1 简介 低能量自适应聚类层次(“LEACH”)是一种基于TDMA的MAC协议,它与聚类和无线传感器网络(WSN)中的简单路由协议相结合。LEACH 的目标是降低创建和维护集群所需的能源消耗,以提高无
1 简介
低能量自适应聚类层次(“LEACH”)是一种基于TDMA的MAC协议,它与聚类和无线传感器网络(WSN)中的简单路由协议相结合。 LEACH 的目标是降低创建和维护集群所需的能源消耗,以提高无线传感器网络的使用寿命。
LEACH 是一种分层协议,其中大多数节点向簇首传输数据,簇首聚合和压缩数据并转发到基站(宿)。每个节点在每一轮使用随机算法来确定它是否会成为本轮的簇头。 LEACH 假设每个节点都有一个足够强大的无线电,可以直接到达基站或最近的簇头,但是一直以全功率使用这个无线电会浪费能量。已经成为簇首的节点在 P 轮中不能再次成为簇首,其中 P 是簇首的期望百分比。此后,每个节点都有 1/P 的概率再次成为簇头。在每一轮结束时,不是簇头的每个节点都会选择最近的簇头并加入该簇。然后,簇头为其簇中的每个节点创建一个调度以传输其数据。根据簇头创建的调度,所有不是簇头的节点仅以 TDMA 方式与簇头通信。他们这样做使用到达簇头所需的最小能量,并且只需要在其时隙内保持无线电开启。
LEACH 还使用 CDMA,以便每个集群使用一组不同的 CDMA 代码,以最大限度地减少集群之间的干扰。
2 部分代码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %
% SEP: A Stable Election Protocol for clustered %
% heterogeneous wireless sensor networks %
% %
% (c) Georgios Smaragdakis %
% WING group, Computer Science Department, Boston University %
% %
% You can find full documentation and related information at: %
% http://csr.bu.edu/sep %
% %
% To report your comment or any bug please send e-mail to: %
% gsmaragd@cs.bu.edu %
% %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% This is the SEP [1] code we have used. %
% %
% [1] Georgios Smaragdakis, Ibrahim Matta and Azer bestavros, %
% "SEP: A Stable Election Protocol for clustered %
% heterogeneous wireless sensor networks", %
% Second International Workshop on Sensor and Actor Network %
% Protocols and Applications (SANPA 2004),Boston MA, August %
% 2004. %
% %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
clear;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% PARAMETERS %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Field Dimensions - x and y maximum (in meters)
xm=100;
ym=100;
%x and y Coordinates of the Sink
sink.x=0.5*xm;
sink.y=0.5*ym;
%Number of Nodes in the field
n=100;
%Optimal Election Probability of a node
%to become cluster head
p=0.1;
%Energy Model (all values in Joules)
%Initial Energy
Eo=0.5;
%Eelec=Etx=Erx
ETX=50*0.000000001;
ERX=50*0.000000001;
%Transmit Amplifier types
Efs=10*0.000000000001;
Emp=0.0013*0.000000000001;
%Data Aggregation Energy
EDA=5*0.000000001;
%Values for Hetereogeneity
%Percentage of nodes than are advanced
m=0.1;
%\alpha
a=1;
%maximum number of rounds
rmax=1000;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% END OF PARAMETERS %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Computation of do
do=sqrt(Efs/Emp);
%Creation of the random Sensor Network
figure(1);
for i=1:1:n
S(i).xd=rand(1,1)*xm;
XR(i)=S(i).xd;
S(i).yd=rand(1,1)*ym;
YR(i)=S(i).yd;
S(i).G=0;
%initially there are no cluster heads only nodes
S(i).type='N';
temp_rnd0=i;
%Random Election of Normal Nodes
if (temp_rnd0>=m*n+1)
S(i).E=Eo;
S(i).ENERGY=0;
%%%%plot(S(i).xd,S(i).yd,'o');
hold on;
end
%Random Election of Advanced Nodes
if (temp_rnd0<m*n+1)
S(i).E=Eo*(1+a)
S(i).ENERGY=1;
%%%%plot(S(i).xd,S(i).yd,'+');
hold on;
end
end
end
hold on;
countCHs;
rcountCHs=rcountCHs+countCHs;
%Code for Voronoi Cells
%Unfortynately if there is a small
%number of cells, Matlab's voronoi
%procedure has some problems
%[vx,vy]=voronoi(X,Y);
%plot(X,Y,'r*',vx,vy,'b-');
% hold on;
% voronoi(X,Y);
% axis([0 xm 0 ym]);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% STATISTICS %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% DEAD : a rmax x 1 array of number of dead nodes/round
% DEAD_A : a rmax x 1 array of number of dead Advanced nodes/round
% DEAD_N : a rmax x 1 array of number of dead Normal nodes/round
% CLUSTERHS : a rmax x 1 array of number of Cluster Heads/round
% PACKETS_TO_BS : a rmax x 1 array of number packets send to Base Station/round
% PACKETS_TO_CH : a rmax x 1 array of number of packets send to ClusterHeads/round
% first_dead: the round where the first node died
% %
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
3 仿真结果
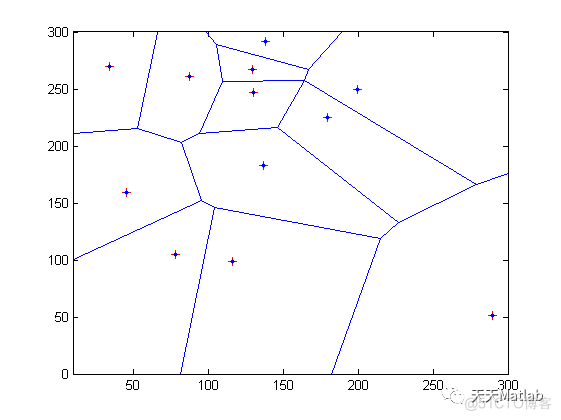
 编辑
编辑
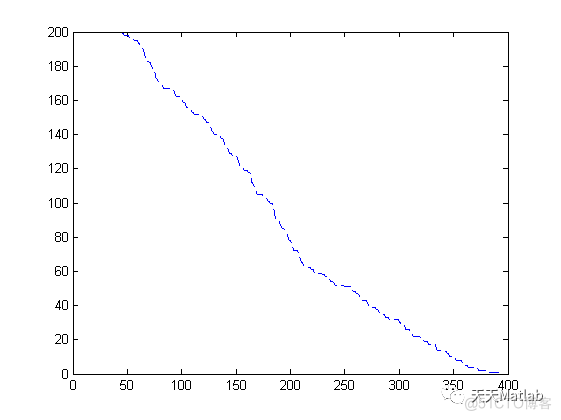
 编辑
编辑
4 参考文献
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

 编辑
编辑
