 数据库类型有:1、关系数据库,有【MySQL、MariaDB】;2、非关系型数据库,【Cassandra、MongoDB】;3、键值【key-value】数据库,有【Dynamo、LevelDB】。
数据库的基本概念
数据库类型有:1、关系数据库,有【MySQL、MariaDB】;2、非关系型数据库,【Cassandra、MongoDB】;3、键值【key-value】数据库,有【Dynamo、LevelDB】。
数据库的基本概念
-
DataBase (DB)用于存储和管理数据的仓库。
-
-
持久化存储数据的。其实数据库就是一个文件系统
-
方便存储和管理数据
-
使用了统一的方式操作数据库 -- SQL
-
-
cmd--> services.msc 打开服务的窗口,启动mysql服务
-
找到对应的mysql服务并启动
-
mysql -uroot -p密码,如果需要输入端口 mysql -uroot -P3305 -p密码
-
退出:exit quit
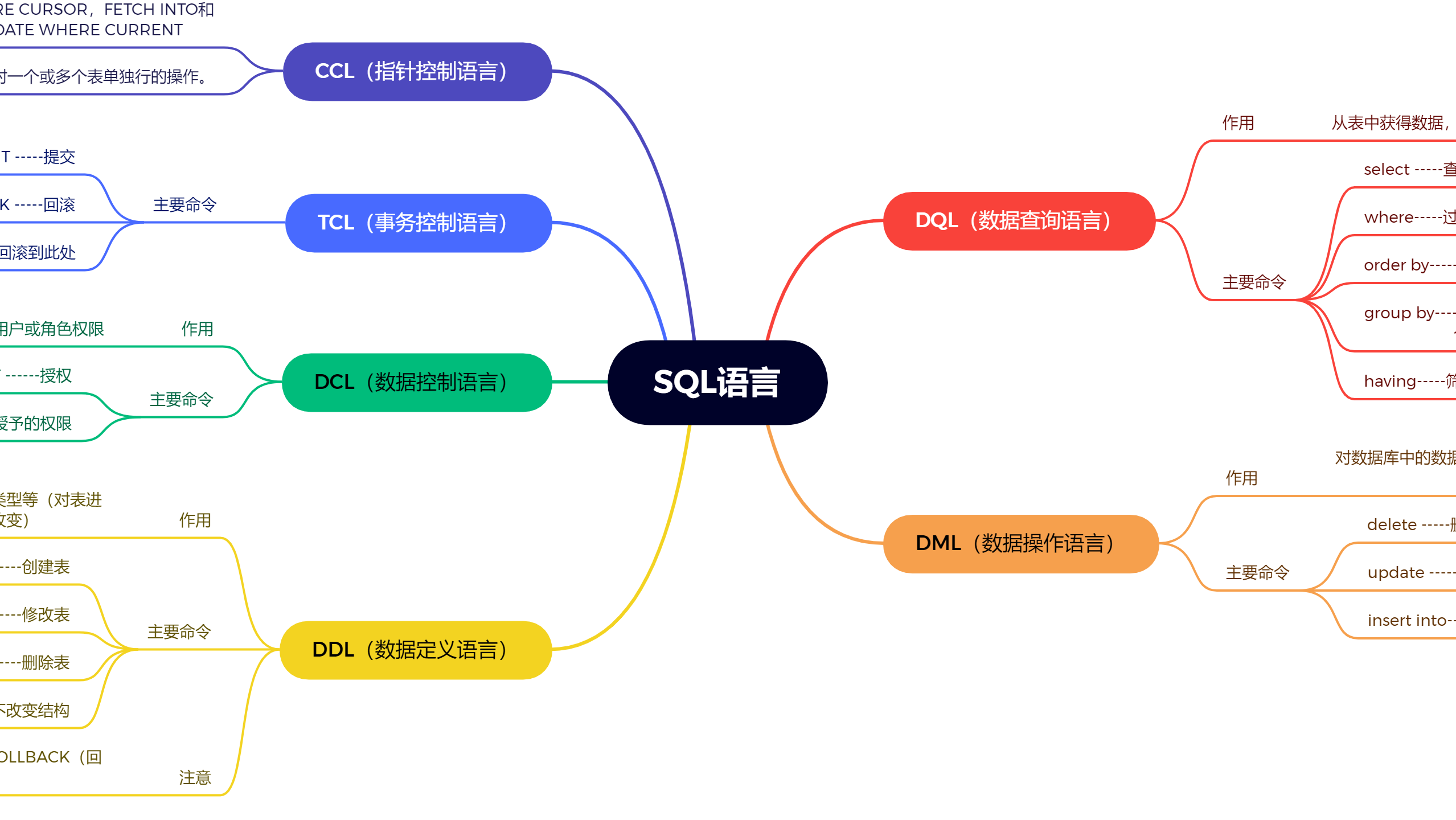
- Structured Query Language:结构化查询语言,其实就是定义了操作所有关系型数据库的规则。
- 每一种数据库操作的方式存在不一样的地方,称为“方言”。
- SQL通用语法
- SQL 语句可以单行或多行书写,以分号结尾。
show databases; - 可使用空格和缩进来增强语句的可读性。
- MySQL 数据库的 SQL 语句不区分大小写。
- 3 种注释
- 单行注释: -- 注释内容 或 # 注释内容(mysql 特有)
- 多行注释: /* 注释 */
- SQL 语句可以单行或多行书写,以分号结尾。
- SQL分类
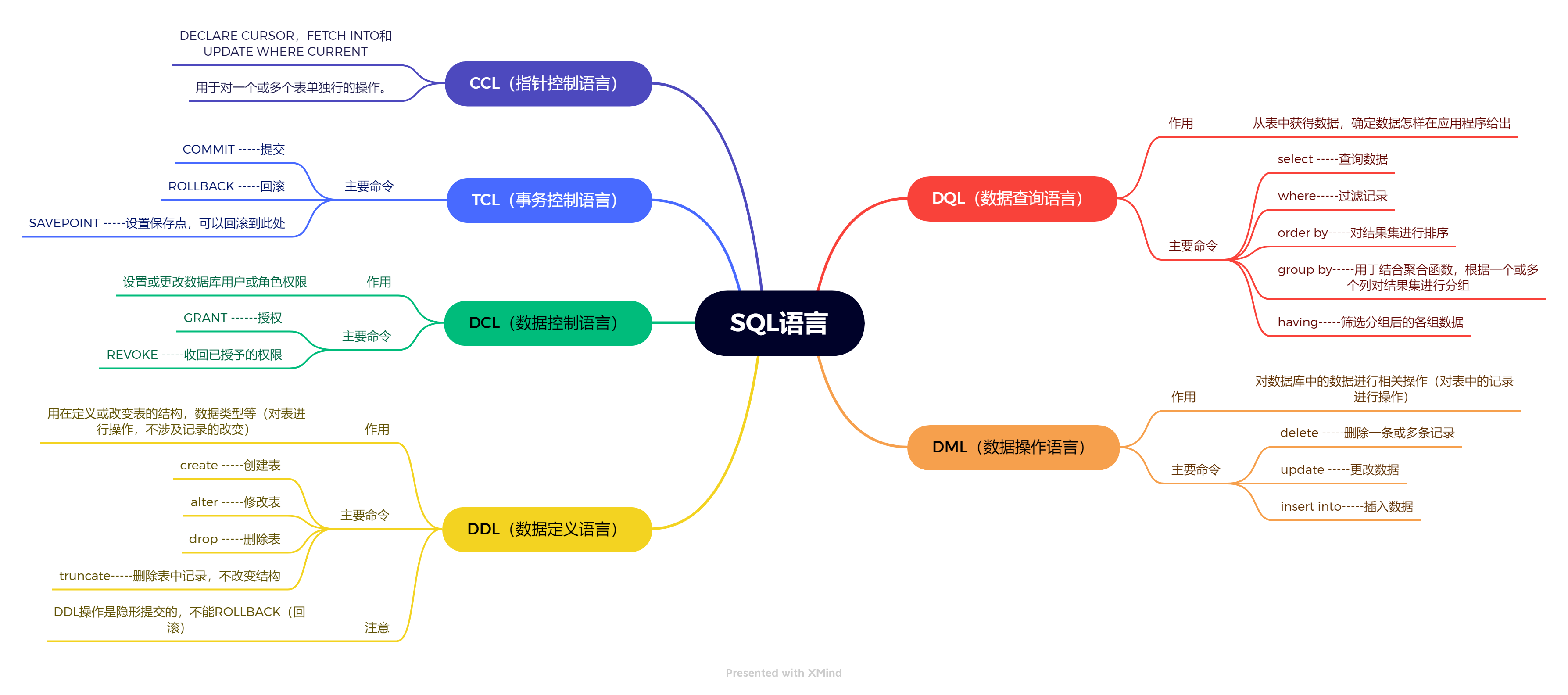
- C(Create):创建
- 创建数据库:create database 数据库名称;
create database db1; - 创建数据库,判断不存在,再创建: create database if not exists 数据库名称;
create database if not exists db; - 创建数据库,并指定字符集 create database 数据库名称 character set 字符集名;
create database db3 character set utf8; - 练习:创建db4数据库,判断是否存在,并制定字符集为gbk
create database if not exists db4 character set gbk; -
R(Retrieve):查询
- 查询所有数据库的名称
show databases; - 查询某个数据库的字符集:查询某个数据库的创建语句
- show create database 数据库名称;
show create database db3;
- 查询所有数据库的名称
-
U(Update):修改
- 修改数据库的字符集
- alter database 数据库名称 character set 字符集名称;
alter database db4 character set utf8;
-
D(Delete):删除
- 删除数据库drop database 数据库名称;
drop database db4; - 判断数据库存在,存在再删除drop database if exists 数据库名称;
drop database if exists db3;
- 删除数据库drop database 数据库名称;
-
使用数据库
- 查询当前正在使用的数据库名称
select database(); - 使用数据库use 数据库名称;
use db1;
- 查询当前正在使用的数据库名称
-
C(Create):创建
- create table 表名( 列名1 数据类型1, 列名2 数据类型2, .... 列名n 数据类型n );
create table student( id int, name varchar(32), age int , score double(4,1), birthday date, insert_time timestamp );
- create table 表名( 列名1 数据类型1, 列名2 数据类型2, .... 列名n 数据类型n );
- R(Retrieve):查询
-
-
查询某个数据库中所有的表名称
show tables; -
查询表结构desc 表名;
desc student;
-
-
U(Update):修改
- 修改表名 alter table 表名 rename to 新的表名;
