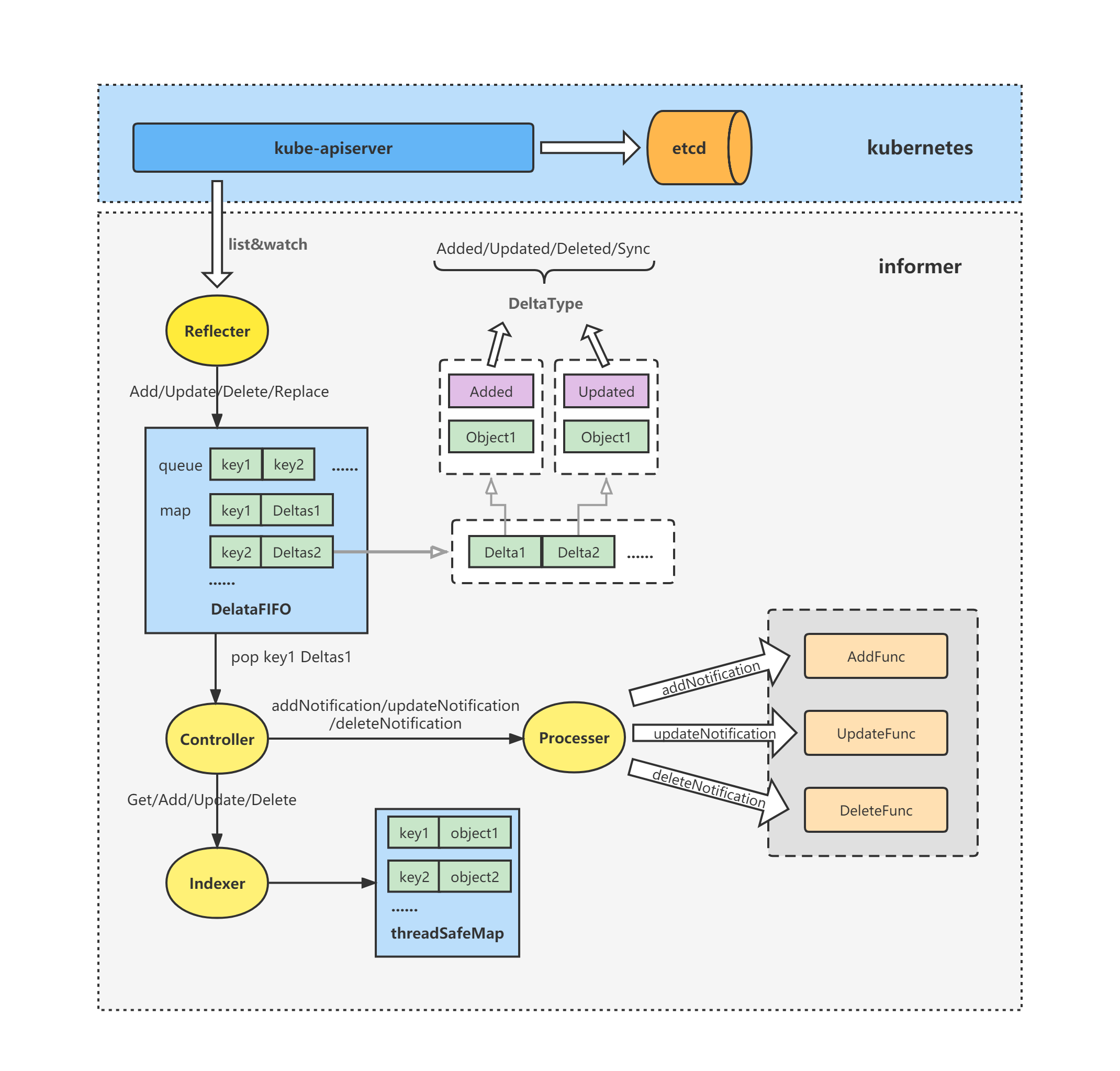
Reflector从kube-apiserver中list&watch资源对象,然后将对象的变化包装成Delta并将其丢到DeltaFIFO中。简单点来说,就是将Etcd 的对象及其变化反射到DeltaFIFO中。
Reflector首先通过List操作获取全量的资源对象数据,调用DeltaFIFO的Replace方法全量插入DeltaFIFO,然后后续通过Watch操作根据资源对象的变化类型相应的调用DeltaFIFO的Add、Update、Delete方法,将对象及其变化插入到DeltaFIFO中。
Reflector的健壮性处理机制Reflector有健壮性处理机制,用于处理与apiserver断连后重新进行List&Watch的场景。也是因为有这样的健壮性处理机制,所以我们一般不去直接使用客户端的Watch 方法来处理自己的业务逻辑,而是使用informers。
Reflector的两个核心操作:
(1)List&Watch;
(2)将对象的变化包装成Delta然后扔进DeltaFIFO。
通过下面这个informer的概要架构图,可以大概看到Reflector在整个informer中所处的位置及其作用。
先来看到Reflector结构体,这里重点看到以下属性:
(1)expectedType:放到Store中(即DeltaFIFO中)的对象类型;
(2)store:store会赋值为DeltaFIFO,具体可以看之前的informer初始化与启动分析即可得知,这里不再展开分析;
(3)listerWatcher:存放list方法和watch方法的ListerWatcher interface实现;
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
type Reflector struct {
// name identifies this reflector. By default it will be a file:line if possible.
name string
// The name of the type we expect to place in the store. The name
// will be the stringification of expectedGVK if provided, and the
// stringification of expectedType otherwise. It is for display
// only, and should not be used for parsing or comparison.
expectedTypeName string
// The type of object we expect to place in the store.
expectedType reflect.Type
// The GVK of the object we expect to place in the store if unstructured.
expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind
// The destination to sync up with the watch source
store Store
// listerWatcher is used to perform lists and watches.
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// period controls timing between one watch ending and
// the beginning of the next one.
period time.Duration
resyncPeriod time.Duration
ShouldResync func() bool
// clock allows tests to manipulate time
clock clock.Clock
// lastSyncResourceVersion is the resource version token last
// observed when doing a sync with the underlying store
