1 简介 移动机器人路径规划一直是一个比较热门的话题,A星算法以及其扩展性算法被广范地应用于求解移动机器人的最优路径.该文在研究机器人路径规划算法中,详细阐述了传统A星算法
1 简介
移动机器人路径规划一直是一个比较热门的话题,A星算法以及其扩展性算法被广范地应用于求解移动机器人的最优路径.该文在研究机器人路径规划算法中,详细阐述了传统A星算法的基本原理,并通过栅格法分割了机器人路径规划区域,利用MATLAB仿真平台生成了机器人二维路径仿真地图对其进行仿真实验,并对结果进行分析和研究,为今后进一步的研究提供经验.
2 部分代码
function [route] = Time_Astar_For_Cooperative_Path_Finding(start_coords, end_coords, space_time_map, reservation_table)%1 - white - clear cell
%2 - black - obstacle
%3 - red - visited
%4 - blue - on list
%5 - green - start
%6 - yellow - destination
cmap = [1 1 1;
0 0 0;
1 0 0;
0 0 1;
0 1 0;
1 1 0;
0.5 0.5 0.5];
colormap(cmap);
[size_x, size_y, size_t] = size(space_time_map);
%add the start point and the end point
space_time_map(start_coords(1), start_coords(2), :) =5;
space_time_map(end_coords(1), end_coords(2), :) =6;
%initial parent array and Heuristic array
parent = zeros(size_x, size_y, size_t);
[X, Y] = meshgrid(1:size_y, 1:size_x);
xd = end_coords(1);
yd = end_coords(2);
H =abs(X-xd) + abs(Y-yd);
H = H';
%initial cost arrays
g = inf(size_x, size_y, size_t);
f = inf(size_x, size_y, size_t);
g(start_coords(1), start_coords(2), 1) = 0;
f(start_coords(1), start_coords(2), 1) = H(start_coords(1), start_coords(2));
end_time = 1;
while true
%find the node with the minimum f values
[min_f, current] = min(f(:));
[current_x, current_y, current_t] = ind2sub(size(space_time_map), current);
if((current_x == end_coords(1) && current_y == end_coords(2)) || isinf(min_f))
end_time = current_t;
disp('hheheh');
break;
end
%add the current node to close list
space_time_map(current) = 3;
f(current) = Inf;
[i, j, k] = ind2sub(size(space_time_map), current);
neighbours = [i-1, j, k+1;
i+1, j, k+1;
i, j-1, k+1;
i, j+1, k+1;
i, j, k+1];
for index = 1:size(neighbours, 1)
px = neighbours(index, 1);
py = neighbours(index, 2);
pt = neighbours(index, 3);
