一、hello word
一、hello word
public class Pro_demo_1 {
/**
* 第一步:建立ConnectionFactory工厂对象,需要填入用户名、密码、以及要连接的地址,均使用默认即可,默认端口为"tcp://localhost:61616"。
* 第二步:通过ConnectionFactory工厂对象我们创建一个Connection连接,并且调用Connection的start方法开启连接,Connection默认是关闭的。
* 第三步:通过Connection对象创建Session会话(上下文环境对象),用于接受消息,参数配置1为是否开启是事务,参数配置2位签收模式,一般我们设置自动签收。
* 第四部:通过Session创建Destination对象,指的是一个客户端用来指定生产消费者目标和消费消息来源的对象。在PTP模式中,Destination被称作Queue即队列;
* 在Pub/Sub模式,Destination被称作主题。在程序中可以使用多个Queue和Topic。
* 第五步:我们需要通过Session对象创建消息的发送和接受对象(生产者和消费者)MessageProducer/MessageConsumer。
* 第六步:我们可以使用MessageProducer的setDeliveryMode方法为其设置持久化特性和非持久化特性(DeliveryMode)。
* 第七补:最后我们使用JMS规范TextMessage形式创建数据(通过Session对象),并用MessageProducer的send方法发送数据。同理客户端使用receive方法进行
* 接受数据。最后不要忘记关闭Connection连接。
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 创建一个链接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(
"admin",
"admin",
"tcp://localhost:61616");
// 从工厂中创建一个链接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
connection.start();
// 创建一个事务(这里通过参数可以设置事务的级别)
Session session = connection.createSession(true, Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE);
// 创建一个消息队列
Queue queue = session.createQueue("queue1");
// 创建生产者
MessageProducer messageProducer = session.createProducer(queue);
// 设置持久化特性和非持久化特性
messageProducer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.PERSISTENT);
// 创建数据
TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("生产者生产");
messageProducer.send(textMessage);
session.commit();
if(connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
session.close();
connection.close();
}
}
过程分析
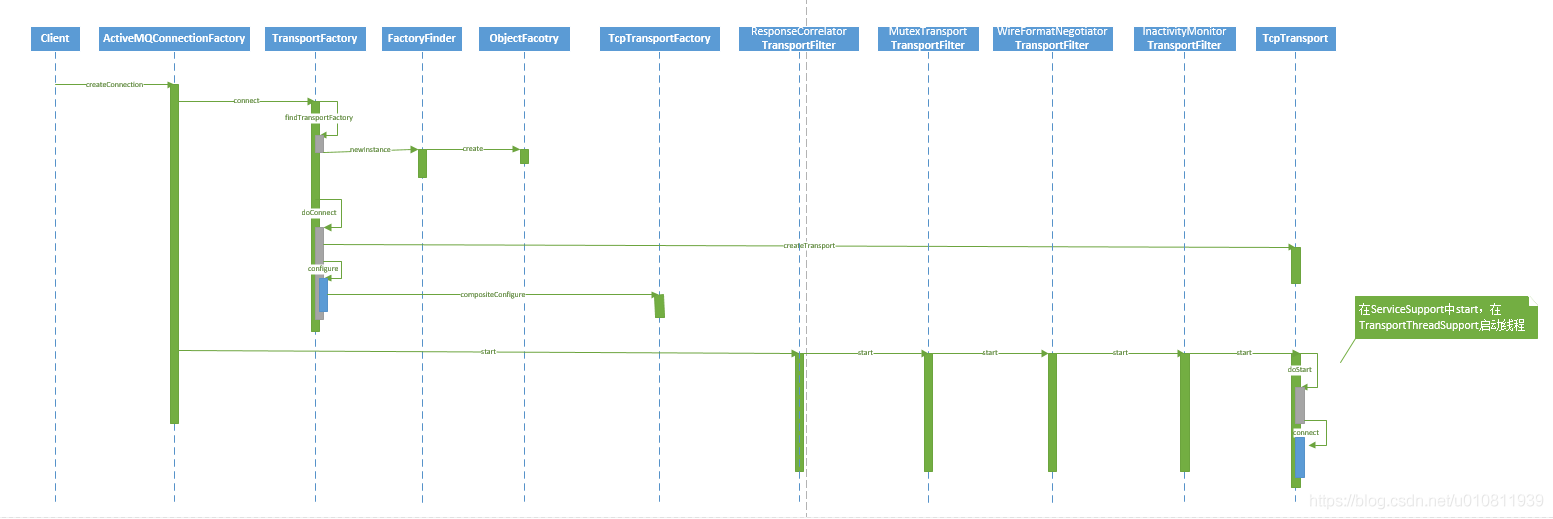
1创建ActiveMQConnectionFactory创建ActiveMQConnectionFactory入参是url,指定schema以及要连接的ip和端口号,
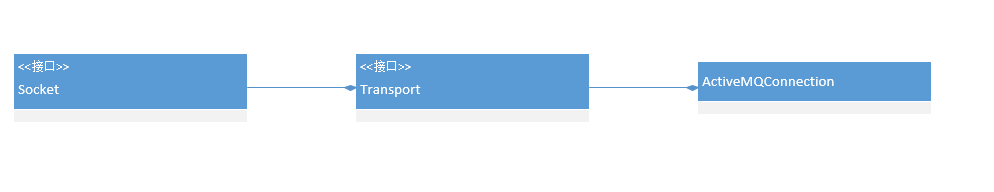
2 创建ActiveMQConnection创建ActiveMQConnection,tcp协议交互肯定是要使用Socket类,所以说明下ActiveMQConnection->Transport->Socket的关系,Transport是对Socket的封装,而ActiveMQConnection则是对Transport的封装,如下图所示:
代码如下:
protected ActiveMQConnection createActiveMQConnection(String userName, String password) throws JMSException {
if (brokerURL == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("brokerURL not set.");
}
ActiveMQConnection connection = null;
try {
// 创建Transport类
Transport transport = createTransport();
connection = createActiveMQConnection(transport, factoryStats);
connection.setUserName(userName);
connection.setPassword(password);
configureConnection(connection);
// 创建连接
transport.start();
if (clientID != null) {