alter table student rename to stu; - 修改表的字符集 alter table 表名 character set 字符集名称;
-- 先查询表字符编码 show create table stu; alter table stu character set gbk; -- 先查询表字符编码 show create table stu; - 添加一列 alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型;
alter table stu add gender int; - 修改列名称 类型 alter table 表名 change 列名 新列名 新数据类型;
alter table 表名 modify 列名 新数据类型;alter table stu change gender sex int; alter table stu modify sex bit(1); - 删除列 altertable 表名 drop 列名;
alter table stu drop sex;
- 修改表名 alter table 表名 rename to 新的表名;
-
D(Delete):删除
- drop table 表名; drop table if exists 表名 ;
drop table if exists stu;
- drop table 表名; drop table if exists 表名 ;
- 客户端图形化工具:Navicat
-
添加数据:
-
语法:insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,...列名n) values(值1,值2,...值n);
insert into student(id,name,age) values(1,'路飞',19); -
注意:
-
列名和值要一一对应。
-
如果表名后,不定义列名,则默认给所有列添加值 insert into 表名 values(值1,值2,...值n);
insert into student values(2,'索隆',21,11.11,null,null); -
除了数字类型,其他类型需要使用引号(单双都可以)引起来
-
-
-
删除数据:
-
语法:delete from 表名 [where 条件]
delete from student where id=1; -
注意:如果不加条件,则删除表中所有记录;
-
delete from 表名; -- 不推荐使用。有多少条记录就会执行多少次删除操作
delete from student; -
TRUNCATE TABLE 表名; -- 推荐使用,效率更高,先删除表,然后再创建一张一样的表
truncate table student;
-
-
修改数据:
-
语法:update 表名 set 列名1 = 值1, 列名2 = 值2,... [where 条件];
update student set age=19 where id=5; update student set age=21,score=100 where id=11;
-
-
-
注意:如果不加任何条件,则会将表中所有记录全部修改。
-
- 创建数据库
CREATE TABLE `student` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增主键', `name` varchar(20), `age` int(11) , `sex` varchar(20) , `address` varchar(50) , `math` int(11) , `english` int(11) , PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ); - 插入数据
insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('路飞',19,'男','风车村',55,60); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('索隆',21,'男','霜月村',70,75); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('娜美',20,'女','可可亚西村',90,90); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('乌索普',19,'男','西罗普村',95,70); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('山治