react 起步 背景其他章节请看:
七天接手react项目 系列
假如七天后必须接手一个 react 项目(spug - 一个开源运维平台),而笔者只会 vue,之前没有接触过 react,此刻能做的就是立刻展开一个“7天 react 扫盲活动”。
react 活动扫盲方针- 以读懂 spug 项目为目标
- 无需对每个知识点深究
- 功能优先能实现,代码质量无需太苛刻
将 spug 克隆到本地:
exercise> git clone https://github.com/openspug/spug spug-dev-demo
Cloning into 'spug-dev-demo'...
fatal: unable to access 'https://github.com/openspug/spug/': OpenSSL SSL_read: Connection was reset, errno 10054
克隆失败,HTTPS 模式换成 SSH 再次下载:
exercise> git clone git@github.com:openspug/spug.git spug-dev-demo
Cloning into 'spug-dev-demo'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 11675, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (4184/4184), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (1161/1161), done.
remote: Total 11675 (delta 3157), reused 3939 (delta 2991), pack-reused 7491
Receiving objects: 100% (11675/11675), 5.09 MiB | 2.32 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (8460/8460), done.
目录结构如下:
exercise\spug-dev-demo> dir
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 2022/3/12 9:52 .github
d----- 2022/3/12 9:52 docs
d----- 2022/3/12 9:52 spug_api
d----- 2022/3/12 9:52 spug_web
-a---- 2022/3/12 9:52 9 .gitignore
-a---- 2022/3/12 9:52 35184 LICENSE
-a---- 2022/3/12 9:52 3732 README.md
我们前端主要关注 spug_web 这个项目。首先安装依赖包:
spug_web> cnpm i
/ [7/23] Installing @babel/plugin-transform-function-name@^7.8.3platform unsupported react-scripts@3.4.3 › babel-jest@24.9.0 › @jest/transform@24.9.0 › jest-haste-map@24.9.0 › fsevents@^1.2.7 Package require os(darwin) not compatible with your platform(win32)
- [7/23] Installing @babel/plugin-transform-classes@^7.16.7[fsevents@^1.2.7] optional install error: Package require os(darwin) not compatible with your platform(win32)
....
本地启动项目:
spug_web> npm run start
> spug_web@3.0.0 start
> react-app-rewired start
注:由于没有后端 api 的支持,所以不能登录进去。但至少可以从代码上分析这个前端项目。
hello-world直接使用 script 的方式引入 react:
// 新建 hello-world.html
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 此元素的内容将替换为您的组件 -->
</div>
<!-- react 库 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 用于处理 Dom 的 react 包 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- Babel 能够转换 JSX 语法 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
ReactDOM.render(
// 注:无需添加字符串
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
</script>
</body>
访问页面,浏览器显示“Hello, world!”
这里我们引入了三个库,分别是 react 核心库、处理 dom 的 react以及用于转换 jsx。
Tip:
- 笔者在 vscode 中安装 “open in browser” 插件,直接右键选择 “Open with Live Server” 即可。
- 此示例来自 react 官网 hello-world
- React 和 ReactDOM 的 cdn 来自 react 官网-CDN 链接
- unpkg 是一个快速的全球内容交付网络,适用于 npm 上的所有内容。 使用它可以快速轻松地从任何包中加载任何文件
- react 和 vue 都是 javascript 库,都能用于构建用户界面
- React 用于构建用户界面的 JavaScript 库 —— 官网
- 渐进式 JavaScript 框架 —— Vue 官网
Babel 是一个 JavaScript 编译器 —— 官网
babel 之前叫 6to5。意把 es6 转为 es5,后来目标变成支持 ECMAScript 所有语法,后来还支持将 JSX 转成 js。2015年2月,改名为 Bable。
Tip:6to5 is now Babel —— not-born-to-die
使用 Babel 最容易上手的是直接在 html 页面中通过 cdn 引入它。就像这样:
<body>
<div id="output"></div>
<!-- Load Babel -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- Your custom script here -->
<script type="text/babel">
const getMessage = () => "Hello World";
document.getElementById("output").innerHTML = getMessage();
</script>
</body>
浏览器页面显示:“Hello World”。
当在浏览器中加载时,@babel/standalone 将自动编译并执行所有类型为 text/babel 或 text/jsx 的脚本标签。
Tip:@babel/standalone 提供了一个独立的 Babel 构建,用于浏览器和其他非 Node.js 环境
为什么使用 JSX我们建议在 React 中配合使用 JSX,JSX 可以很好地描述 UI 应该呈现出它应有交互的本质形式 —— react 官网-JSX 简介
JSX 仅仅只是 React.createElement(component, props, ...children) 函数的语法糖 —— react 官网-深入 JSX
语法糖,通常用起来更方便,功能或许也更强大。比如类(Class)只是我们自定义类的一个语法糖。jsx 是 React.createElement 的语法糖,意义应该也差不多。
在 hello-world 中我们使用的是语法糖(jsx)。就像这样:
// jsx
const reactElem = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>
ReactDOM.render(
reactElem,
document.getElementById('root')
);
若不使用语法糖(使用 React.createElement)。就像这样:
const reactElem = React.createElement(
'h1',
{/* className: 'greeting' */ },
'Hello, world!'