connection.setDefaultClientID(clientID);
}
return connection;
} catch (JMSException e) {
// Clean up!
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
}
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
// Clean up!
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
}
throw JMSExceptionSupport.create("Could not connect to broker URL: " + brokerURL + ". Reason: " + e, e);
}
}
创建Transport ,因为上图已经说明ActiveMQConnection和Transport是组合关系,所以创建ActiveMQConnection时首先要创建Transport,因为ActiveMQ的交互方式分为Tcp、Udp以及HTTP协议,ActiveMQ使用了非常经典的简单工厂设计模式,使用这个模式的好处是工厂可以根据uri的schema头动态创建相应的TransportFactory工厂,例如用户输入tcp://localhost:61616,ObjectFactory则可以获取到schema是tcp然后来实例化TcpTransportFactory,然后在调用TcpTransportFactory工厂来生产TcpTransport对象,简单工厂模式如下图,我是把2个工厂画到了一起: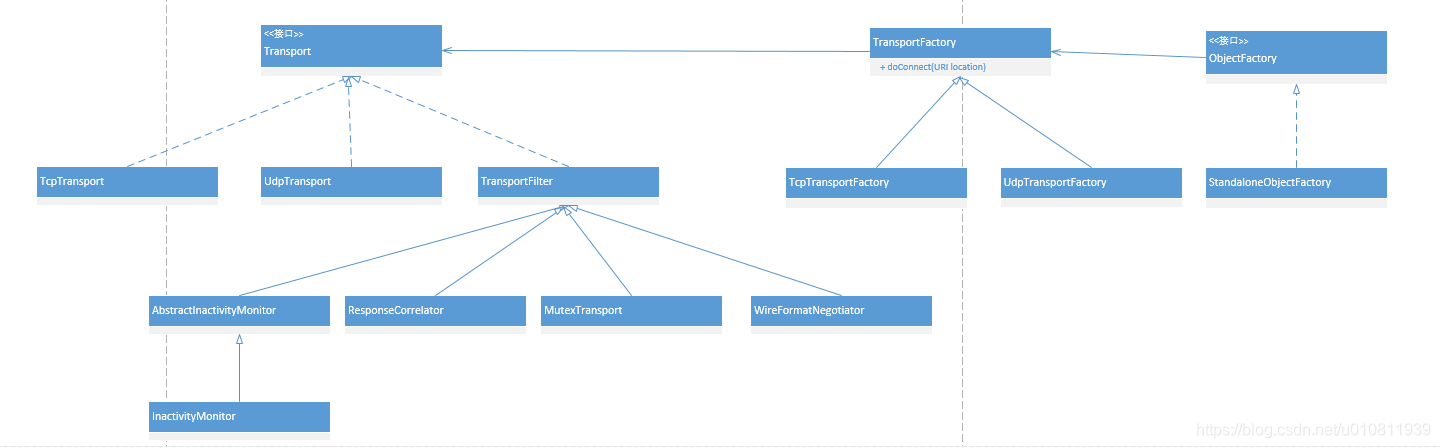
代码如下:
protected Transport createTransport() throws JMSException {
try {
return TransportFactory.connect(brokerURL);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw JMSExceptionSupport.create("Could not create Transport. Reason: " + e, e);
}
}
public static Transport connect(URI location) throws Exception {
// 根据uri的schema头动态创建相应的TransportFactory工厂
TransportFactory tf = findTransportFactory(location);
// 创建Transport,封装来实现相应的业务处理
return tf.doConnect(location);
}
获取对应的TransportFacotry工厂
private static TransportFactory findTransportFactory(URI location) throws IOException {
String scheme = location.getScheme();
if (scheme == null) {
throw new IOException("Transport not scheme specified: [" + location + "]");
}
TransportFactory tf = TRANSPORT_FACTORYS.get(scheme);
if (tf == null) {
// Try to load if from a META-INF property.
try {
tf = (TransportFactory)TRANSPORT_FACTORY_FINDER.newInstance(scheme);
TRANSPORT_FACTORYS.put(scheme, tf);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw IOExceptionSupport.create("Transport scheme NOT recognized: [" + scheme + "]", e);
}
}
return tf;
}
创建Transport,封装来实现相应的业务处理
public Transport doConnect(URI location) throws Exception {
try {
Map<String, String> options = new HashMap<String, String>(URISupport.parseParameters(location));
// 创建WireFormat
WireFormat wf = createWireFormat(options);
// 创建TcpTransport
Transport transport = createTransport(location, wf);
// 封装来实现相应的业务处理
Transport rc = configure(transport, wf, options);
if (!options.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid connect parameters: " + options);
}
return rc;
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
throw IOExceptionSupport.create(e);
