无向环 一个含有环的无向图如下所示,其中有两个环,分别是 0-2-1-0 和 2-3-4-2: 要检测无向图中的环,可以使用深度优先搜索。假设从顶点 0 出发,再走到相邻的顶点 2,接着走到顶点
一个含有环的无向图如下所示,其中有两个环,分别是 0-2-1-0 和 2-3-4-2:
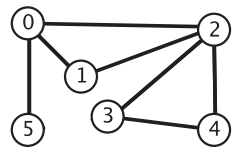
要检测无向图中的环,可以使用深度优先搜索。假设从顶点 0 出发,再走到相邻的顶点 2,接着走到顶点 2 相邻的顶点 1,由于顶点 0 和顶点 1 相邻,并且顶点 0 被标记过了,说明我们饶了一圈,所以无向图中存在环。虽然顶点 2 和顶点 1 相邻,但是并不能说明存在环,因为我们就是从顶点 2 直接走到顶点 1 的,这二者只有边的关系。算法如下所示:
package com.zhiyiyo.graph;
import com.zhiyiyo.collection.stack.LinkStack;
import com.zhiyiyo.collection.stack.Stack;
/**
* 无向图中的环
*/
public class Cycle {
private boolean[] marked;
private Graph graph;
private boolean hasCycle;
public Cycle(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
marked = new boolean[graph.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < graph.V(); ++v) {
if (!marked[v]) {
dfs(v);
}
}
}
private void dfs(int s) {
if (hasCycle()) return;
Stack<Integer> vertexes = new LinkStack<>();
vertexes.push(s);
marked[s] = true;
int lastVertex = s;
while (!vertexes.isEmpty()) {
int v = vertexes.pop();
for (int w : graph.adj(v)) {
if (!marked[w]) {
marked[w] = true;
vertexes.push(w);
} else if (w != lastVertex) {
hasCycle = true;
return;
}
}
lastVertex = v;
}
}
/**
* 图中是否有环
*/
public boolean hasCycle() {
return hasCycle;
}
}
有向图的实现方式和上一篇博客 《如何在 Java 中实现无向图》 中无向图的实现方式几乎一样,只是在添加边 v-w 时只在顶点 v 的链表上添加顶点 w,而不对顶点 w 的链表进行操作。如果把 LinkGraph 中成员变量的访问权限改成 protected,只需继承并重写 addEdge 方法即可:
package com.zhiyiyo.graph;
public class LinkDigraph extends LinkGraph implements Digraph {
public LinkDigraph(int V) {
super(V);
}
@Override
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].push(w);
E++;
}
@Override
public Digraph reverse() {
Digraph digraph = new LinkDigraph(V());
for (int v = 0; v < V(); ++v) {
for (int w : adj(v)) {
digraph.addEdge(w, v);
}
}
return digraph;
}
}
一个含有有向环的有向图如下所示,其中 5-4-3-5 构成了一个环:
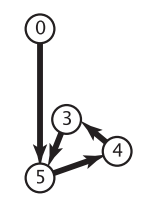
这里使用递归实现的深度优先搜索来检测有向环。假设从顶点 0 开始走,一路经过 5、4、3 这三个顶点,最终又碰到了与顶点 3 相邻的顶点 5,这时候如果知道顶点 5 已经被访问过了,并且递归函数还被压在栈中,就说明深度优先搜索从顶点 5 开始走,又回到了顶点 5,也就是找到了有向环。算法如下所示:
package com.zhiyiyo.graph;
import com.zhiyiyo.collection.stack.LinkStack;
import com.zhiyiyo.collection.stack.Stack;
/**
* 有向图中的环
*/
public class DirectedCycle {
private boolean[] marked;
private boolean[] onStack;
private int[] edgeTo;
private Graph graph;
private Stack<Integer> cycle;
public DirectedCycle(Digraph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
marked = new boolean[graph.V()];
onStack = new boolean[graph.V()];
edgeTo = new int[graph.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < graph.V(); ++v) {
if (!marked[v]) {
dfs(v);
}
}
}
private void dfs(int v) {
marked[v] = true;
onStack[v] = true;
for (int w : graph.adj(v)) {
if (hasCycle()) return;
if (!marked[w]) {
marked[w] = true;
edgeTo[w] = v;
dfs(w);
} else if (onStack[w]) {
cycle = new LinkStack<>();
cycle.push(w);
for (int i = v; i != w; i = edgeTo[i]) {
cycle.push(i);
}
cycle.push(w);
}
}
onStack[v] = false;
}
/**
* 图中是否有环
*/
public boolean hasCycle() {
return cycle != null;
}
/**
* 图中的一个环
*/
public Iterable<Integer> cycle() {
return cycle;
}
}
