对于数据分析师而言,Python与SQL可能是大家用的比较多的两个工具,两者都可以对数据集进行深度的分析,挖掘出有价值的信息,但是二者的语法有着诸多的不同,今天小编就来总结归纳一下Python与SQL这两者之间在语法上到底有哪些不同。
导入数据
对于Pandas而言,我们需要提前导入数据集,然后再进行进一步的分析与挖掘
import pandas as pdairports = pd.read_csv('data/airports.csv')
airport_freq = pd.read_csv('data/airport-frequencies.csv')
runways = pd.read_csv('data/runways.csv')
基础语法
在SQL当中,我们用SELECT来查找数据,WHERE来过滤数据,DISTINCT来去重,LIMIT来限制输出结果的数量,
输出数据集
## SQLselect * from airports
## Pandas
airports
输出数据集的前三行数据,代码如下
## SQLselect * from airports limit 3
## Pandas
airports.head(3)
对数据集进行过滤筛查
## SQLselect id from airports where ident = 'KLAX'
## Pandas
airports[airports.ident == 'KLAX'].id
对于筛选出来的数据进行去重
## SQLselect distinct type from airport
## Pandas
airports.type.unique()
多个条件交集来筛选数据
多个条件的交集来筛选数据,代码如下
## SQLselect * from airports
where iso_region = 'US-CA' and
type = 'seaplane_base'
## Pandas
airports[(airports.iso_region == 'US-CA') &
(airports.type == 'seaplane_base')]
或者是
## SQLselect ident, name, municipality from airports
where iso_region = 'US-CA' and
type = 'large_airport'
## Pandas
airports[(airports.iso_region == 'US-CA') &
(airports.type == 'large_airport')][['ident', 'name', 'municipality']]
排序
在Pandas当中默认是对数据进行升序排序,要是我们希望对数据进行降序排序,需要设定ascending参数
## SQLselect * from airport_freq
where airport_ident = 'KLAX'
order by type
## Pandas
airport_freq[airport_freq.airport_ident == 'KLAX']
.sort_values('type')
又或者是
## SQLselect * from airport_freq
where airport_ident = 'KLAX'
order by type desc
## Pandas
airport_freq[airport_freq.airport_ident == 'KLAX']
.sort_values('type', ascending=False)
筛选出列表当中的数据
要是我们需要筛选出来的数据在一个列表当中,这里就需要用到isin()方法,代码如下
## SQLselect * from airports
where type in ('heliport', 'balloonport')
## Pandas
airports[airports.type.isin(['heliport', 'balloonport'])]
又或者是
## SQLselect * from airports
where type not in ('heliport', 'balloonport')
## Pandas
airports[~airports.type.isin(['heliport', 'balloonport'])]
删除数据
在Pandas当中删除数据用的是drop()方法,代码如下
## SQLdelete from dataframe where col_name = 'MISC'
## Pandas
df = df[df.type != 'MISC']
df.drop(df[df.type == 'MISC'].index)
更新数据
在SQL当中更新数据使用的是update和set方法,代码如下
### SQLupdate airports set home_link = '......'
where ident == 'KLAX'
### Pandas
airports.loc[airports['ident'] == 'KLAX', 'home_link'] = '......'
调用统计函数
对于给定的数据集,如下图所示
runways.head()output
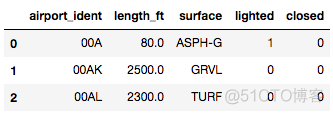
我们调用min()、max()、mean()以及median()函数作用于length_ft这一列上面,代码如下
## SQLselect max(length_ft), min(length_ft),
avg(length_ft), median(length_ft) from runways
## Pandas
runways.agg({'length_ft': ['min', 'max', 'mean', 'median']})
合并两表格
在Pandas当中合并表格用的是pd.concat()方法,在SQL当中则是UNION ALL,代码如下
## SQLselect name, municipality from airports
where ident = 'KLAX'
union all
select name, municipality from airports
where ident = 'KLGB'
## Pandas
pd.concat([airports[airports.ident == 'KLAX'][['name', 'municipality']],
airports[airports.ident == 'KLGB'][['name', 'municipality']]])
分组
顾名思义也就是groupby()方法,代码如下
## SQLselect iso_country, type, count(*) from airports
group by iso_country, type
order by iso_country, type
## Pandas
airports.groupby(['iso_country', 'type']).size()
分组之后再做筛选
在Pandas当中是在进行了groupby()之后调用filter()方法,而在SQL当中则是调用HAVING方法,代码如下
## SQLselect type, count(*) from airports
where iso_country = 'US'
group by type
having count(*) > 1000
order by count(*) desc
## Pandas
airports[airports.iso_country == 'US']
.groupby('type')
.filter(lambda g: len(g) > 1000)
.groupby('type')
.size()
.sort_values(ascending=False)
TOP N records
代码如下
## SQLselect 列名 from 表名
order by size
desc limit 10
## Pandas
表名.nlargest(10, columns='列名')
技术交流

目前开通了技术交流群,群友已超过2000人,添加时最好的备注方式为:来源+兴趣方向,方便找到志同道合的朋友
方式①、发送如下图片至微信,长按识别,后台回复:加群;
方式②、微信搜索公众号:Python学习与数据挖掘,后台回复:加群