// it is thread safe, but not synchronized with the underlying store
lastSyncResourceVersion string
// lastSyncResourceVersionMutex guards read/write access to lastSyncResourceVersion
lastSyncResourceVersionMutex sync.RWMutex
// WatchListPageSize is the requested chunk size of initial and resync watch lists.
// Defaults to pager.PageSize.
WatchListPageSize int64
}
NewReflector为Reflector的初始化方法,返回一个Reflector结构体,这里主要看到初始化Reflector的时候,需要传入ListerWatcher interface的实现。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func NewReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
}
// NewNamedReflector same as NewReflector, but with a specified name for logging
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
r := &Reflector{
name: name,
listerWatcher: lw,
store: store,
period: time.Second,
resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,
clock: &clock.RealClock{},
}
r.setExpectedType(expectedType)
return r
}
ListerWatcher interface定义了Reflector应该拥有的最核心的两个方法,即List与Watch,用于全量获取资源对象以及监控资源对象的变化。关于List与Watch什么时候会被调用,怎么被调用,在后续分析Reflector核心处理方法的时候会详细做分析。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/listwatch.go
type Lister interface {
// List should return a list type object; the Items field will be extracted, and the
// ResourceVersion field will be used to start the watch in the right place.
List(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error)
}
type Watcher interface {
// Watch should begin a watch at the specified version.
Watch(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
}
type ListerWatcher interface {
Lister
Watcher
}
继续看到ListWatch struct,其实现了ListerWatcher interface。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/listwatch.go
type ListFunc func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error)
type WatchFunc func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
type ListWatch struct {
ListFunc ListFunc
WatchFunc WatchFunc
// DisableChunking requests no chunking for this list watcher.