);
ReactDOM.render(reactElem, ...)
对比发现,jsx 更简洁。
React 元素react 元素是创建起来开销极小的普通对象,用于描述你在屏幕上想看到的内容。与浏览器的 dom 元素不同。
react 元素是构成 React 应用的最小砖块 —— react 官网-元素渲染
注:不要混淆元素与组件,react 组件是由 react 元素构成的。
React.createElement 创建并返回指定类型的新的 react 元素。下面我们将 react 元素打印出来:
const reactElem = React.createElement(
'h1',
{},
'Hello, world!'
)
console.log('reactElem: ', reactElem)
react 元素:
reactElem: {$$typeof: Symbol(react.element), type: 'h1', key: null, ref: null, props: {…}, …}
$$typeof: Symbol(react.element)
key: null
props: {children: 'Hello, world!'}
ref: null
type: "h1"
_owner: null
_store: {validated: false}
_self: null
_source: null
[[Prototype]]: Object
Tip:使用 jsx,输出也是一样的:
const reactElem = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>
console.log('reactElem: ', reactElem)
react 元素只有极少的几个属性。而真实 dom 元素上的属性却要多得多。你可以通过浏览器运行以下代码,将鼠标移到 root 和 reactElem 对比查看属性数量。
const reactElem = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>
let root = document.getElementById('root')
// 打个断点
debugger
react 元素是不可变对象。一旦被创建,你就无法更改它的子元素或者属性。
React 只更新它需要更新的部分React DOM 会将元素和它的子元素与它们之前的状态进行比较,并只会进行必要的更新来使 DOM 达到预期的状态。
JSX 语法规则JSX,是一个 JavaScript 的语法扩展。JSX 可能会使人联想到模板语言,但它具有 JavaScript 的全部功能。
不要写引号JSX 标签语法既不是字符串也不是 HTML。
// 正确。页面显示“Hello, world!”
const reactElem = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>
// 错误。页面显示“<h1>Hello, world!</h1>”
const reactElem = '<h1>Hello, world!</h1>'
let _class = 'greeting'
let cnt = 'Hello, world!'
const reactElem = (
<h1 className={_class}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
)
浏览器显示:”HELLO, WORLD!“。元素内容:
<h1 class="greeting">HELLO, WORLD!</h1>
倘若是用 class。就像这样:
const reactElem = (
<h1 class={_class}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
)
元素内容正常:
<h1 class="greeting">HELLO, WORLD!</h1>
但浏览器控制台报错:Warning: Invalid DOM property 'class'. Did you mean 'className'?
倘若使用 style="color:pink":
const reactElem = (
<h1 className={_class} style="color:pink">
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
)
控制台报错:
react-dom.development.js:2716 Uncaught Error: The 'style' prop expects a mapping from style properties to values, not a string. For example, style={{marginRight: spacing + 'em'}} when using JSX.
