或redis中),通过动态获取字段类型来实现不同类型的累加运算
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import static io.renren.modules.test1.ReflectionUtil.GET;
import static io.renren.modules.test1.ReflectionUtil.SET;
/**
* * @ClassName CalculationUtil
* * @Description TODO(计算工具类)
* * @Author 我恰芙蓉王
* * @Date 2020年04月21日 11:37
* * @Version 1.0.0
*
**/
public class CalculationUtil {
/**
* 功能描述: 公用统计小计方法
*
* @param list 原数据列表集合
* @param functions 参与运算的方法引用
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09
* @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回统计好的对象
**/
public static <T> T totalCalculation(List<T> list, SerializableFunction<T, ?>... functions) throws Exception {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
return null;
}
//获取集合中类型的class对象
Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass();
//Getter Setter缓存
Map<SerializableFunction, Map<String, Method>> methodMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//遍历字段,将Getter Setter放入缓存中
for (SerializableFunction function : functions) {
Field field = ReflectionUtil.getField(function);
//获取get方法
Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + StringUtils.capitalize(field.getName()));
//获取set方法
Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + StringUtils.capitalize(field.getName()), field.getType());
//将get set方法封装成一个map放入缓存中
methodMap.put(function, new HashMap<String, Method>() {
{
put(GET, getMethod);
put(SET, setMethod);
}
});
}
//计算
T result = list.parallelStream().reduce((x, y) -> {
try {
Object newObject = x.getClass().newInstance();
Arrays.asList(functions).parallelStream().forEach(f -> {
try {
Map<String, Method> fieldMap = methodMap.get(f);
//获取缓存的get方法
Method getMethod = fieldMap.get(GET);
//获取缓存的set方法
Method setMethod = fieldMap.get(SET);
//调用x参数t属性的get方法
Object xValue = getMethod.invoke(x);
//调用y参数t属性的get方法
Object yValue = getMethod.invoke(y);
//反射赋值到newObject对象
setMethod.invoke(newObject, add(xValue, yValue, getMethod.getReturnType()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
return (T) newObject;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}).get();
return result;
}
/**
* 功能描述: 提供精确的加法运算
*
* @param v1 加数
* @param v2 被加数
* @param clazz 参数的class类型
* @创建人: 我恰芙蓉王
* @创建时间: 2020年09月08日 10:55:56
* @return: java.lang.Object 相加之和
**/
public static Object add(Object v1, Object v2, Class clazz) throws Exception {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString());
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString());
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class);
return constructor.newInstance(b1.add(b2).toString());
}
}
测试实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class People {
//名字
private String name;
//年龄
private Integer age;
//存款
private BigDecimal money;
//身高
private Double height;
}
调用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<People> list = new ArrayList<People>() {
{
add(new People("张三", 18, BigDecimal.valueOf(10000), 168.45));
add(new People("李四", 20, BigDecimal.valueOf(20000), 155.68));
add(new People("王五", 25, BigDecimal.valueOf(30000), 161.54));
add(new People("赵六", 21, BigDecimal.valueOf(30000), 166.66));
}
};
People total = CalculationUtil.totalCalculation(list, People::getAge, People::getMoney, People::getHeight);
System.out.println("总计数据为 :" + total);
}
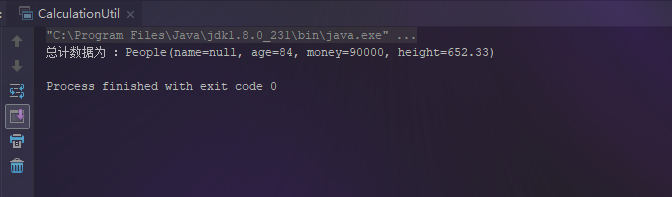
总结
java8的lambda表达式确实极大的简化了我们的代码,提高了编码的效率,流计算更是使数据的运算变得高效快捷,也增加了代码的可(zhuang)读(bi)性。如今java14都出来了,希望在空余时间也能多去了解一下新版本的新特性,而不能老是抱着(你发任你发,我用java8)的心态去学习,毕竟技术的更新迭代是极快的。
到此这篇关于使用java8的方法引用替换硬编码的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java8的方法引用替换硬编码内容请搜索易盾网络以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持易盾网络!
