这篇文章主要介绍了springboot配置文件绑定实现解析,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
先创建一个peron类,然后需要注解configurationProperties(prefix ="person")<br data-filtered="filtered">然后需要加一个@component<br data-filtered="filtered">因为只有在springboot的容器才能提供容器提供的@configurationProperties<br data-filtered="filtered">@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean isBoss() {
return boss;
}
public void setBoss(boolean boss) {
this.boss = boss;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [lastName=" + lastName + ", age=" + age + ", boss=" + boss + ", birth=" + birth + ", maps="
+ maps + ", lists=" + lists + ", dog=" + dog + "]";
}
}
dog类
public class Dog {
private String Name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [Name=" + Name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
写完后,ide会提示需要在pom.xml中导入组件处理器。
<!-- 配置文件的处理器 ,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后创建配置文件,有两种方式,一个时yml文件,另一个时properties
1,application.yml
person:
last-name: zhangsan
age: 24
boss: false
birth: 2017/12/5
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists: [lisi, zhangsan]
dog:
Name: xiaohei
age: 4
2.application.properties
中文字,在eclipse中自动转为unicode码
person.age=24 person.last-name=\u5F20\u4E09 person.birth=2000/1/1 person.boss=false person.maps.k1=value1 person.maps.k2=12 person.dog.name=\u5C0F\u9ED1 person.dog.age=2
在test中使用spring boot的单元测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class Helloworld01QuickApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
运行,会看到得到配置文件中的数据
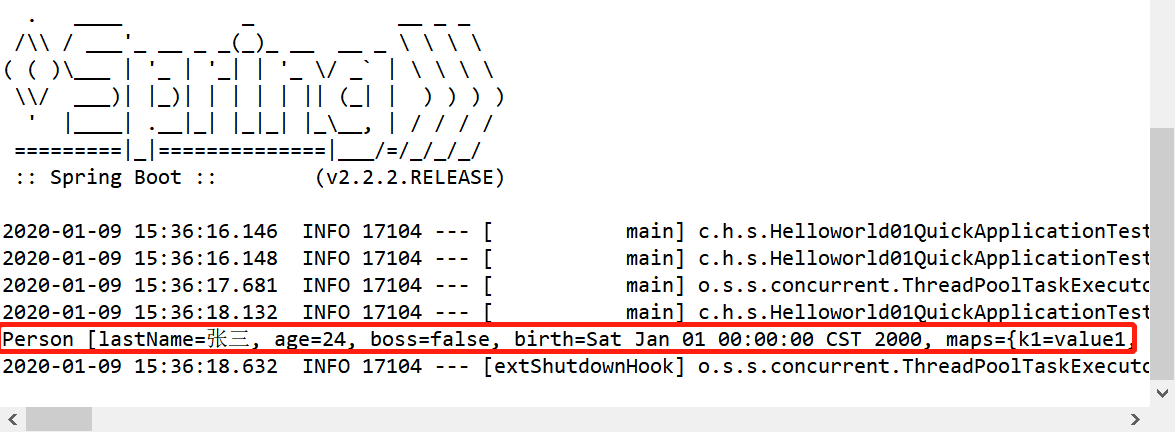
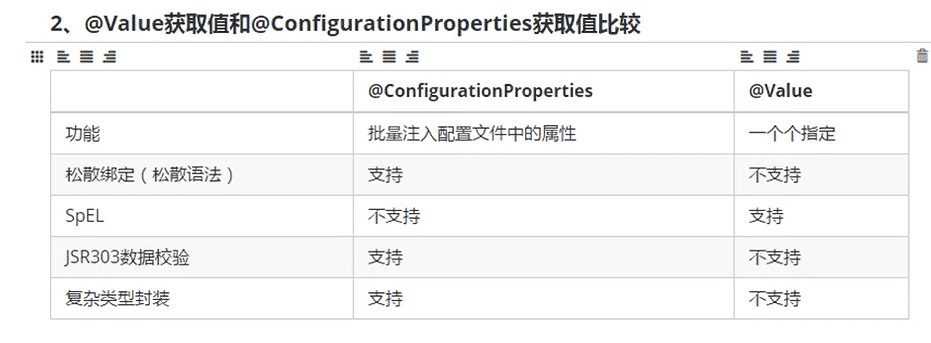
在获取配置文件中注入值得时候,可以使用@value,也可以使用@configurationProperties;
如果只是在逻辑中获取一下配置文件中得值,那么就使用@value
在配置文件注入值得时候也可以校验
在类加入注解@validate
配置文件注入数据校验
@validate
public class person{
@Email
private String last-name;
....
}
@PropertySource("classpath:person.properties") :加载指定的配置文件
@ImportResource(“classpath:beans.xml”):导入spring配置文件,让配置文件生效;
springboot推荐给容器增加组件
1.配置类--》spring配置文件
2.使用@bean给容器中增加组件;
配置文件占位符
1.随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}
2.配置文件中找不到属性时的默认值。
${app.name:金毛}来指定找不到属性时的默认值。
profile
1.多个profile文件
Profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活、指定参数等方式快速切换环境
一般我们在开发的时候有测试环境,开发环境等。
我们在编写多个配置文件的时候,文件名字是application-(profile).properties/yml(这二种格式的都行)。
默认使用application.properties.
2.yml支持多文档块方式
application.yml
#三个横线属于一个文档块 #激活哪个环境 spring: profiles: active: test #测试环境 --- server: port: 8081 spring: profiles: test #开发环境 --- server: port: 8082 spring: profiles: dev
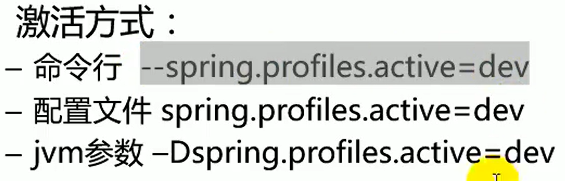
3.激活指定profile
在配置文件中指定spring.profiles.active =dev
springboot配置文件加载位置

这些配置都会加载,然后进行互补配置。


以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。
