最近看HashMap的源码,其中相同下标容易产生hash冲突,但是调试需要发生hash冲突,本文模拟hash冲突。 hash冲突原理 HashMap 冲突是key首先调用 hash() 方法: static final int hash(Object key) { int
hash冲突原理最近看HashMap的源码,其中相同下标容易产生hash冲突,但是调试需要发生hash冲突,本文模拟hash冲突。
HashMap冲突是key首先调用hash()方法:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
然后使用hash值和tab数组长度做与操作:
(n - 1) & hash
算出来的下标,如果一致就会产生冲突。
通过ASKII码获取单个字符开始想到单字符,比如a、b、c、d、e这类字符,但是如果一个一个试的话特别繁琐,想到了ASKII码:
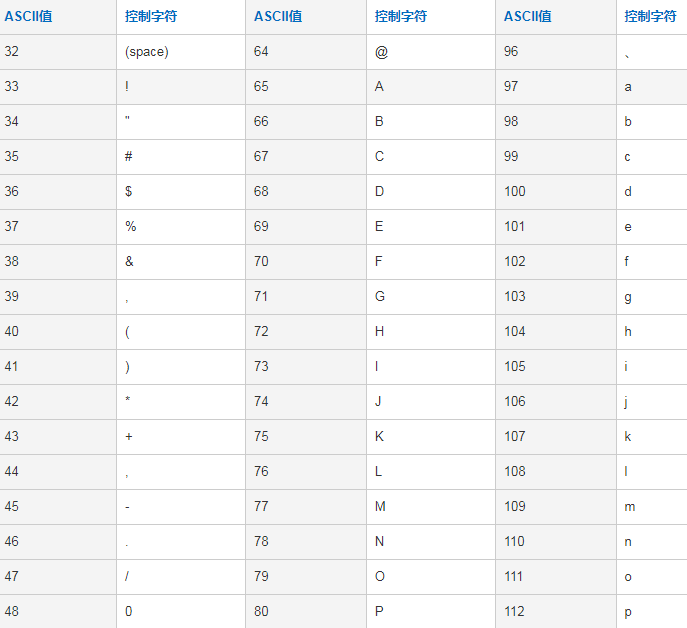
遍历1~100的ASKII码。通过ASKII码获取单字符:
for (int i = 33; i < 100; i++) {
char ch = (char) i;
String str = String.valueOf(ch);
}
通过str获取下标,HashMap默认长度为16,所以n-1为15:
int index = 15 & hash(str);
算出index一致的话,就放在一个列表中。不同的index放在HashMap中,完整代码如下:
Map<Integer, List<String>> param = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 33; i < 100; i++) {
char ch = (char) i;
String str = String.valueOf(ch);
int index = 15 & hash(str);
List<String> list = param.get(index);
if (list == null) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
}
list.add(str);
param.put(index,list);
}
param.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + " " + Arrays.toString(v.toArray())));
输出结果:
0 [0, @, P, `]
1 [!, 1, A, Q, a]
2 [", 2, B, R, b]
3 [#, 3, C, S, c]
4 [$, 4, D, T]
5 [%, 5, E, U]
6 [&, 6, F, V]
7 [', 7, G, W]
8 [(, 8, H, X]
9 [), 9, I, Y]
根据上面算出来的结果,使用其中的一个例子:
1 [!, 1, A, Q, a]
先添加数据:
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("!",1);
map.put("1",1);
map.put("A",1);
先添加1, A, Q三个数据。然后添加Q。
打开调式,定位到putVal方法:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
在源码解析文章详解HashMap源码解析(下)中知道,发生hash冲突是会在上面代码的第16行,一直for循环遍历链表,替换相同的key或者在链表中添加数据:
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
调式:
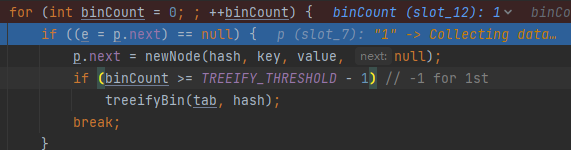
会一直遍历for循环,直到p.next==null遍历到链尾,然后在链表尾部添加节点数据:
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
- 通过
(h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)高位运算hash码和(n - 1) & hash哈希表数组长度取模,分析hash冲突原理。 - 通过
ASKII码遍历获取字符串,获取发生hash冲突的字符。 - 调用
put方法,调用hash冲突源码。