DisableChunking bool
}
再来看到ListWatch struct初始化的一个例子。在NewDeploymentInformer初始化Deployment对象的informer中,会初始化ListWatch struct并定义其ListFunc与WatchFunc,可以看到ListFunc与WatchFunc即为其资源对象客户端的List与Watch方法。
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/informers/apps/v1beta1/deployment.go
func NewDeploymentInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return NewFilteredDeploymentInformer(client, namespace, resyncPeriod, indexers, nil)
}
func NewFilteredDeploymentInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.AppsV1beta1().Deployments(namespace).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.AppsV1beta1().Deployments(namespace).Watch(options)
},
},
&appsv1beta1.Deployment{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
最后来看到Reflector的启动入口Run方法,其主要是循环调用r.ListAndWatch,该方法是Reflector的核心处理方法,后面会详细进行分析。另外,也可以看到Reflector有健壮性处理机制,即循环调用r.ListAndWatch方法,用于处理与apiserver断连后重新进行List&Watch的场景。也是因为有这样的健壮性处理机制,所以我们一般不去直接使用客户端的Watch 方法来处理自己的业务逻辑,而是使用informers。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(3).Infof("Starting reflector %v (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
wait.Until(func() {
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(err)
}
}, r.period, stopCh)
}
分析完了初始化与启动后,现在来看到Reflector的核心处理方法ListAndWatch。
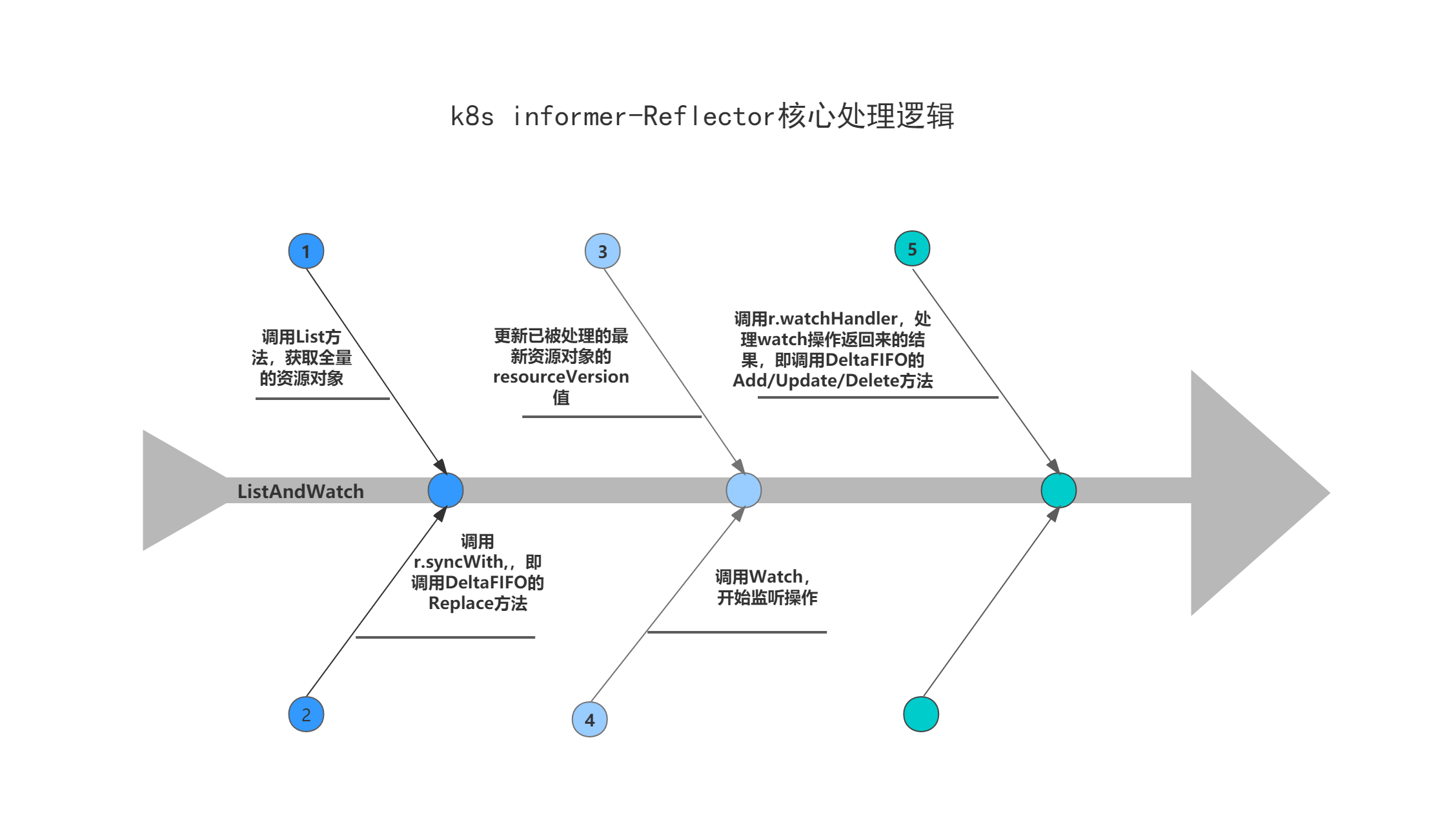
ListAndWatch的主要逻辑分为三大块:
A.List操作(只执行一次):
(1)设置ListOptions,将ResourceVersion设置为“0”;
(2)调用r.listerWatcher.List方法,执行list操作,即获取全量的资源对象;
(3)根据list回来的资源对象,获取最新的resourceVersion;
(4)资源转换,将list操作获取回来的结果转换为[]runtime.Object结构;
(5)调用r.syncWith,根据list回来转换后的结果去替换store里的items;
(6)调用r.setLastSyncResourceVersion,为Reflector更新已被处理的最新资源对象的resourceVersion值;
B.Resync操作(异步循环执行);
(1)判断是否需要执行Resync操作,即重新同步;
(2)需要则调用r.store.Resync操作后端store做处理;
C.Watch操作(循环执行):
(1)stopCh处理,判断是否需要退出循环;
(2)设置ListOptions,设置resourceVersion为最新的resourceVersion,即从list回来的最新resourceVersion开始执行watch操作;
(3)调用r.listerWatcher.Watch,开始监听操作;
(4)watch监听操作的错误返回处理;
(5)调用r.watchHandler,处理watch操作返回来的结果,操作后端store,新增、更新或删除items;
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
klog.V(3).Infof("Listing and watching %v from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.name)
var resourceVersion string
// A.List操作(只执行一次)
// (1)设置ListOptions,将ResourceVersion设置为“0”
// Explicitly set "0" as resource version - it's fine for the List()
// to be served from cache and potentially be delayed relative to
// etcd contents. Reflector framework will catch up via Watch() eventually.
options := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: "0"}
