前言:
1.最近项目上在测试人员压测过程中发现了OOM问题,项目使用springboot搭建项目工程,通过查看日志中包含信息:unable to create new native thread
内存溢出的三种类型:
1.第一种OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space,发生这种问题的原意是程序中使用了大量的jar或class
2.第二种OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space,发生这种问题的原因是java虚拟机创建的对象太多
3.第三种OutOfMemoryError:unable to create new native thread,创建线程数量太多,占用内存过大
初步分析:
1.初步怀疑是线程创建太多导致,使用jstack 线程号 > /tmp/oom.log将应用的线程信息打印出来。查看oom.log,发现大量线程处于Runnable状态,基本可以确认是线程创建太多了。
代码分析:
1.出问题的微服务是日志写库服务,对比日志,锁定在writeLog方法上,wirteLog方法使用spring-@Async注解,写库操作采用的是异步写入方式。
2.之前没有对@Async注解深入研究过,只是知道可以自定义内部线程池,经查看,日志写库服务并未自定义异步配置,使用的是spring-@Async默认异步配置
3.首先简单百度了下,网上提到@Async默认异步配置使用的是SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor,该线程池默认来一个任务创建一个线程,在压测情况下,会有大量写库请求进入日志写库服务,这时就会不断创建大量线程,极有可能压爆服务器内存。
借此机会也学习了下SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor源码,总结如下:
1.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor提供了限流机制,通过concurrencyLimit属性来控制开关,当concurrencyLimit>=0时开启限流机制,默认关闭限流机制即concurrencyLimit=-1,当关闭情况下,会不断创建新的线程来处理任务,核心代码如下:
public void execute(Runnable task, long startTimeout) {
Assert.notNull(task, "Runnable must not be null");
Runnable taskToUse = (this.taskDecorator != null ? this.taskDecorator.decorate(task) : task);
//判断是否开启限流机制
if (isThrottleActive() && startTimeout > TIMEOUT_IMMEDIATE) {
//执行前置操作,进行限流
this.concurrencyThrottle.beforeAccess();
//执行完线程任务,会执行后置操作concurrencyThrottle.afterAccess(),配合进行限流
doExecute(new ConcurrencyThrottlingRunnable(taskToUse));
}
else {
doExecute(taskToUse);
}
}
2.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor限流实现
首先任务进来,会循环判断当前执行线程数是否超过concurrencyLimit,如果超了,则当前线程调用wait方法,释放monitor对象锁,进入等待
protected void beforeAccess() {
if (this.concurrencyLimit == NO_CONCURRENCY) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Currently no invocations allowed - concurrency limit set to NO_CONCURRENCY");
}
if (this.concurrencyLimit > 0) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
synchronized (this.monitor) {
boolean interrupted = false;
while (this.concurrencyCount >= this.concurrencyLimit) {
if (interrupted) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Thread was interrupted while waiting for invocation access, " +
"but concurrency limit still does not allow for entering");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Concurrency count " + this.concurrencyCount +
" has reached limit " + this.concurrencyLimit + " - blocking");
}
try {
this.monitor.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// Re-interrupt current thread, to allow other threads to react.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
interrupted = true;
}
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Entering throttle at concurrency count " + this.concurrencyCount);
}
this.concurrencyCount++;
}
}
}
2.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor限流实现:首先任务进来,会循环判断当前执行线程数是否超过concurrencyLimit,如果超了,则当前线程调用wait方法,释放monitor对象锁,进入等待状态。
protected void beforeAccess() {
if (this.concurrencyLimit == NO_CONCURRENCY) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Currently no invocations allowed - concurrency limit set to NO_CONCURRENCY");
}
if (this.concurrencyLimit > 0) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
synchronized (this.monitor) {
boolean interrupted = false;
while (this.concurrencyCount >= this.concurrencyLimit) {
if (interrupted) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Thread was interrupted while waiting for invocation access, " +
"but concurrency limit still does not allow for entering");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Concurrency count " + this.concurrencyCount +
" has reached limit " + this.concurrencyLimit + " - blocking");
}
try {
this.monitor.wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// Re-interrupt current thread, to allow other threads to react.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
interrupted = true;
}
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Entering throttle at concurrency count " + this.concurrencyCount);
}
this.concurrencyCount++;
}
}
}
线程任务执行完毕后,当前执行线程数会减一,会调用monitor对象的notify方法,唤醒等待状态下的线程,等待状态下的线程会竞争monitor锁,竞争到,会继续执行线程任务。
protected void afterAccess() {
if (this.concurrencyLimit >= 0) {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
this.concurrencyCount--;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Returning from throttle at concurrency count " + this.concurrencyCount);
}
this.monitor.notify();
}
}
}
虽然看了源码了解了SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor有限流机制,实践出真知,我们还是测试下:
一、测试未开启限流机制下,我们启动20个线程去调用异步方法,查看Java VisualVM工具如下:
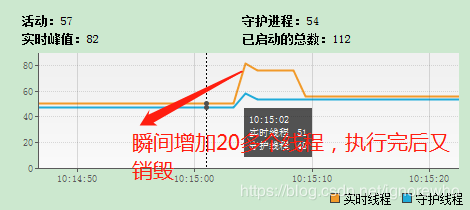
二、测试开启限流机制,开启限流机制的代码如下:
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncCommonConfig extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor executor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor();
//设置允许同时执行的线程数为10
executor.setConcurrencyLimit(10);
return executor;
}
}
同样,我们启动20个线程去调用异步方法,查看Java VisualVM工具如下:
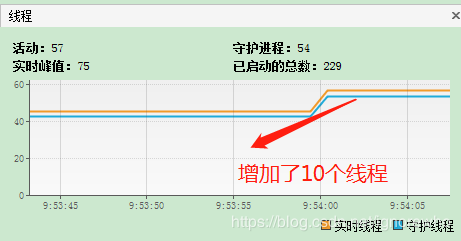
通过上面验证可知:
1.开启限流情况下,能有效控制应用线程数
2.虽然可以有效控制线程数,但执行效率会降低,会出现主线程等待,线程竞争的情况。
3.限流机制适用于任务处理比较快的场景,对于应用处理时间比较慢的场景并不适用。==
最终解决办法:
1.自定义线程池,使用LinkedBlockingQueue阻塞队列来限定线程池的上限
2.定义拒绝策略,如果队列满了,则拒绝处理该任务,打印日志,代码如下:
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer{
private Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger();
@Value("${thread.pool.corePoolSize:10}")
private int corePoolSize;
@Value("${thread.pool.maxPoolSize:20}")
private int maxPoolSize;
@Value("${thread.pool.keepAliveSeconds:4}")
private int keepAliveSeconds;
@Value("${thread.pool.queueCapacity:512}")
private int queueCapacity;
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler((Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor exe) -> {
logger.warn("当前任务线程池队列已满.");
});
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex , Method method , Object... params) {
logger.error("线程池执行任务发生未知异常.", ex);
}
};
}
}
到此这篇关于springboot中@Async默认线程池导致OOM问题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot @Async线程池导致OOM内容请搜索易盾网络以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持易盾网络!
