学习笔记,仅供参考,有错必纠
参考自:Django打造大型企业官网–Huang Y;
文章目录
- WSGIRequest对象
- WSGIRequest对象常用属性
- WSGIRequest对象常用方法
WSGIRequest对象
Django在接收到http请求之后,会根据http请求携带的参数以及报文信息创建一个WSGIRequest对象,并且作为视图函数第一个参数传给视图函数,也就是我们经常看到的request参数。
WSGIRequest对象常用属性
- 常用属性
属性
解释
path
请求服务器的完整“路径”,但不包含域名和参数
method
代表当前请求的http方法,比如是GET还是POST
GET
一个django.http.request.QueryDict对象,操作起来类似于字典,这个属性中包含了所有以?xxx=xxx的方式上传上来的参数
POST
也是一个django.http.request.QueryDict对象,这个属性中包含了所有以POST方式上传上来的参数。
FILES
也是一个django.http.request.QueryDict对象,这个属性中包含了所有上传的文件
COOKIES
一个标准的Python字典,包含所有的cookie,键值对都是字符串类型
session
一个类似于字典的对象,用来操作服务器的session
META
存储的客户端发送上来的所有header信息
REMOTE_ADDR
客户端的IP地址
- 举个例子
在主views.py文件中,敲入如下代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,reverse
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
context = {
"path":request.path, #请求服务器的完整“路径”,但不包含域名和参数
"method":request.method, #当前请求的http方法
"GET":request.GET, #一个django.http.request.QueryDict对象,这个属性中包含了所有以?xxx=xxx的方式上传上来的参数
}
return render(request, "index.html", context = context)
def redir(request):
return redirect(reverse("index"))
主urls.py文件:
from django.contrib import adminfrom django.urls import path
from . import views
from django.conf.urls import include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', views.index, name = "index"),
path("redirect/", views.redir, name = "redir"),
path("front/", include("front.urls"))
]
模板文件index.html:
{% extends "basePage.html" %}{% block content %}
<h1>首页</h1>
<p>欢迎来到图书管理系统!</p>
<table>
<tr>
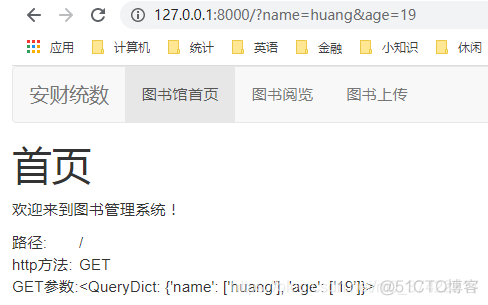
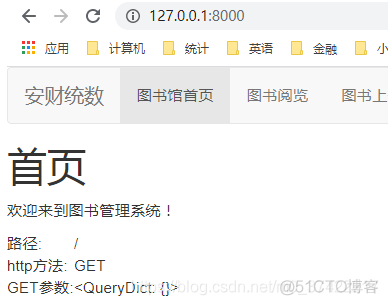
<td>路径:</td>
<td>{{ path }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>http方法:</td>
<td>{{ method }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>GET参数:</td>
<td>{{ GET }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
{% endblock %}
向http://127.0.0.1:8000/?name=huang&age=19发起请求:
向http://127.0.0.1:8000/redirect发起请求:
WSGIRequest对象常用方法
- 常用方法
方法
说明
is_secure()
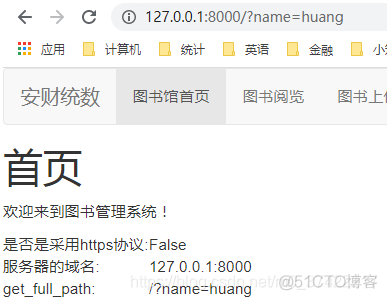
是否是采用https协议
is_ajax()
是否采用ajax发送的请求
get_host()
服务器的域名
get_full_path()
返回完整的path,如果有查询字符串,还会加上查询字符串
get_raw_uri()
获取请求的完整url
- 举个例子
在主views.py文件中,敲入如下代码:
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,reversefrom django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
context = {
"is_secure":request.is_secure(), #请求服务器的完整“路径”,但不包含域名和参数
"get_host":request.get_host(), #当前请求的http方法
"get_full_path":request.get_full_path(), #一个django.http.request.QueryDict对象,这个属性中包含了所有以?xxx=xxx的方式上传上来的参数
}
return render(request, "index.html", context = context)
index.html:
{% extends "basePage.html" %}{% block content %}
<h1>首页</h1>
<p>欢迎来到图书管理系统!</p>
<table>
<tr>
<td>是否是采用https协议:</td>
<td>{{ is_secure }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>服务器的域名:</td>
<td>{{ get_host }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>get_full_path:</td>
<td>{{ get_full_path }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
{% endblock %}
向http://127.0.0.1:8000/?name=huang发起请求: