1 简介 2 部分代码 function [d,path,position]= verify(bestpath,threat,R,startX,startY,endX,endY,gridCount) %此函数主要是避开雷达的检测以及计算航线的距离 %path input:规划的路径 %threat input:雷达的威胁
1 简介


2 部分代码
%此函数主要是避开雷达的检测以及计算航线的距离
%path input:规划的路径
%threat input:雷达的威胁
%R input:雷达的半径
% % % 整合路径
position(1,1)=startX;position(1,2)=startY;
for i=2:gridCount
position(i,1)=bestpath(i*2-1);
position(i,2)=bestpath(i*2);
end
position(gridCount+1,1)=endX;position(gridCount+1,2)=endY;
% % % 计算代价函数矩阵
[n,m]=size(position);
sign=ones(n);
sign=sign-diag(diag(sign));
[n,m]=size(sign);
cost=ones(size(sign))*Inf;
for i=1:n
for j=1:n
cost(i,j)=sqrt( sum ( ( position(i,:)-position(j,:) ).^2 ) );
end
end
%山峰威胁判断
% 判断节点是否位于山峰底座辐射范围内,更改代价矩阵
[a,b]=find(cost~=Inf);
Allowed=[a,b];
for i=1:length(Allowed)
for j=1:length(threat)
x_1=position(Allowed(i,1),1);
y_1=position(Allowed(i,1),2);
x_2=position(Allowed(i,2),1);
y_2=position(Allowed(i,2),2);
x_min=min(x_1,x_2);
x_max=max(x_1,x_2);
y_min=min(y_1,y_2);
y_max=max(y_1,y_2);
A=(y_2-y_1);
B=-(x_2-x_1);
C=y_1*(x_2-x_1)-x_1*(y_2-y_1);
d=abs(threat(j,1)*A+threat(j,2)*B+C)/sqrt(A^2+B^2);
C_bar=A*threat(j,2)-B*threat(j,1);