react-dom.development.js:2716 未捕获的错误:“样式”道具需要从样式属性到值的映射,而不是字符串。 例如,使用 JSX 时 style={{marginRight: spacing + 'em'}}。
改成 {{ color: 'pink' }} 则正常:
const reactElem = (
<h1 className={_class} style={{ color: 'pink' }}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
)
const reactElem = (
<h1 className={_class} style={{ color: 'pink' }}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
<p>apple</p>
)
vscode 红波浪线提示:JSX expressions must have one parent element(JSX 表达式必须有一个父元素)
包裹一个 div 即可。就像这样:
const reactElem = (
<div>
<h1 className={_class} style={{ color: 'pink' }}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
<p>apple</p>
</div>
)
<div>
<h1 className={_class} style={{ color: 'pink' }}>
{cnt.toLocaleUpperCase()}
</h1>
/* input 标签未闭合 */
<input type="text">
</div>
vscode 红波浪线提示:JSX element 'input' has no corresponding closing tag(JSX 元素“输入”没有相应的结束标记)。
浏览器运行控制台报错:Uncaught SyntaxError: /Inline Babel script: Unterminated JSX contents(未终止的 JSX 内容)。
以下两种闭合方式都可以:
<input type="text" />
<input type="text"></input>
const reactElem = (
<div>
<mybutton>18</mybutton>
</div>
)
页面显示:“18”。浏览器报错:
react-dom.development.js:61 Warning: The tag <mybutton> is unrecognized in this browser. If you meant to render a React component, start its name with an uppercase letter.
react-dom.development.js:61 警告:标签 <mybutton> 在此浏览器中无法识别。 如果您打算渲染一个 React 组件,请以大写字母开头。
以小写字母开头的元素代表一个 HTML 内置组件,比如 <div> 或者 <span> 会生成相应的字符串 'div' 或者 'span' 传递给 React.createElement(作为参数)。大写字母开头的元素则对应着在 JavaScript 引入或自定义的组件,如 <Foo /> 会编译为 React.createElement(Foo)。
官网示例中的 jsx 用括号包围起来。就像这样:
// 有括号
const element = (
<h1 className="greeting">
Hello, world!
</h1>
);
感觉就是在写 html,而且还有缩进。
笔者尝试将括号去除:
const reactElem =
<h1 className="greeting">
Hello, world!
</h1>
ReactDOM.render(
reactElem,
document.getElementById('root')
)
浏览器还是正常显示:“Hello, world!”。
我们建议将内容包裹在括号中,虽然这样做不是强制要求的,但是这可以避免遇到自动插入分号陷阱 —— 官网-JSX 简介
JSX 小练习JavaScript 表达式可以被包裹在 {} 中作为子元素。例如,以下表达式是等价的:
<MyComponent>foo</MyComponent>
<MyComponent>{'foo'}</MyComponent>
例如将下面 ul 列表改为动态:
<ul>
<li>finish doc</li>
<li>submit pr</li>
<li>nag dan to review</li>
</ul>
