在linux中,管道符是“|”,主要用于将两个或者多个命令连接到一起,把一个命令的输出作为下一个命令的输入;语法“command1 | command2 [ | commandN... ]”,“|”符左边命令的输出会作为“|”符右边命令的输入。管道符是可以连续使用的,第一个命令的输出会作为第二个命令的输入,第二个命令的输出又会作为第三个命令的输入,依此类推。

本教程操作环境:linux7.3系统、Dell G3电脑。
Shell 还有一种功能,就是可以将两个或者多个命令(程序或者进程)连接到一起,把一个命令的输出作为下一个命令的输入,以这种方式连接的两个或者多个命令就形成了管道(pipe)。
Linux 管道使用竖线|连接多个命令,这被称为管道符。
command1 | command2 command1 | command2 [ | commandN... ]
当在两个命令之间设置管道时,管道符|左边命令的输出就变成了右边命令的输入。只要第一个命令向标准输出写入,而第二个命令是从标准输入读取,那么这两个命令就可以形成一个管道。大部分的 Linux 命令都可以用来形成管道。
管道符是可以连续使用的,第一个命令的输出会作为第二个命令的输入,第二个命令的输出又会作为第三个命令的输入,依此类推。
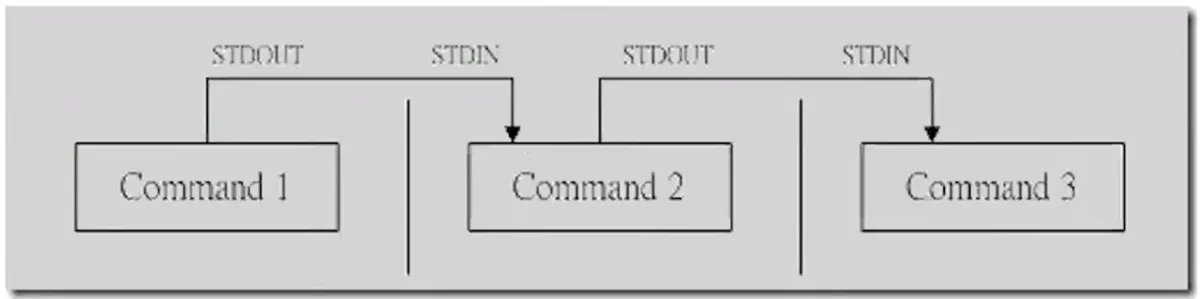
这里需要注意,command1 必须有正确输出,而 command2 必须可以处理 command2 的输出结果;而且 command2 只能处理 command1 的正确输出结果,不能处理 command1 的错误信息。
举个栗子:对hello.sh文件进行排序去重以后找出包含"better"的行
命令为:cat hello.sh | sort | uniq | grep 'better’
- 查看文本
- 排序
- 去重
- 过滤
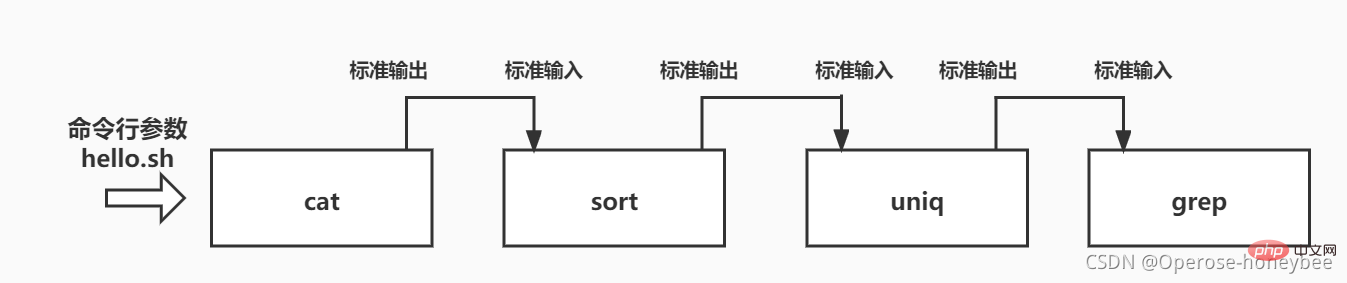
【1】第一道工序——查看文本
首先使用cat命令查看文本,打印到屏幕上内容即为cat命令的输出结果
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat hello.sh hello this is linux be better be better i am lhj hello this is linux i am lhj i am lhj be better i am lhj have a nice day have a nice day hello this is linux hello this is linux have a nice day zzzzzzzzzzzzzz dddddddd gggggggggggggggggggg [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
【2】第二道工序——排序
将前面cat命令输出的结果通过管道丢给sort命令,所以sort命令是对前面cat命令输出的文本进行排序
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat hello.sh | sort be better be better be better dddddddd gggggggggggggggggggg have a nice day have a nice day have a nice day hello this is linux hello this is linux hello this is linux hello this is linux i am lhj i am lhj i am lhj i am lhj zzzzzzzzzzzzzz [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
【3】第三道工序——去重
前面介绍uniq的文章中提到,sort跟uniq结合使用才能有效去重,所以通过管道将sort处理后输出的文本丢给uniq处理,所以uniq处理的是排序好的文本,可以进行有效去重
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat hello.sh | sort | uniq be better dddddddd gggggggggggggggggggg have a nice day hello this is linux i am lhj zzzzzzzzzzzzzz [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
【4】第四道工序——过滤
最后一步过滤则同样是将前面命令即uniq命令处理后输出的文本进行过滤
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat hello.sh | sort | uniq | grep 'better' be better [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
重点来了!
重点来了!
重点来了!
以上的cat、sort、uniq、grep等命令均支持管道符,是因为这些命令均可从标准输入中读取要处理的文本(即从标准输入中读取参数);而对于部分命令,例如rm、kill等命令则不支持从标准输入中读取参数,只支持从命令行中读取参数(即rm命令后面必须指定删除的文件或者目录,kill命令后面必须要指定杀死的进程号等)
那什么样的命令支持管道,什么样的命令不支持管道呢?
一般情况下,处理文本的命令,例如sort、uniq、grep、awk、sed等命令均支持管道;像rm、ls这类的不是处理文本的命令均不支持管道
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat hello.sh | sort be better be better be better dddddddd gggggggggggggggggggg have a nice day have a nice day have a nice day hello this is linux hello this is linux hello this is linux hello this is linux i am lhj i am lhj i am lhj i am lhj zzzzzzzzzzzzzz [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
sort后面没有参数时,则对管道符丢给它的前一个命令的输出结果进行处理(即前一个命令的标准输出作为本次命令的标准输入)
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# ls beifen.txt hello.sh mk read.ln read.sh read.txt sub.sh [root@linuxforliuhj test]# ls | grep read.sh read.sh [root@linuxforliuhj test]# ls | grep read.sh | rm rm: missing operand Try 'rm --help' for more information. [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
当rm后面不指定删除的文件时,则会报错丢失参数,所以,rm等命令不支持从标准输入读取参数,只支持在命令行指定参数,即指定删除的文件。
标准输入和命令行参数那个优先?
有如下两个文件
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat a.txt aaaa dddd cccc bbbb [root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat b.txt 1111 3333 4444 2222 [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
执行命令:cat a.txt | sort
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat a.txt | sort aaaa bbbb cccc dddd [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
当sort的命令行参数为空时,默认使用前一个命令的输出结果作为本次命令的输入
执行命令:cat a.txt | sort b.txt
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat a.txt | sort b.txt 1111 2222 3333 4444 [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
可以看到,当sort的命令行参数(此处为b.txt)不为空时,sort不会读取标准输入里的参数,而时读取命令行参数
执行命令:cat a.txt | sort b.txt -
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# cat a.txt | sort b.txt - 1111 2222 3333 4444 aaaa bbbb cccc dddd [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
" - "表示标准输入,即命令cat a.txt 的输出,相当与对文件b.txt和标准输入一起进行排序,相当于sort a.txt b.txt
[root@linuxforliuhj test]# sort a.txt b.txt 1111 2222 3333 4444 aaaa bbbb cccc dddd [root@linuxforliuhj test]#
思考:对于rm、kill等命令,我们写脚本时常常会遇到需要查询某个进程的进程号然后杀掉该进程,查找某个文件然后删除它这样的需求,该怎么办呢?那就用xargs吧!
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
以上就是linux中管道符是什么的详细内容,更多请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