X=(-A*C-B*C_bar)/(A^2+B^2);
Y=(C_bar*A-B*C)/(A^2+B^2);
%这里记载的是位置有没有触碰到山峰
d_1=sqrt((x_1-threat(j,1))^2+(y_1-threat(j,2))^2);
d_2=sqrt((x_2-threat(j,1))^2+(y_2-threat(j,2))^2);
if (d<R(j)&&(X<=x_max&&X>=x_min)&&(Y<=y_max&&Y>=y_min))||d_1<=R(j)||d_2<=R(j)
cost(Allowed(i,1),Allowed(i,2))=Inf;
end
end
end
u=1;
%计算次优航程,这里的原理主要是从蝙蝠个体的坐标中选取合适的点,然后在之后的流程由点成线
dist=cost(1,:);
s=zeros(size(dist));
s(1)=1;
dist(1)=0;
path=zeros(size(dist));
path(1,:)=1;
for num=2:n
mindist=Inf;
for i=1:length(dist)
if s(i)==0
if dist(i)<mindist
mindist=dist(i);
u=i;
end
end
end
s(u)=1;
for w=1:length(dist)
if s(i)==0
if dist(u)+cost(u,w)<dist(w)
dist(w)=dist(u)+cost(u,w);
path(w)=u;
end
end
end
end
i=n;
d=0;
count=0;
while i>1
j=path(i);
%plot([position(i,1),position(j,1)],[position(i,2),position(j,2)],'Linewidth',2)
%axis([0,700,0,700]);
d=d+sqrt((position(i,1)-position(j,1))^2+(position(i,2)-position(j,2))^2);
i=j;
count=count+1;
end
%这里这么做主要是避免无人机航线中只存在两个点
if count==1
d=Inf;
end
d;path;position;
3 仿真结果
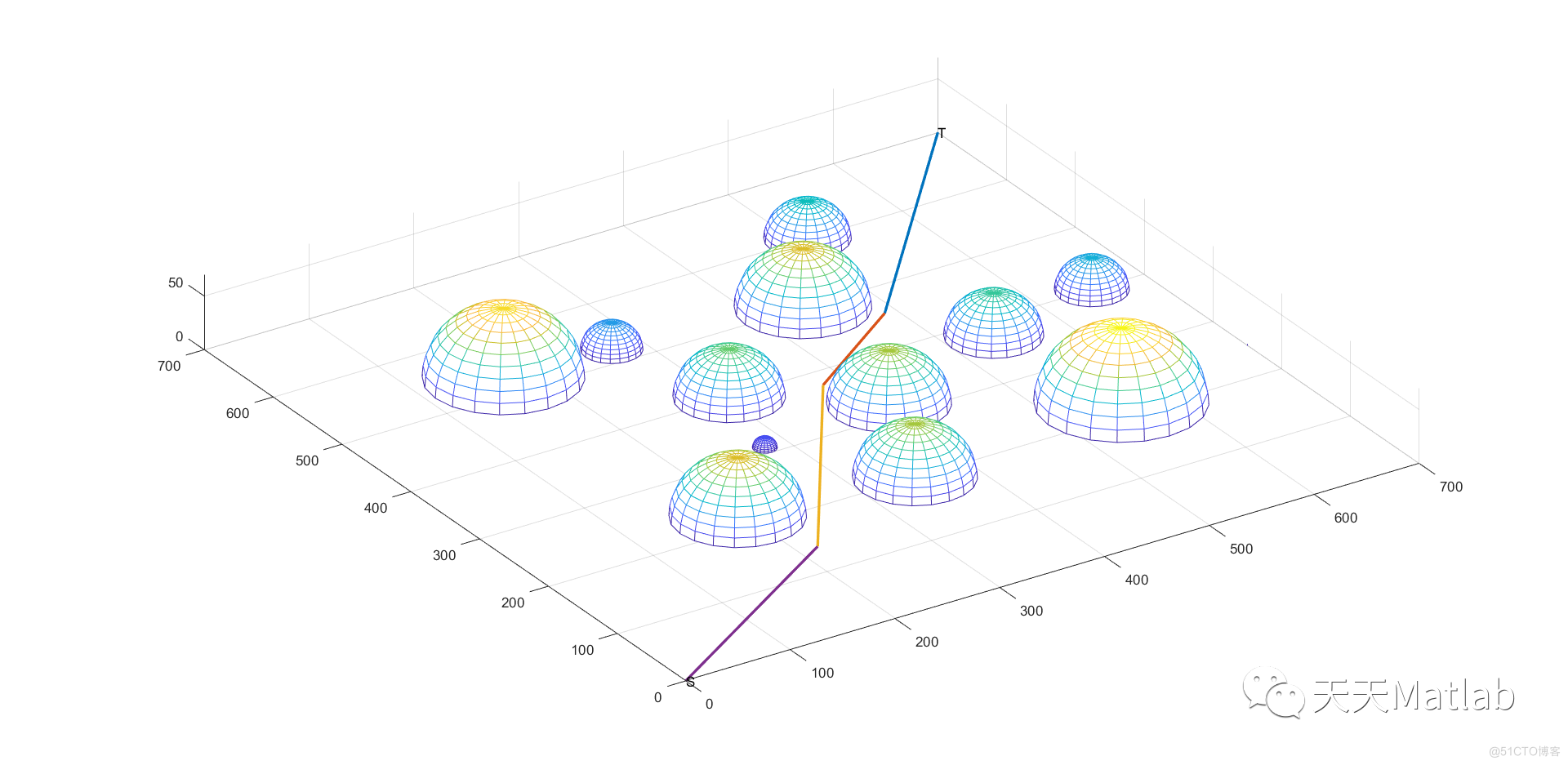
4 参考文献
[1]倪昌浩, 邹海. 基于改进蝙蝠算法的移动机器人路径规划方法研究[J]. 制造业自动化, 2021.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

