pytest执行的顺序【收集测试用例、运行fixture函数、运行测试用例】 1、首先,pytest测试用例在执行之前,首先先收集测试套件中所有的测试用例。【对于参数化的测试用例(即使用了
pytest执行的顺序【收集测试用例、运行fixture函数、运行测试用例】
1、首先,pytest测试用例在执行之前,首先先收集测试套件中所有的测试用例。【对于参数化的测试用例(即使用了parametrize装饰器的用例),其实在测试收集阶段已经自动准备好了这些用例】
可以参考【pytest修改测试用例执行顺序(钩子函数:pytest_collection_modifyitems)】这篇博客
import pytestfrom tools.read_config import *
class TestLogin1:
def test_1(self):
print(ReadConfig().read_config('project_GHelper', 'token'))
@pytest.mark.skip
def test_2(self):
print('用例执行2')
class TestLogin2:
@pytest.mark.parametrize('data1, data2', [(1, 2), ('a', 'b')], ids=['第一个测试用例', '第二个测试用例'])
def test_3(self, data1, data2):
print(data1, data2)
运行结果:
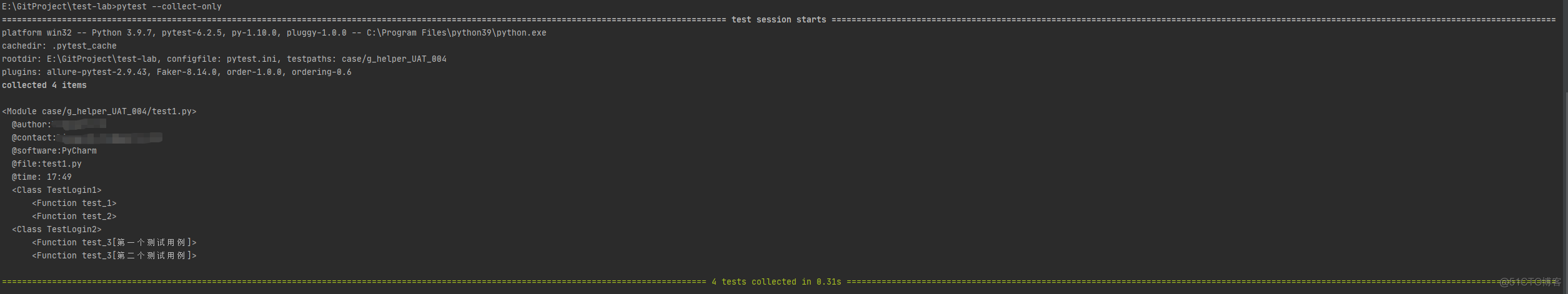
【注意】收集需要运行的测试用例时,用例参数化部分会提前运行,即需要收集所有的测试用例数量;然后才开始执行测试用例,即执行测试方法体里面的程序。
示例:不能在用例参数化的时候替换token,因为每次运行fixture函数是在测试用例收集之后,此时的参数化已经完成。(此时的token时fixture函数执行之前的旧的token)
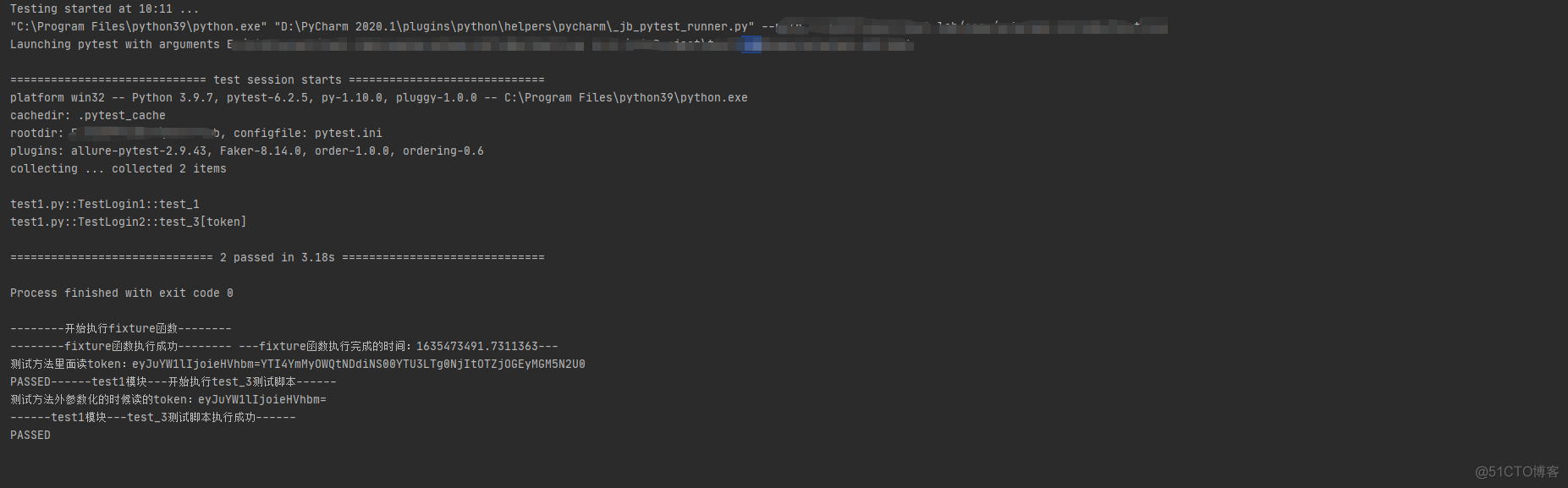
