IO: 向设备输入数据和输出数据C++的IO流

c++中,必须通过特定的已经定义好的类, 来处理IO(输入输出)
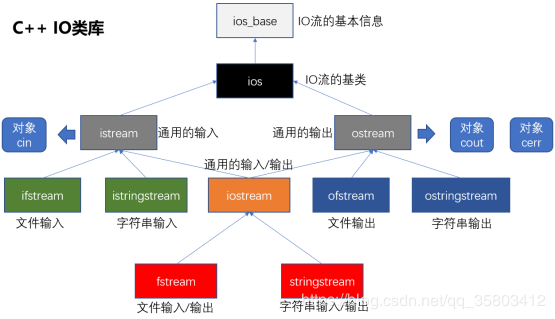
文件流: 对文件进行读写操作
头文件:
类库:
ifstream 对文件输入(读文件)
ofstream 对文件输出(写文件)
fstream 对文件输入或输出
//写文件
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
ofstream outfile; //也可以使用fstream, 但是fstream的默认打开方式不截断文件长度
// ofstream的默认打开方式是, 截断式写入 ios::out | ios::trunc
// fstream的默认打开方式是, 截断式写入 ios::out
// 建议指定打开方式
outfile.open("user.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
while (1) {
cout << "请输入姓名: [ctrl+z退出] ";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
outfile << name << "\t";
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
outfile << age << endl; //文本文件写入
}
// 关闭打开的文件
outfile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//读文件
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("user.txt");
while (1) {
infile >> name;
if (infile.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
cout << name << "\t";
infile >> age;
cout << age << endl;
}
// 关闭打开的文件
infile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
对二进制文件流读写
文本文件和二进制文件的区别?
文本文件: 写数字1, 实际写入的是 ‘1'
二进制文件:写数字1, 实际写入的是 整数1(4个字节,最低字节是1, 高3个字节都是0)
写字符‘R'实际输入的还是‘R'
写二进制文件
使用文件流对象的write方法写入二进制数据.
//写二进制文件
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.dat", ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
while (1) {
cout << "请输入姓名: [ctrl+z退出] ";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
outfile << name << "\t";
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
//outfile << age << endl; //会自动转成文本方式写入
outfile.write((char*)&age, sizeof(age));
}
// 关闭打开的文件
outfile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//读二进制文件
使用文件流对象的read方法.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("user.dat", ios::in | ios::binary);
while (1) {
infile >> name;
if (infile.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
cout << name << "\t";
// 跳过中间的制表符
char tmp;
infile.read(&tmp, sizeof(tmp));
//infile >> age; //从文本文件中读取整数, 使用这个方式
infile.read((char*)&age, sizeof(age));
cout << age << endl; //文本文件写入
}
// 关闭打开的文件
infile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
对文件流按格式读写取数据
使用stringstream
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("user.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
while (1) {
cout << "请输入姓名: [ctrl+z退出] ";
cin >> name;
if (cin.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
stringstream s;
s << "name:" << name << "\t\tage:" << age << endl;
outfile << s.str();
}
// 关闭打开的文件
outfile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
按指定格式读文件
没有优雅的C++解决方案, 使用C语言的sscanf
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
char name[32];
int age;
string line;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("user.txt");
while (1) {
getline(infile, line);
if (infile.eof()) { //判断文件是否结束
break;
}
sscanf_s(line.c_str(), "姓名:%s 年龄:%d", name, sizeof(name),&age);
cout << "姓名:" << name << "\t\t年龄:" << age << endl;
}
infile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
文件流的状态检查
s.is_open( )
文件流是否打开成功,
s.eof( ) 流s是否结束
s.fail( )
流s的failbit或者badbit被置位时, 返回true
failbit: 出现非致命错误,可挽回, 一般是软件错误
badbit置位, 出现致命错误, 一般是硬件错误或系统底层错误, 不可挽回
s.bad( )
流s的badbit置位时, 返回true
s.good( )
流s处于有效状态时, 返回true
s.clear( )
流s的所有状态都被复位
文件流的定位
seekg( off_type offset, //偏移量
ios::seekdir origin ); //起始位置
作用:设置输入流的位置
参数1: 偏移量
参数2: 相对位置
beg 相对于开始位置
cur 相对于当前位置
end相对于结束位置
读取当前程序的最后50个字符
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
ifstream infile;
infile.open("定位.cpp");
if (!infile.is_open()) {
return 1;
}
infile.seekg(-50, infile.end);
while (!infile.eof()) {
string line;
getline(infile, line);
cout << line << endl;
}
infile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//tellg返回该输入流的当前位置(距离文件的起始位置的偏移量)
获取当前文件的长度
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
ifstream infile;
infile.open("定位.cpp");
if (!infile.is_open()) {
return 1;
}
// 先把文件指针移动到文件尾
infile.seekg(0, infile.end);
int len = infile.tellg();
cout << "len:" << len;
infile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
seekp设置该输出流的位置
先向新文件写入:“123456789”
然后再在第4个字符位置写入“ABC”
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("test.txt");
if (!outfile.is_open()) {
return 1;
}
outfile << "123456789";
outfile.seekp(4, outfile.beg);
outfile << "ABC";
outfile.close();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
计算机英语
ioinput output的简写
输出输出
iosC++ 输出输出流的基类
stream流
istream输入流
ostream输出流
iostream输出输出流
fstreamfile stream的简写 文件流
ifstream文件输入流
ofstream文件输出流
stringstream字符串流
istringstream字符串输入流
ostringstream字符串输出流
seek寻找
seekg 设置输入流的位置
seekp设置输出流的位置
tell告诉
tellg返回当前流的位置
open打开
is_open是否打开成功
eofend of file的简写
文件结束
good好的
bad坏的
fail失败
常见错误总结
1.文件没有关闭
文件没有关闭, close(),可能导致写文件失败
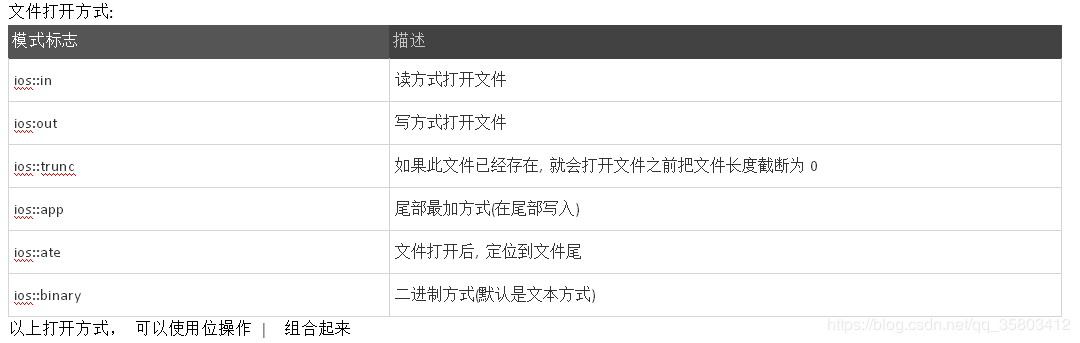
2.文件打开方式不合适
3.在VS2015的部分版本中,当sscanf和sscanf_s的格式字符串中含有中文时,可能会读取失败。
在vs2019中未发现该类问题。
到此这篇关于C++ I/O文件读写操作的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ I/O文件读写操作内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