% judge whether out of bound or not
if (px >0 && px<=size_x && py >0 && py<= size_y )
sub_neighbours = sub2ind(size(space_time_map), px, py, pt);
%judge whether the node is obstacle, start point, end
%point, or not
if(space_time_map(sub_neighbours) ~= 2 && space_time_map(sub_neighbours) ~= 5 && space_time_map(sub_neighbours) ~= 3)
%judge whether the node has less f
if(g(current) +1+ H(px, py) < f(sub_neighbours))
%judge whether the node is in reservation table or not
if (~reservation_table(sub_neighbours ))
%judge whether the special action
[special_action] = Special_action(current, sub_neighbours,reservation_table);
if (~special_action)
g(sub_neighbours) = g(current) + 1;
f(sub_neighbours) = g(sub_neighbours) + H(px, py);
parent(sub_neighbours) = current;
space_time_map(sub_neighbours) = 4;
end
end
end
end
end
end
end
%obstain the route
dest_node = sub2ind(size(space_time_map), end_coords(1), end_coords(2), end_time);
route = [];
route = [dest_node];
while (parent(route(1)) ~= 0)
route = [parent(route(1)), route];
end
% for i = 1:end_time-1
% image(1.5, 1.5, space_time_map(:,:, i));
% grid on;
% axis image;
% drawnow;
% pause(1);
% end
end
function [special_action] = Special_action(current, sub_neighbours, reservation_table)
special_action = false;
[c_x, c_y, c_t] = ind2sub(size(reservation_table), current);
[s_x, s_y, s_t] = ind2sub(size(reservation_table), sub_neighbours);
if(reservation_table(c_x, c_y, s_t) &&reservation_table(s_x, s_y, c_t) && (reservation_table(c_x, c_y, s_t) ==reservation_table(s_x, s_y, c_t)))
special_action = true;
else
special_action = false;
end
end
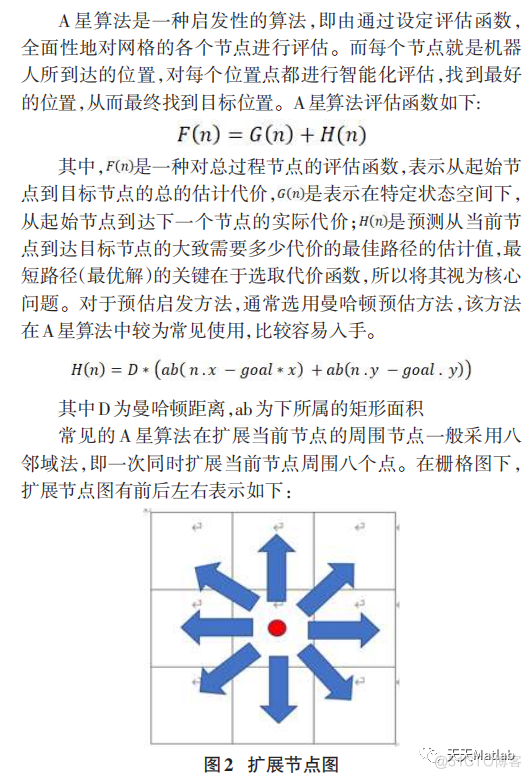
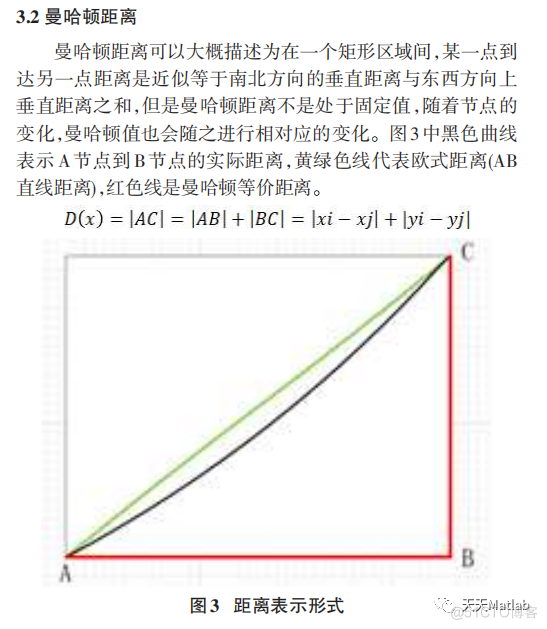
3 仿真结果
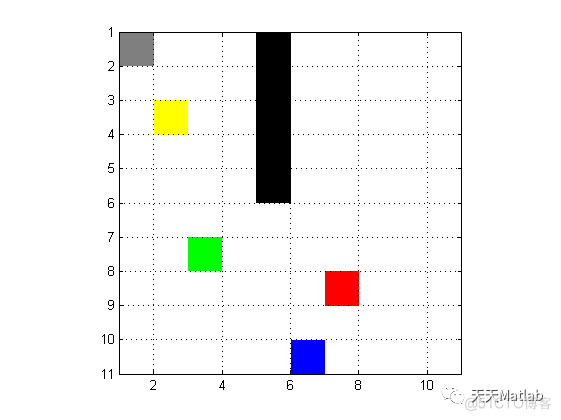
4 参考文献
[1]李吉功, 冯宜伟, 郭戈. 基于栅格地图的通用机器人避障算法[C]// 中国自动化学会第21届青年学术年会. 0.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