',21,'男','巴拉蒂',88,NULL); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('乔巴',17,'男','磁鼓王国',99,90); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('罗宾',30,'女','欧哈拉',100,100); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('弗兰奇',36,'男','水之王国',99,66); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('布鲁克',90,'男','西海',66,77); insert into student(name,age,sex,address,math,english) VALUES('甚平',46,'男','鱼人街',99,99); -
基础查询
-
多个字段的查询 select 字段名1,字段名2... from 表名;
注意:如果查询所有字段,则可以使用*来替代字段列表。
select id,name,age from student; select * from student;
-
-
-
去除重复:distinct
select distinct address from student;
-
-
union和union all
-
可以将两个表的数据按照一定的查询条件查询出来后,将结果合并到一起显示
SELECT * FROM t1 UNION SELECT * FROM t2 SELECT * FROM t1 UNION ALL SELECT * FROM t2
-
-
-
union all是把结果集直接合并在一起
-
union是将union all后的结果进行一次DISTINCT,去除重复记录后的结果。
-
-
计算列
一般可以使用四则运算计算一些列的值。(一般只会进行数值型的计算:+ - * /)
ifnull(表达式1,表达式2):null参与的运算,计算结果都为null
-
表达式1:哪个字段需要判断是否为null
-
如果该字段为null后的替换值
-- 计算math 和 english 分数之和 ,发现 math+english 结果有null select name,math,english,math+english from student; -- 解决 math+english 结果有null select name,math,english,math+IFNULL(english,0) from student; -- 别名 select name,math,english,math+IFNULL(english,0) as 总分 from student;
-
-
条件查询
-
where子句后跟条件
-
运算符:< 、<= 、>= 、= 、<>
-
BETWEEN...AND;IN( 集合)
-
LIKE:模糊查询
IS NULL;IS NOT NULL-
占位符: _:单个任意字符 %:多个任意字符
-
-
and;or;not
-- 查询年龄大于20岁 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age > 20; -- 查询年龄等于20岁 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age = 20; -- 查询年龄不等于20岁 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age != 20; SELECT * FROM student WHERE age <> 20; -- 查询年龄大于等于20 小于等于30 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age >= 20 AND age <=30; SELECT * FROM student WHERE age BETWEEN 20 AND 30; -- 查询年龄21岁,19岁,46岁的信息 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age = 21 OR age = 19 OR age = 46 SELECT * FROM student WHERE age IN (21,19,46); -- 查询英语成绩为null SELECT * FROM student WHERE english = NULL; -- 不对的。null值不能使用 = (!