}
}
创建Transport,这里只是创建了一个空的Sokcet,没有建立连接,
protected Transport createTransport(URI location, WireFormat wf) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
URI localLocation = null;
String path = location.getPath();
// see if the path is a local URI location
if (path != null && path.length() > 0) {
int localPortIndex = path.indexOf(':');
try {
Integer.parseInt(path.substring(localPortIndex + 1, path.length()));
String localString = location.getScheme() + ":/" + path;
localLocation = new URI(localString);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("path isn't a valid local location for TcpTransport to use", e.getMessage());
if(LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Failure detail", e);
}
}
}
SocketFactory socketFactory = createSocketFactory();
return createTcpTransport(wf, socketFactory, location, localLocation);
}
public TcpTransport(WireFormat wireFormat, SocketFactory socketFactory, URI remoteLocation,
URI localLocation) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
this.wireFormat = wireFormat;
this.socketFactory = socketFactory;
try {
// 创建空的Socket,没有建立连接
this.socket = socketFactory.createSocket();
} catch (SocketException e) {
this.socket = null;
}
this.remoteLocation = remoteLocation;
this.localLocation = localLocation;
setDaemon(false);
}
封装来实现相应的业务处理,此时ResponseCorrelator持有MutexTransportFilter,MutexTransportFilter持有WireFormatNegotiator,WireFormatNegotiator持有InactivityMonitor,InactivityMonitor持有TcpTransport,当建立连接或获取参数时一次调用
public Transport configure(Transport transport, WireFormat wf, Map options) throws Exception {
// 创建InactivityMonitor和WireFormatNegotiator
transport = compositeConfigure(transport, wf, options);
// 创建MutexTransportFilter
transport = new MutexTransport(transport);
// 创建ResponseCorrelator
transport = new ResponseCorrelator(transport);
return transport;
}
MutexTransportFilter类实现了对每个请求的同步锁,同一时间只允许发送一个请求,如果有第二个请求需要等待第一个请求发送完毕才可继续发送。
WireFormatNegotiator类实现了在客户端连接broker的时候先发送数据解析相关的协议信息,例如解析版本号,是否使用缓存等信息。
InactivityMonitor类实现了连接成功后启动心跳检查机制,客户端每10秒发送一次心跳信息,服务端每30秒读一次心跳信息,如果没有读到则会断开连接,心跳检测是相互的,客户端也会每30秒读取服务端发送来的心跳信息,如果没有读到也一样会断开连接。
ResponseCorrelator类实现了异步请求但需要获取响应信息否则就会阻塞等待功能。
从上面我们知道在创建TcpTransport会创建一个没有连接的Socket,并且创建了TcpTransport的包装类, 当transport.start();,会依次建立连接,代码如下
public void start() throws Exception {
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
boolean success = false;
stopped.set(false);
try {
preStart();
doStart();
success = true;
} finally {