if err := func() error {
initTrace := trace.New("Reflector ListAndWatch", trace.Field{"name", r.name})
defer initTrace.LogIfLong(10 * time.Second)
var list runtime.Object
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
//(2)调用r.listerWatcher.List方法,执行list操作,即获取全量的资源对象
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicCh <- r
}
}()
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
if r.WatchListPageSize != 0 {
pager.PageSize = r.WatchListPageSize
}
// Pager falls back to full list if paginated list calls fail due to an "Expired" error.
list, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
close(listCh)
}()
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
case r := <-panicCh:
panic(r)
case <-listCh:
}
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Failed to list %v: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects listed")
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to understand list result %#v: %v", r.name, list, err)
}
//(3)根据list回来的资源对象,获取最新的resourceVersion
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")
//(4)资源转换,将list操作获取回来的结果转换为```[]runtime.Object```结构
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", r.name, list, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")
//(5)调用r.syncWith,根据list回来转换后的结果去替换store里的items
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to sync list result: %v", r.name, err)
}
initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")
//(6)调用r.setLastSyncResourceVersion,为Reflector更新已被处理的最新资源对象的resourceVersion值
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
// B.Resync操作(异步循环执行)
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
defer func() {
cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup
}()
for {
select {
case <-resyncCh:
case <-stopCh:
return
case <-cancelCh:
return
}
//(1)判断是否需要执行Resync操作,即重新同步
if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: forcing resync", r.name)
//(2)需要则调用r.store.Resync操作后端store做处理
if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {
resyncerrc <- err
return
}
}
cleanup()
resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()
}
}()
// C.Watch操作(循环执行)
for {
//(1)stopCh处理,判断是否需要退出循环
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
}
//(2)设置ListOptions,设置resourceVersion为最新的resourceVersion,即从list回来的最新resourceVersion开始执行watch操作
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options = metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
//(3)调用r.listerWatcher.Watch,开始监听操作
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
//(4)watch监听操作的错误返回处理
if err != nil {
switch err {
case io.EOF:
// watch closed normally
case io.ErrUnexpectedEOF:
klog.V(1).Infof("%s: Watch for %v closed with unexpected EOF: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: Failed to watch %v: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err))
}
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case wait and resend watch request.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
return nil
}
//(5)调用r.watchHandler,处理watch操作返回来的结果,操作后端store,新增、更新或删除items
if err := r.watchHandler(w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case apierrs.IsResourceExpired(err):
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
}
}
}
这里主要讲一下ListOptions中的ResourceVersion属性的作用。
上述讲到的Reflector中,list操作时将 resourceVersion 设置了为“0”,此时返回的数据是apiserver cache中的,并非直接读取 etcd 而来,而apiserver cache中的数据可能会因网络或其他原因导致与etcd中的数据不同。
list操作时,resourceVersion 有三种设置方法:
(1)第一种:不设置,此时会从直接从etcd中读取,此时数据是最新的;
(2)第二种:设置为“0”,此时从apiserver cache中获取;
(3)第三种:设置为指定的resourceVersion,获取resourceVersion大于指定版本的所有资源对象。
详细参考:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/using-api/api-concepts/#resource-versions
3.1 r.syncWithr.syncWith方法主要是调用r.store.Replace方法,即根据list的结果去替换store里的items,具体关于r.store.Replace方法的分析,在后续对DeltaFIFO进行分析时再做具体的分析。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func (r *Reflector) syncWith(items []runtime.Object, resourceVersion string) error {
found := make([]interface{}, 0, len(items))
for _, item := range items {
found = append(found, item)
}
return r.store.Replace(found, resourceVersion)
}
lastSyncResourceVersion属性为Reflector struct的一个属性,用于存储已被Reflector处理的最新资源对象的ResourceVersion,r.setLastSyncResourceVersion方法用于更新该值。
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
func (r *Reflector) setLastSyncResourceVersion(v string) {
r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Lock()
defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Unlock()
r.lastSyncResourceVersion = v
}
type Reflector struct {
...
lastSyncResourceVersion string
...
}
r.watchHandler主要是处理watch操作返回来的结果,其主要逻辑为循环做以下操作,直至event事件处理完毕:
(1)从watch操作返回来的结果中获取event事件;
(2)event事件相关错误处理;
(3)获得当前watch到资源的ResourceVersion;
(4)区分watch.Added、watch.Modified、watch.Deleted三种类型的event事件,分别调用r.store.Add、r.store.Update、r.store.Delete做处理,具体关于r.store.xxx的方法分析,在后续对DeltaFIFO进行分析时再做具体的分析;
(5)调用r.setLastSyncResourceVersion,为Reflector更新已被处理的最新资源对象的resourceVersion值;
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
// watchHandler watches w and keeps *resourceVersion up to date.