2、运行测试用例之前,会先查看该测试函数中的参数,然后搜索与这些参数具有相同名称的fixture。一旦pytest找到这些对象,它就会运行这些fixture。
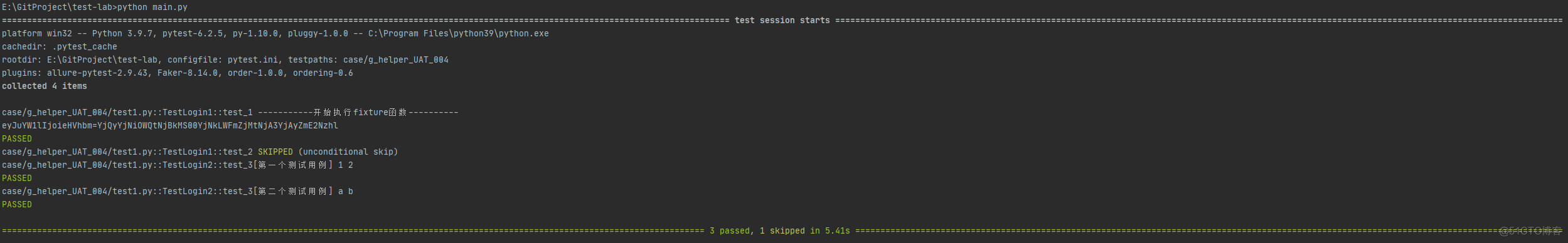
【衍生:fixture的执行顺序】:
3、开始执行测试用例
用例异常机制
1、测试用例收集完成后,在执行测试用例期间的时候如果setup前置函数发生异常,则会中断测试用例的执行(即不会执行任何测试用例)
代码:
# conftest.pyimport pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='session', autouse=True)
def get_token():
raise Exception('用例执行时setup前置操作执行期间发生异常')
# 在收集完测试用例后才会执行
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
print('\npytest 收集到的所有测试用例:\n', items)
for item in items:
item.name = item.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
item._nodeid = item.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
print('---' * 10)
print('用例名:', item.name)
print('用例节点:', item.nodeid) # 打印出每条参数化后的测试用例路径以及每条测试用例的ids# test_002.py
import pytest
class TestDemoB:
def test_B_001(self):
pass
def test_B_002(self):
pass
def test_B_003(self):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['-vs', __file__])
