在折腾中成长,在折腾中永生。
接着玩模板匹配,最近主要研究了3个课题。
1、创建模型的Optimization选项模拟(2022.5.16日)
这两天又遇到一个做模板匹配隐藏的高手,切磋起来后面就还是和halcon比,于是有看了下create_shape_model这个函数,前面一直忙实现细节,对halcon的Optimization这个参数真的没怎么在意,几天一看,原来这里面还隐藏了比较深的细节。halcon原始的英文描述如下:
For particularly large models, it may be useful to reduce the number of model points by setting Optimization to a value different from 'none'. If Optimization = 'none', all model points are stored. In all other cases, the number of points is reduced according to the value of Optimization. If the number of points is reduced, it may be necessary in find_shape_model to set the parameter Greediness to a smaller value, e.g., 0.7 or 0.8. For small models, the reduction of the number of model points does not result in a speed-up of the search because in this case usually significantly more potential instances of the model must be examined. If Optimization is set to 'auto', create_shape_model automatically determines the reduction of the number of model points.
Optionally, a second value can be passed in Optimization. This value determines whether the model is pregenerated completely or not. To do so, the second value of Optimization must be set to either 'pregeneration' or 'no_pregeneration'. If the second value is not used (i.e., if only one value is passed), the mode that is set with set_system('pregenerate_shape_models',...) is used. With the default value ('pregenerate_shape_models' = 'false'), the model is not pregenerated completely. The complete pregeneration of the model normally leads to slightly lower runtimes because the model does not need to be transformed at runtime. However, in this case, the memory requirements and the time required to create the model are significantly higher. It should also be noted that it cannot be expected that the two modes return exactly identical results because transforming the model at runtime necessarily leads to different internal data for the transformed models than pregenerating the transformed models. For example, if the model is not pregenerated completely, find_shape_model typically returns slightly lower scores, which may require setting a slightly lower value for MinScore than for a completely pregenerated model. Furthermore, the poses obtained by interpolation may differ slightly in the two modes. If maximum accuracy is desired, the pose of the model should be determined by least-squares adjustment.
翻译成中文的核心意思是,对于大的模板图像,将改参数设置而为非"none"的其他值,可以降低匹配时需要的模型点的数量,从而提高速度,当然,如果模型点数量降低了,在调用find_shape_model 时最好把那个贪婪值稍微吊的小一点,比如改成0.7或者0.8,以便保证稳定性。当然,这个操作对于小模型可能作用不大。一般情况下,可以设置为"atuo",这样create_shape_model 自动绝对如何来降低取样点数。