started.set(success);
}
for(ServiceListener l:this.serviceListeners) {
l.started(this);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doStart() throws Exception {
connect();
stoppedLatch.set(new CountDownLatch(1));
super.doStart();
}
protected void connect() throws Exception {
if (socket == null && socketFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot connect if the socket or socketFactory have not been set");
}
InetSocketAddress localAddress = null;
InetSocketAddress remoteAddress = null;
if (localLocation != null) {
localAddress = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByName(localLocation.getHost()),
localLocation.getPort());
}
if (remoteLocation != null) {
String host = resolveHostName(remoteLocation.getHost());
remoteAddress = new InetSocketAddress(host, remoteLocation.getPort());
}
// Set the traffic class before the socket is connected when possible so
// that the connection packets are given the correct traffic class.
this.trafficClassSet = setTrafficClass(socket);
if (socket != null) {
if (localAddress != null) {
socket.bind(localAddress);
}
// If it's a server accepted socket.. we don't need to connect it
// to a remote address.
if (remoteAddress != null) {
if (connectionTimeout >= 0) {
socket.connect(remoteAddress, connectionTimeout);
} else {
socket.connect(remoteAddress);
}
}
} else {
// For SSL sockets.. you can't create an unconnected socket :(
// This means the timout option are not supported either.
if (localAddress != null) {
socket = socketFactory.createSocket(remoteAddress.getAddress(), remoteAddress.getPort(),
localAddress.getAddress(), localAddress.getPort());
} else {
socket = socketFactory.createSocket(remoteAddress.getAddress(), remoteAddress.getPort());
}
}
initialiseSocket(socket);
initializeStreams();
}
TcpTransport实现了Runnable接口,当start()时候也就启动了线程
public void run() {
LOG.trace("TCP consumer thread for " + this + " starting");
this.runnerThread=Thread.currentThread();
try {
while (!isStopped()) {
doRun();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
stoppedLatch.get().countDown();
onException(e);
} catch (Throwable e){
stoppedLatch.get().countDown();
IOException ioe=new IOException("Unexpected error occured: " + e);
ioe.initCause(e);
onException(ioe);
}finally {
stoppedLatch.get().countDown();
}
}
protected void doRun() throws IOException {
try {
// 获取数据,消费
Object command = readCommand();
doConsume(command);
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
}
}