运行结果:
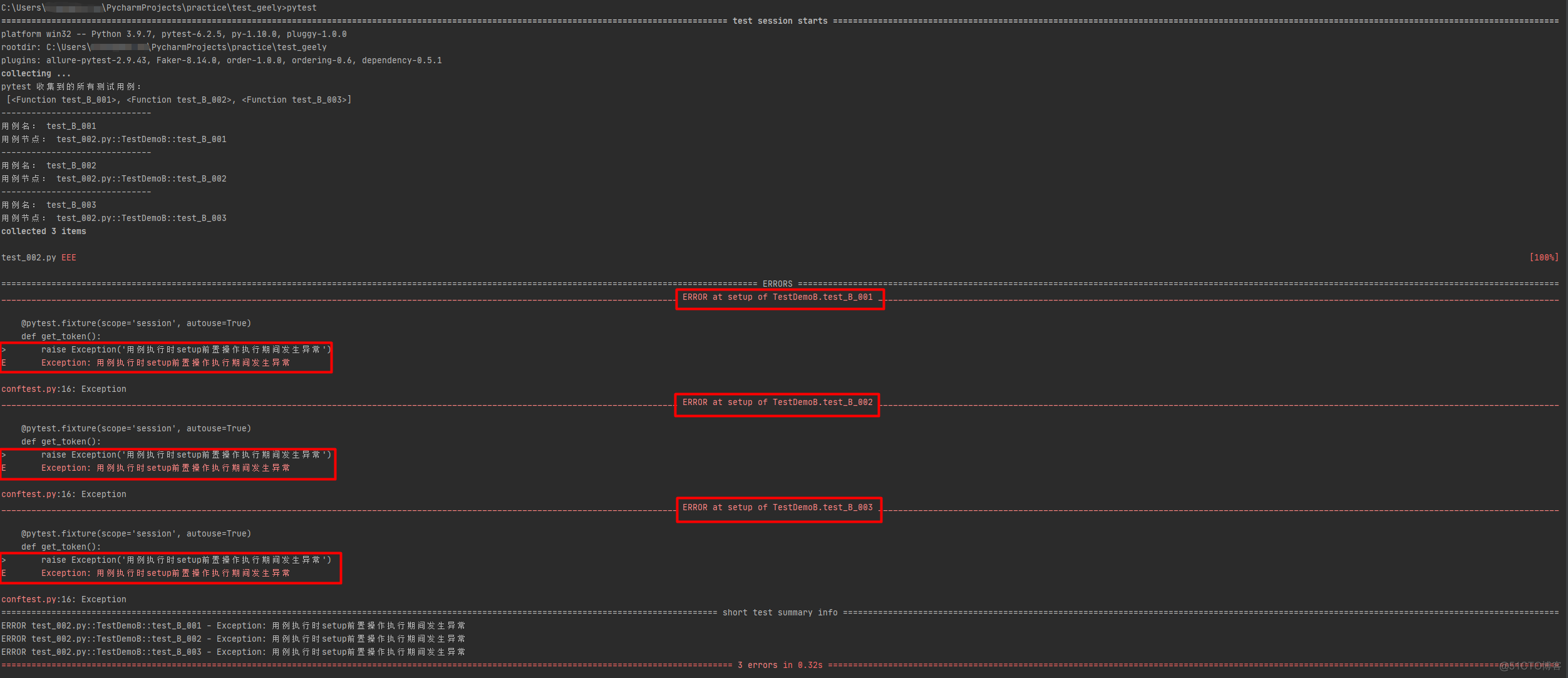
2、测试用例收集完成后,在执行完测试用例后如果teardown后置函数发生异常,不会中断测试用例的执行(因为此时的测试用例已经执行完成)
代码1:
# conftest.pyimport pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='function', autouse=True)
def get_token():
print('用例执行前setup前置操作执行期间没有发生异常')
yield
raise Exception('用例执行完成后teardown后置函数执行期间发生异常')
# 在收集完测试用例后才会执行
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
print('\npytest 收集到的所有测试用例:\n', items)
for item in items:
item.name = item.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
item._nodeid = item.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
print('---' * 10)
print('用例名:', item.name)
print('用例节点:', item.nodeid) # 打印出每条参数化后的测试用例路径以及每条测试用例的ids# test_002.py
import pytest
class TestDemoB:
def test_B_001(self):
pass
def test_B_002(self):
pass
def test_B_003(self):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['-vs', __file__])