另外,这个函数还可以有第二个类型的值和前面的模型点数量集合,即pregeneration和no_pregeneration选项,这个是关键。 默认情况是no_pregeneration,当选择pregeneration时,create_shape_model就会和我现在的实现方式一样,对每层金字塔以及金字塔内不同角度均计算特征点数据,因此,这个创建函数就会比较慢和占用大量的内存。但是带来的好处就是find_shape_model函数可能执行时间会快一些。no_pregeneration选项只会计算未旋转模板的相关信息,在find_shape_model时候会对信息进行转换,因此创建时非常快。特别注意,两个选项得到的匹配结果会有轻微的不同。比如说,如果使用no_pregeneration,find_shape_model 函数的得分可能要稍微低一点。 所以,我目前实现的相当于使用了pregeneration选项的halcon功能。
具体来说:optimization 有7种选项可以选择
List of values: 'auto', 'no_pregeneration', 'none', 'point_reduction_high', 'point_reduction_low', 'point_reduction_medium', 'pregeneration'
我们看到point_reduction相关的有point_reduction_high point_reduction_low point_reduction_medium选项,我在想内部肯定是某个固定的方式减少模型点数量,这个我们也可以模拟,比如分别取1/8,1/4,1/2等等,经过测试,这个在提高速度的同时,对结果的准确度和精度基本没有什么影响。
2、no_pregeneration选项的模拟(2022.5.18日)
这个很早以前就已经在考虑了,目前已经有过几种尝试,均已失败告终,记录如下。
(1)create_shape_model 只记录每层金字塔未旋转模板图像的模型点特征和位置(整形位置),然后在find_shape_model 时,旋转特征点的坐标,并且四舍五入位置坐标,使用0度模型点特征和这个坐标位置的查找图中特征做匹配。
(2)create_shape_model 只记录每层金字塔未旋转模板图像的模型点特征和位置(整形位置),然后在find_shape_model 时,旋转特征点的坐标,使用0度模型点特征和查找图中这个坐标位置周边的领域的双线性插值中特征做匹配。
(3)create_shape_model 只记录每层金字塔未旋转模板图像的模型点特征和位置(亚像素特征值和位置),然后在find_shape_model 时,旋转特征点的坐标,使用0度模型点特征和查找图中这个坐标位置周边的领域的双线性插值中特征做匹配。
测试结果均会出现目标丢失,如下所示:
3、3D的亚像素插值(2022.5.23)
最近在看一篇台湾人开源的基于NCC的模板匹配代码,详见:https://github.com/DennisLiu1993/Fastest_Image_Pattern_Matching,在其代码中看到3D(X坐标,Y坐标和角度)的亚像素计算方法, 在后续和作者的沟通中,作者提供了该算法的论文出处。其详细的推到过程见下图:

编码上其实也很简单,主要是一些矩阵的乘法、转置和求逆等。
他实际上就是在3*3*3的空间内拟合曲面,在编码时,我们需要在初步求得的X和Y坐标以及角度值3领域范围内(X加减1,Y加减1,Angle加减AngleStep)计算出27个得分值后进行矩阵运算即可。
其实我一直在找这方面的资料,终于找到了,本来希望能得到一个比以前的2D或1D亚像素更为精确的结果,不过实际测试起来还是有点失望的。
以一个我常用的测试图中一个结果为例说明(使用基于边缘的匹配算法):



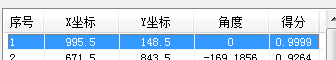
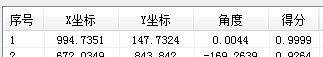
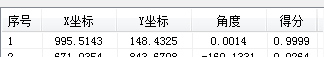
不使用亚像素时的结果 使用3D亚像素时的结果 使用2D亚像素时的结果
这个图理论的准确得分应该是1,不过由于中间的浮点计算误差,导致得分无限接近于1,因此在不使用亚像素时得到的结果其实是精确值,当使用3D亚像素后,我们看到了X和Y坐标结果有了很大的偏移,这个明显是错误的。
后面为了分析这个问题,我一直在查找3D亚像素插值的代码,以为是代码写错了,后面用同样的数据,使用matlab计算,得到的结果也是一样的,说明不是代码问题,于是我打印出了对应的27个点的得分,如下所示:
Score X - 1 X X + 1 X - 1 X X + 1 X - 1 X X + 1
Y - 1 0.9891 0.9213 0.7208 | 0.9274 0.9720 0.9080 | 0.9855 0.9324 0.7223
Y 0.9579 0.8836 0.6884 | 0.9491 0.9999 0.9562 | 0.9522 0.8850 0.6925
Y + 1 0.8395 0.7772 0.6303 | 0.8922 0.9662 0.9717 | 0.7830 0.7373 0.5660
Angle - AngleStep Angle Angle+ AngleStep
我们仔细的观察数据,发现只有在角度为 Angle时,(X,Y)点的得分为环绕最大值,而在其他角度时,得分的中心感觉都有点向左上角偏移,因此3D插值后的结果也会向左上角偏移,计算结果是符合数据的特性的。
后面想一想啊,基于边缘的查找啊和边缘的位置有着非常紧密的关系,稍微旋转一个角度,边缘的位置就有可能有一两个像素的偏移,这样就会导致得分又较为明显的差异,出现这个情况应该是正常点的。
后面我把基于NCC的用3D的亚像素插值试了一下,结果就好很多了,这个也很正常,因为NCC的相似度计算是基于全图的,旋转一个角度后,有多个点作用于结果得分值。
因此,个人最后还是认为,在基于边缘的匹配中可以使用2D的亚像素作用于X和Y坐标,使用1D的亚像素作用于角度。
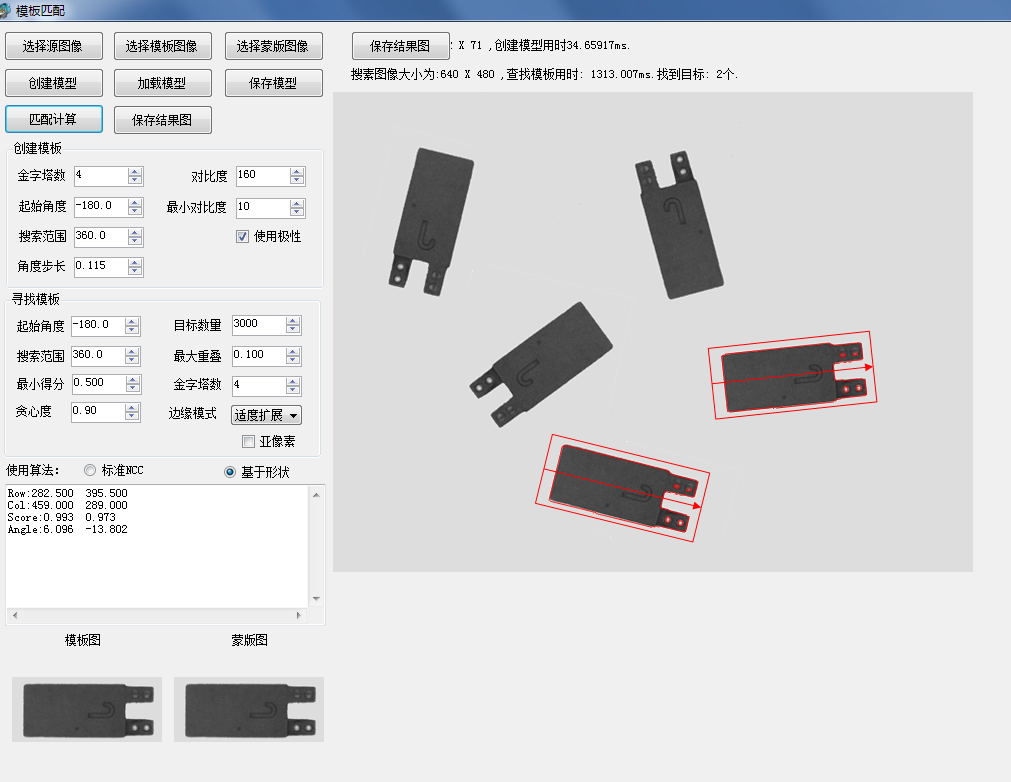
最新版的一个测试DEMO: 带蒙版的模板匹配。
如果想时刻关注本人的最新文章,也可关注公众号或者添加本人微信: laviewpbt