let todos = ['finish doc', 'submit pr', 'nag dan to review'];
const reactElem = (
<ul>
{
todos.map(item => {
return <li>{item}</li>
})
}
</ul>
)
浏览器控制台告警:
Warning: Each child in a list should have a unique "key" prop.
警告:列表中的每个孩子都应该有一个唯一的“key”属性。
添加 key 即可:
todos.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={index}>{item}</li>
})
注:用元素在数组中的下标作为 key,有时会存在问题 —— 正确使用 key
Tip:相同功能,官网(JavaScript 表达式作为子元素)是这样实现的:
function Item(props) {
return <li>{props.message}</li>;
}
function TodoList() {
const todos = ['finish doc', 'submit pr', 'nag dan to review'];
return (
<ul>
{todos.map((message) => <Item key={message} message={message} />)}
</ul>
);
}
const reactElem = TodoList()
在 vue 中我们会这样使用组件:
// 注册组件
Vue.component('component-a', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-b', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-c', { /* ... */ })
new Vue({ el: '#app' })
<div id="app">
<component-a></component-a>
<component-b></component-b>
<component-c></component-c>
</div>
Tip:仅作示意,通常我们会使用 spa 单页面应用开发。
于是可以将应用界面抽象成一棵组件树:
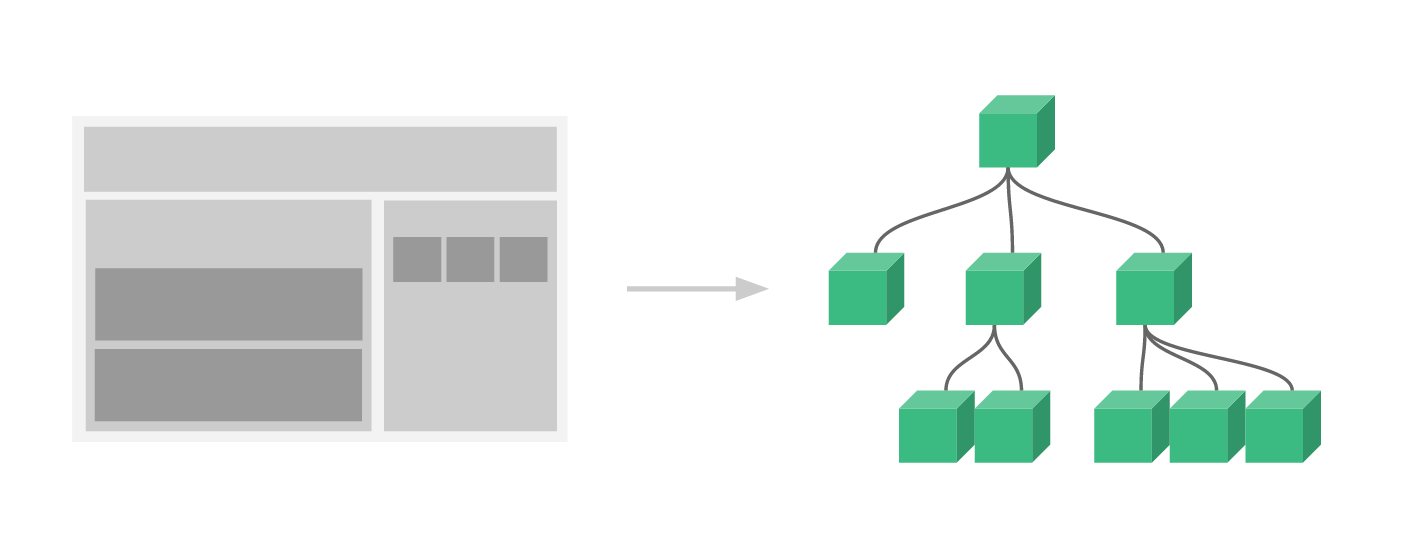
对比 vue 项目和react 项目的入口文件,其实都是将 App 组件挂载到 dom 元素上:
// vue项目/main.js
import App from './App.vue'
...
new Vue({
router,
store,
// 将 App 挂载到 #app
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
// spug_web/src/index.js
import App from './App';
...
// 将 App 挂载到 #root
ReactDOM.render(
<Router history={history}>
<ConfigProvider locale={zhCN} getPopupContainer={() => document.fullscreenElement || document.body}>
<App/>
</ConfigProvider>
</Router>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
定义组件最简单的方式是使用函数。请看示例:
<script type="text/babel">
// 函数组件
function MyComponent(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<MyComponent name="peng" />
</div>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
</script>
页面显示“Hello, peng”。组件对应的 html 为:<h1>Hello, peng</h1>。
我们还可以使用 es6 的 class 来定义组件。就像这样:
// class 组件。
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// 必须定义 render()。否则会报错:
// MyComponent(...): No `render` method found on the returned component instance: you may have forgotten to define `render`.