运行结果:
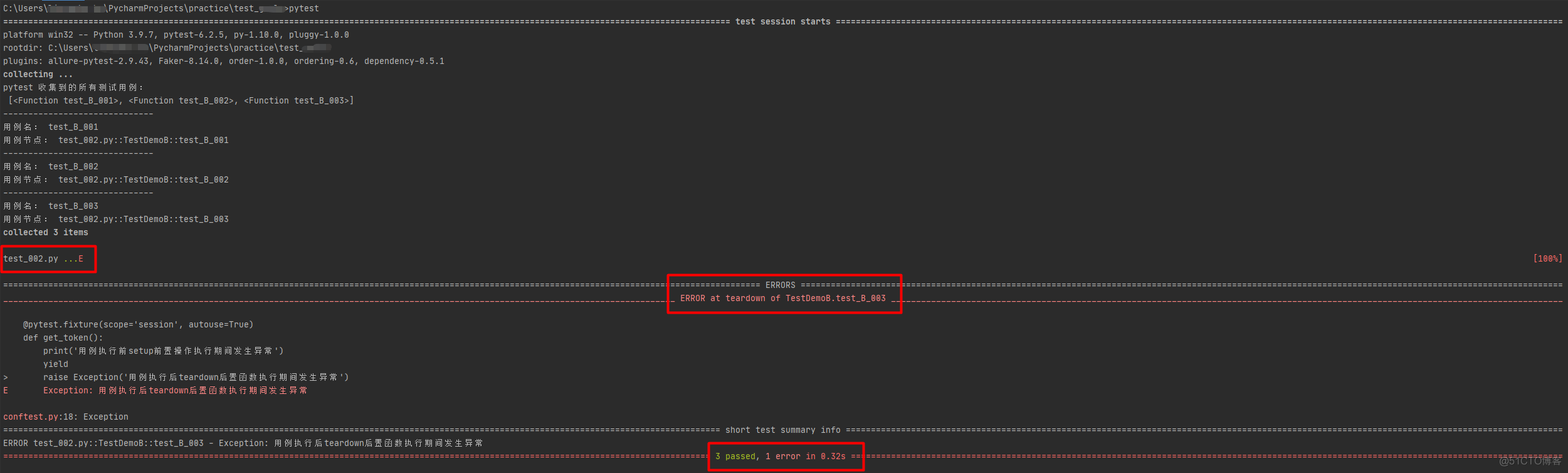
代码2:
# conftest.pyimport pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='function', autouse=True)
def get_token():
print('用例执行前setup前置操作执行期间没有发生异常')
yield
raise Exception('用例执行完成后teardown后置函数执行期间发生异常')
# 在收集完测试用例后才会执行
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
print('\npytest 收集到的所有测试用例:\n', items)
for item in items:
item.name = item.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
item._nodeid = item.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
print('---' * 10)
print('用例名:', item.name)
print('用例节点:', item.nodeid) # 打印出每条参数化后的测试用例路径以及每条测试用例的ids# test_002.py
import pytest
class TestDemoB:
def test_B_001(self):
print(1*100)
def test_B_002(self):
print('*'*100)
def test_B_003(self):
print('&'*100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['-vs', __file__])
运行结果:

3、测试用例收集完成后,在执行测试用例时setup前置函数和teardown后置函数都没有发生异常,用例正常执行,正常断言获取测试用例执行结果。
代码:
# conftest.pyimport pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='function', autouse=True)
def get_token():
print('用例执行前setup前置操作执行期间没有发生异常')
yield
print('用例执行完成后teardown后置函数执行期间没有发生异常')
# 在收集完测试用例后才会执行
def pytest_collection_modifyitems(items):
print('\npytest 收集到的所有测试用例:\n', items)
for item in items:
item.name = item.name.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
item._nodeid = item.nodeid.encode("utf-8").decode("unicode_escape")
print('---' * 10)
print('用例名:', item.name)
print('用例节点:', item.nodeid) # 打印出每条参数化后的测试用例路径以及每条测试用例的ids# test_002.py
import pytest
class TestDemoB:
def test_B_001(self):
assert False
def test_B_002(self):
print('*'*100)
def test_B_003(self):
print('&'*100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main(['-vs', __file__])
运行结果:
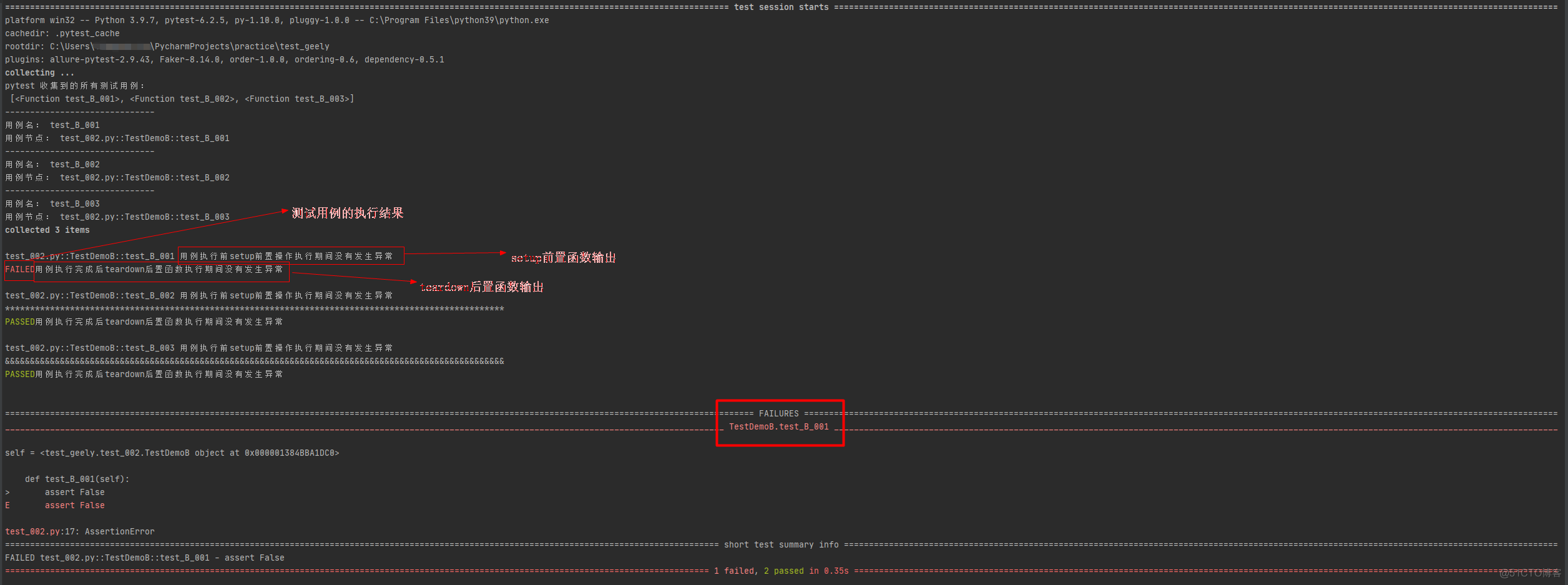
去期待陌生,去拥抱惊喜。