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
start := r.clock.Now()
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
// (1)从watch操作返回来的结果中获取event事件
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
// (2)event事件相关错误处理
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrs.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if r.expectedType != nil {
if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
if r.expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
// (3)获得当前watch到资源的ResourceVersion
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
// (4)区分watch.Added、watch.Modified、watch.Deleted三种类型的event事件,分别调用r.store.Add、r.store.Update、r.store.Delete做处理
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
// (5)调用r.setLastSyncResourceVersion,为Reflector更新已被处理的最新资源对象的resourceVersion值
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
eventCount++
}
}
watchDuration := r.clock.Since(start)
if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", r.name)
}
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, eventCount)
return nil
}
至此Reflector的分析就结束了,最后来总结一下。
总结 Reflector核心处理逻辑先来用一幅图来总结一下Reflector核心处理逻辑。
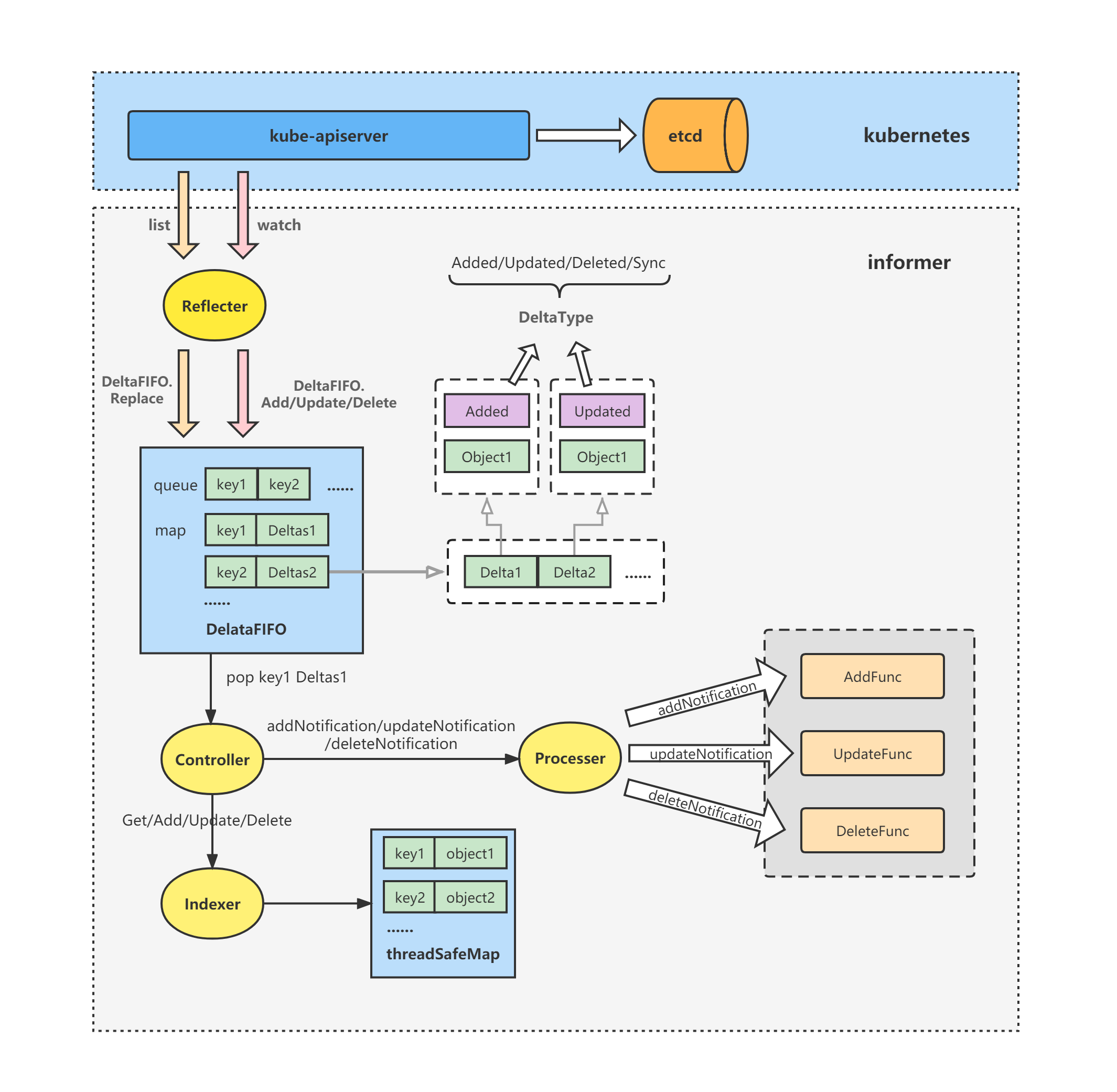
下面这个架构图相比文章开头的informer的概要架构图,将Refletor部分详细分解了,也顺带回忆一下Reflector在informer架构中的主要作用:
(1)Reflector首先通过List操作获取全量的资源对象数据,调用DeltaFIFO的Replace方法全量插入DeltaFIFO;
(2)然后后续通过Watch操作根据资源对象的变化类型相应的调用DeltaFIFO的Add、Update、Delete方法,将对象及其变化插入到DeltaFIFO中。
在对informer中的Reflector分析完之后,接下来将分析informer中的DeltaFIFO。