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>
}
}
// 省略。用法相同
Tip:
- 在
React.Component的子类中,必须定义render()函数 - 我们强烈建议你不要创建自己的组件基类。 在 React 组件中,代码重用的主要方式是组合而不是继承。 —— 官网
- class 组件目前提供了更多的功能
首先看函数组件中的 this:
// 函数组件
function MyComponent(props) {
+ console.log('this', this)
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}
浏览器制台输出:this undefined。说明没有 this。
上文我们已经在 class 组件的 render() 中使用了 this,我们将其打印出来看一下:
// class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
+ console.log('this', this)
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>
}
}
this MyComponent {props: {…}, context: {…}, refs: {…}, updater: {…}, _reactInternals: FiberNode, …}
context: {}
props: {name: 'peng'}
refs: {}
state: null
updater: {isMounted: ƒ, enqueueSetState: ƒ, enqueueReplaceState: ƒ, enqueueForceUpdate: ƒ}
_reactInternalInstance: {_processChildContext: ƒ}
_reactInternals: FiberNode {tag: 1, key: null, stateNode: MyComponent, elementType: ƒ, type: ƒ, …}
isMounted: (…)
replaceState: (…)
[[Prototype]]: Component
将函数组件 MyComponent 放入 bable 的试一试中,会被翻译成:
"use strict";
function MyComponent(props) {
console.log('this', this);
return /*#__PURE__*/React.createElement("h1", null, "Hello, ", props.name);
}
注:jsx 被 babel 识别了处理啊,因为翻译成了 React.createElement。
严格模式下,如果没有指定 this 的话,它值是 undefined。
我们将 class 组件 MyComponent 也翻译一下:
"use strict";
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
console.log('this', this);
return /*#__PURE__*/React.createElement("h1", null, "Hello, ", this.props.name);
}
}
我们首先回忆一下 vue 中的 props:
- props 用于接收来自父组件的数据。就像这样:
<div id='app'>
<button-counter :msg='message'></button-counter>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('button-counter', {
props: ['msg'],
template: `<div>
来自父组件的信息: {{msg}}
</div>`
})
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello'
}
})
</script>
- 可以使用.sync 修饰符来实现一个 prop 进行“双向绑定”。即子组件不要直接更改父组件的这个属性,而应该通知父组件,让父组件自己去更改这个属性。
- prop 验证。就像这样:
Vue.component('my-component', {
props: {
// 基础的类型检查 (`null` 和 `undefined` 会通过任何类型验证)
propA: Number,
// 必填的字符串
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// 带有默认值的数字
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 带有默认值的对象
propE: {
type: Object,
// 对象或数组默认值必须从一个工厂函数获取
default: function () {
return { message: 'hello' }
}
},
...
}
})
在 react 中,props 的作用也类似,即用于接收父组件传来的属性。
props 基本用法给组件 MyComponent 定义了两个 prop(属性):
name,字符串类型,默认值是 defaultNamesay,函数类型,必填
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- 使用 PropTypes 进行类型检查 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/prop-types@15.6/prop-types.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, say } = this.props
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}, {say()}</h1>
}
}
// 属性类型
MyComponent.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string,
// 注:函数不是 function,而是 func
// 函数类型,并且必填
say: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
// 默认值
MyComponent.defaultProps = {
name: 'defaultName'
}
const props2 = { say: () => 'I know you' }
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<MyComponent name="peng" say={() => 'I love you'} />
<MyComponent {...props2} />
</div>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
</script>
</body>
页面显示:
Hello, peng, I love you
Hello, defaultName, I know you
自 React v15.5 起,React.PropTypes 已移入另一个包中。请使用 prop-types 库 代替 —— 官网
Tip:有关类型检测更多介绍请看 使用 PropTypes 进行类型检查
Props 的只读性组件无论是使用函数声明还是通过 class 声明,都决不能修改自身的 props。倘若我们尝试修改 props 属性,就像这样:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
+ this.props.name = 'aName'
...
}
}
浏览器控制台将报错如下:
Inline Babel script:10 Uncaught TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object '#<Object>'
内联 Babel 脚本:10 未捕获的类型错误:无法分配给对象 '#<Object>' 的只读属性 'name'
上文中,类型检测的相关代码,从语法上来说就是给 MyComponent 类增加两个静态属性:
// 类型检测相关代码
MyComponent.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string,
say: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
MyComponent.defaultProps = {
name: 'defaultName'
}
我们可以使用 static 语法来对其优化。就像这样:
// class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// 属性类型
static propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string,
say: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
// 默认值
static defaultProps = {
name: 'defaultName'
}
render() {
...
}
}
上文我们已经使用过了:
function MyComponent(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}
虽然函数组件中没有 this,不能像 class 组件那样通过 this 去使用 props(this.props.name),但函数组件可以通过参数接收 props。
在 React 组件挂载之前,会调用它的构造函数。在为 React.Component 子类实现构造函数时,应在其他语句之前调用 super(props)。否则,this.props 在构造函数中可能会出现未定义的 bug —— 官网
这句话什么意思?请看示例:
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 输出 {}。表明 this.props 有值
console.log(this.props.name)
}
render() {
...
}
}
将 super(props) 改为 super():
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super()
// 输出 undefined
console.log(this.props)
}
render() {
...
}
}
其他章节请看:
七天接手react项目 系列