=) 判断 SELECT * FROM student WHERE english IS NULL; -- 查询英语成绩不为null SELECT * FROM student WHERE english IS NOT NULL; -- 查询姓罗的有哪些? like SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME LIKE '罗%'; -- 查询姓名第二个字是美的人 SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME LIKE "_美%"; -- 查询姓名是3个字的人 SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME LIKE '___'; -- 查询姓名中包含索的人 SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME LIKE '%索%';
-
-
排序查询
-
order by asc升序 desc 降序
select * from student order by math asc; -- 多个条件排序 先按照math升序排列,如果math相同 则按照english降序排列 select * from student order by math desc,english asc;
-
-
聚合函数
-
将一列数据作为一个整体,进行纵向的计算
-
注意:聚合函数计算,排除null值:解决办法:选择非空列:如主键,使用IFNULL函数
-
count:计算个数
-- 计算多少人 select count(name) from student; -- 10 -- 聚合函数计算,排除null值 select count(english) from student; -- 9 select count(IFNULL(english,0)) from student; -- 10 -
max:计算最大值
select max(math) from student; --100 -
min:计算最小值
select min(math) from student; --55 -
sum:计算和
select sum(english) from student; --727 -
avg:计算平均值
select avg(math) from student; --86.1000
-
-
分组查询
- group by
-
分组之后查询的字段 :分组字段 或者 聚合函数
-- 分别查询男、女同学的数学平均分 select sex,avg(math) from student group by sex; -- 分别查询男、女同学的数学平均分,人数 select sex,avg(math),count(id) from student group by sex; -- 分别查询男、女同学的数学平均分,人数 要求:math分数低于70分不参与分组 select sex,avg(math),count(id) from student where math>70 group by sex; -
having
-- 分别查询男、女同学的数学平均分,人数,要求math分数低于70分不参与分组,分组之后人数大于2 select sex,avg(math),count(id) from student where math>70 group by sex having count(id)>2;
-
where和having的区别
-
where 在分组前进行限定,如果不满足条件,则不参与分组。
-
having在分组后进行限定,如果不满足结果,则不会被查询出来。
-
where 后不可以跟聚合函数,having可以进行聚合函数的判断。
-
-
as
select sex,avg(math),count(id) as count from student where math>70 group by sex having count>2; -- as,起别名,可省略
-
分页查询
-
语法:limit 开始的索引,每页查询的条数
-
开始的索引 = (当前页码-1)*每页显示的条数
-
limit是mysql的"方言"
-- 每页显示3条记录(第1,2,3页) select * from student limit 0,3; select * from student limit 3,3; select * from student limit 6,3;
-
-
总结查询语句
select
字段列表
from
表名列表
where
条件列表
group by
分组字段
having
分组之后的条件
order by
排序
limit
分页限定
