学习笔记,仅供参考,有错必纠
文章目录
- 模板
- 过滤器
- 常用的过滤器
- 举个例子
- 转义(escape)
- 自动转义(autoscape)
- 举个例子
模板
过滤器
- 作用
在变量输出前对变量的值进行处理,我们可以通过使用过滤器来改变变量的显示。
- 语法
常用的过滤器
过滤器
说明
default
如果value的计算结果为False,则使用给定的默认值,否则,使用该value
default_if_none
如果(且仅当) value为None,则使用给定的默认值否则,使用该value
floatformat
当不使用参数时,将浮点数舍入到小数点后一位,但前提是要显示小数部分。
truncatechars
如果字符串字符多于指定的字符数量,那么会被截断。
截断的字符串将以可翻译的省略号序列("…")结尾。
truncatewords
在一定数量的字后截断字符串
lower
将字符串全部转换为小写
upper
将字符串全部转换为大写
举个例子
page7.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>过滤器</title>
</head>
<body>
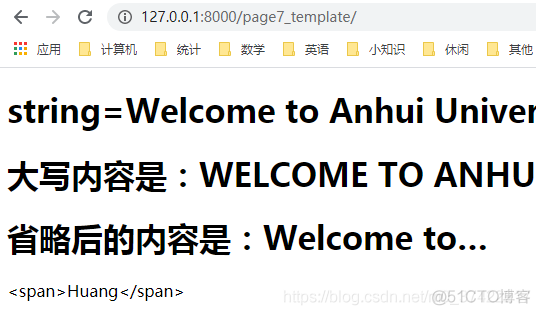
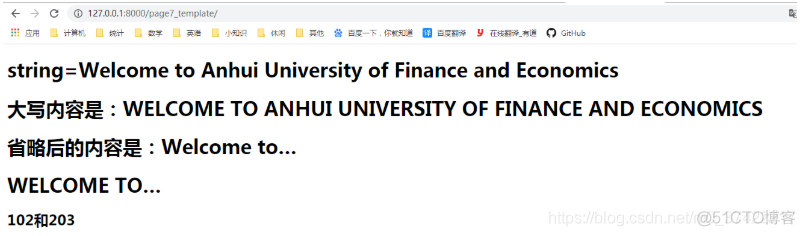
<h1>string={{ string }}</h1>
<h1>大写内容是:{{ string | upper }}</h1>
<h1>省略后的内容是:{{ string | truncatechars:11 }}</h1>
<h1>{{ string | truncatechars:11 | upper }}</h1>
<h2>{{a|add:2}}和{{b|add:3}}</h2>
</body>
</html>
views.py
def page7_template(request):string = "Welcome to Anhui University of Finance and Economics"
a = 100
b = 200
return render(request, "page7.html", locals())
locals方法会返回局部变量的字典,在本例中locals方法会返回{“string”:“Welcome to Anhui University of Finance and Economics”,“a”:100,“b”:200}
urls.py
urlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
re_path(r'page7_template/$', views.page7_template),
]
向http://127.0.0.1:8000/page7_template/发起请求:
转义(escape)
在这里,转义就是把HTML语言的关键字过滤掉。例如,<a>为html的标签,如果要在HTML页面上呈现<a>,其源代码就必须是<a>
- Django中对HTML关键字的替换
HTML关键字
替换
<
<
>
>
'单引号
'
"双引号
"
&
&
自动转义(autoscape)
语法:
{% autoescape on %}{{body}}
{% endautoescape %}
举个例子
page7.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>过滤器</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>string={{ string }}</h1>
<h1>大写内容是:{{ string | upper }}</h1>
<h1>省略后的内容是:{{ string | truncatechars:11 }}</h1>
{% autoescape on %}
{{ a }}
{% endautoescape %}
</body>
</html>
views.py
def page7_template(request):string = "Welcome to Anhui University of Finance and Economics"
a = "<span>Huang</span>"
b = 200
return render(request, "page7.html", locals())
urls.py
urlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
re_path(r'page7_template/$', views.page7_template),
]
向http://127.0.0.1:8000/page7_template/发起请求: