目录 爬虫实战(九):爬微博评论 一、 网站分析 1、 页面分析 2、 请求参数分析 3、搜索功能 4、 爬取过程 二、 编写代码 1、 通过搜索获取参数 2、 获取第一个评论 3、 使用递归获取
- 爬虫实战(九):爬微博评论
- 一、 网站分析
- 1、 页面分析
- 2、 请求参数分析
- 3、搜索功能
- 4、 爬取过程
- 二、 编写代码
- 1、 通过搜索获取参数
- 2、 获取第一个评论
- 3、 使用递归获取每页信息
- 4、 写入文件
- 5、 处理数据
- 6、 生成词云
- 三、 总代码
- 一、 网站分析
安倍jj了,那就让我们来看一看大家对此的评价如何?并且做词云
我们对这条微博的评论进行爬取
首先,还是先分析一下评论数据吧:
通过源码分析,我们发现,微博的评论数据是动态加载出来的,所以我们要进行抓包分析,最后,我们找到了一个,名为buildComments的数据包,里面存储了响应数据,以及发起下一次评论请求的一个必要参数max_id,当max_id = 0时,评论加载完全!
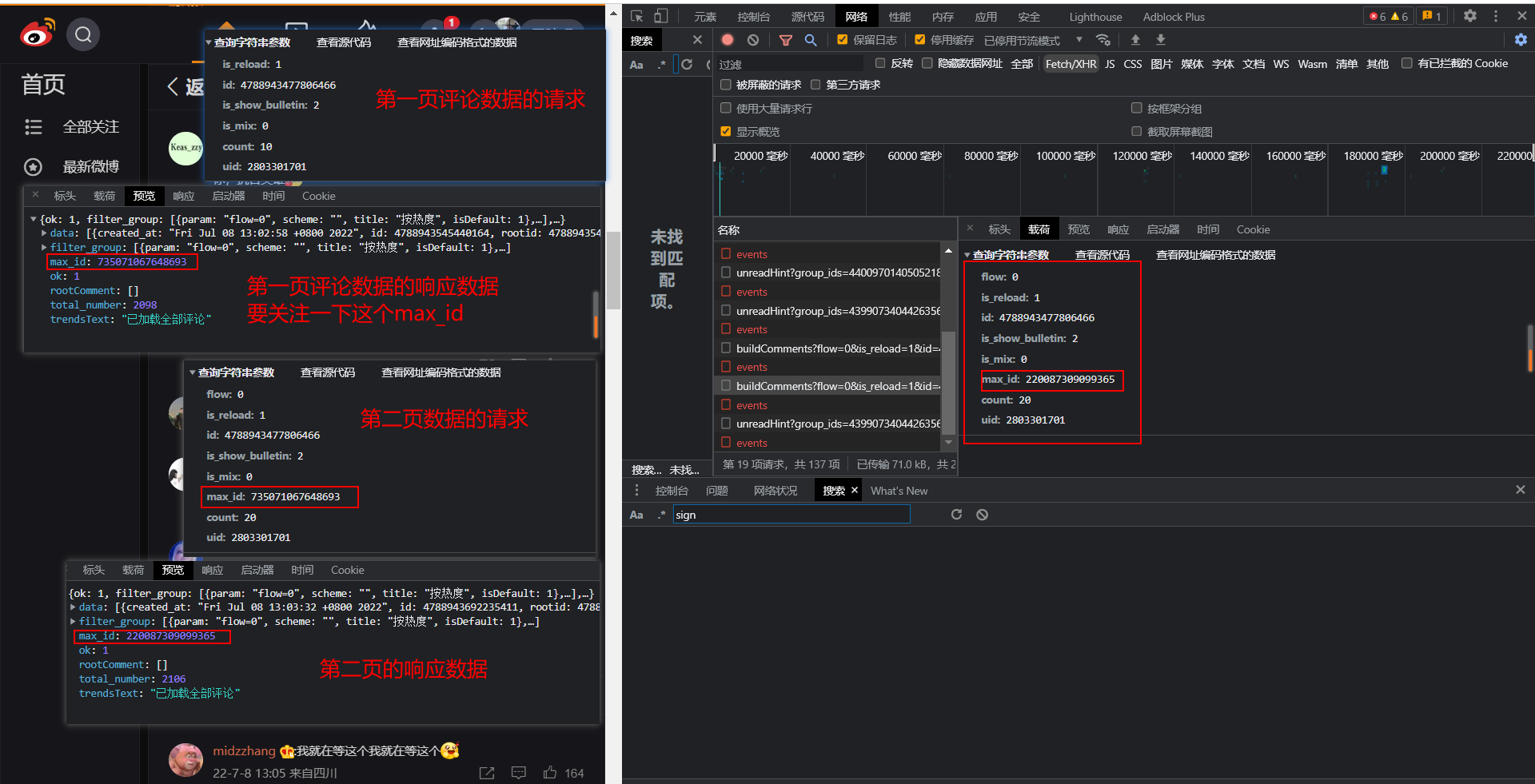 2、 请求参数分析
2、 请求参数分析
请求的url:https://weibo.com/ajax/statuses/buildComments
第一个请求包的请求参数:
params = {
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': 4788943477806466, # 微博文章的id,可以在搜索页面中获得
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'count': 10, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': 2803301701, # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
第二个请求包的请求参数:
params = {
'flow': 0, # 根据什么获取,0为热度,1为发布时间
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': 4788943477806466, # 微博文章的id
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'max_id': 748402646132114, # 用来控制页数的,这个可以在上一个数据包的响应的max_id
'count': 20, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': 2803301701, # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
通过源码分析,我们发现搜索出来的内容是直接存放到源码中,然后返回的,故其为静态网站
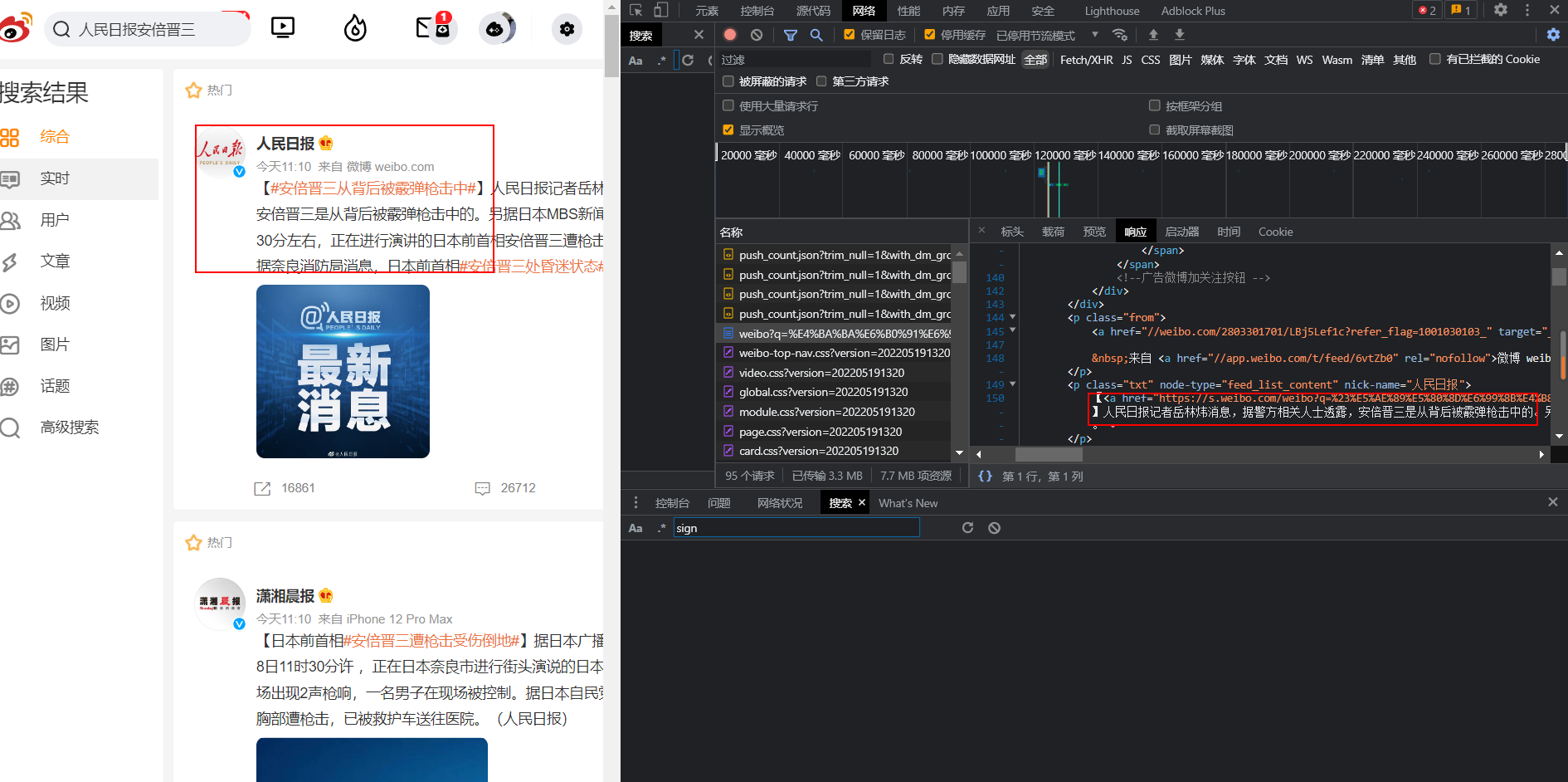
同时,通过对网站分析,我们发现了,id和uid的位置
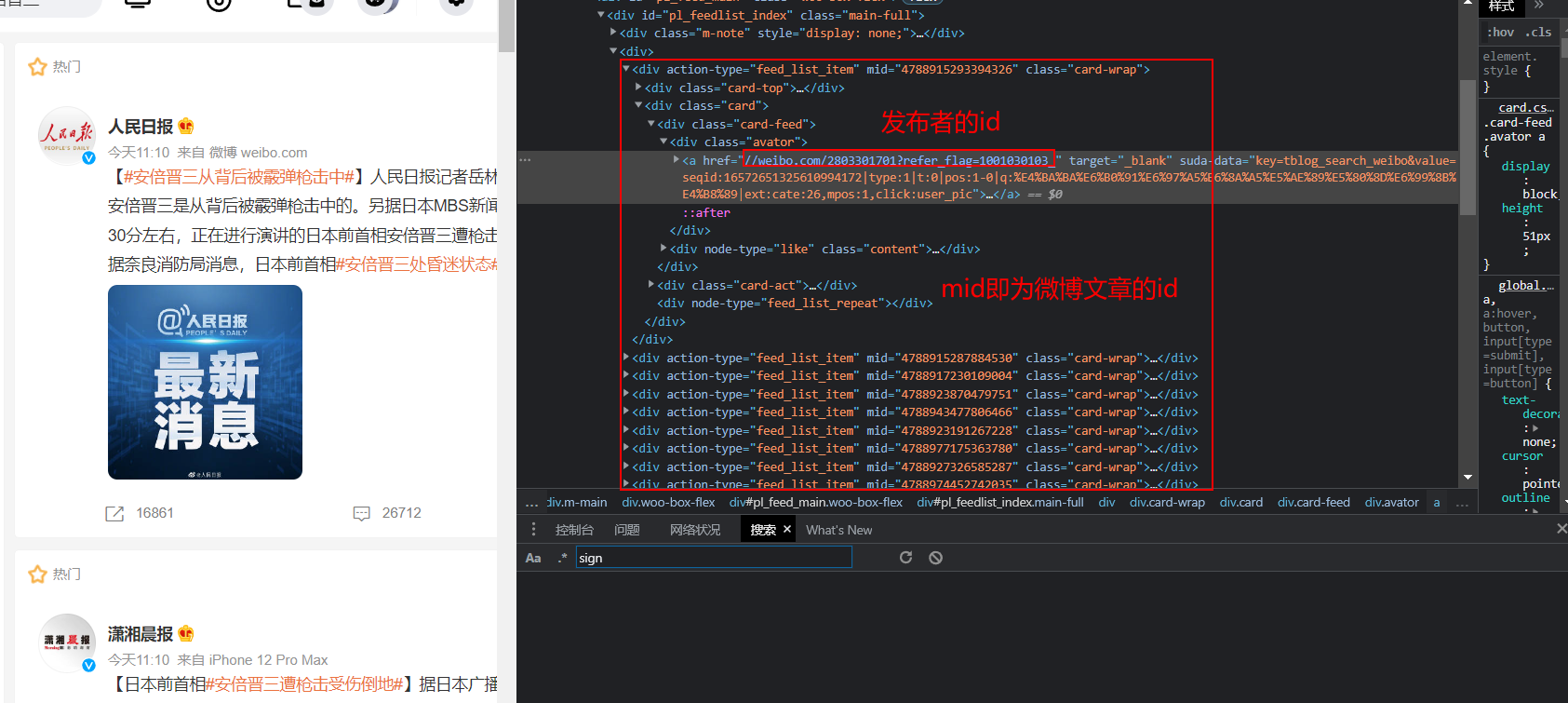 4、 爬取过程
4、 爬取过程
-
如果是要通过搜索框
- 则可以获取文章的id,和用户的uid来获取到第一个请求链接的params参数
如果是直接使用文章id,和用户uid来获取,则不需要这一步
-
通过第一个评论链接来获取后续的参数,使用递归持续发送请求,注意请求的间隔
-
对数据进行处理
-
生成词云
import requests, time, re # 发送请求,接收JSON数据,正则解析
from prettytable import PrettyTable # 美化展示
from fake_useragent import UserAgent # 随机请求头
from lxml import etree # 进行xpath解析
from urllib import parse # 将中文转换为url编码
search_url = "https://s.weibo.com/weibo?q=%s"
# 微博有cookie反爬,如果要使用其搜索功能的话,最好添加cookie
headers = {
'authority': 's.weibo.com',
'method': 'GET',
'scheme': 'https',
'accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9',
'accept-encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'accept-language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8',
'cache-control': 'no-cache',
'cookie': 'SINAGLOBAL=6849256018210.763.1640318151683; UOR=,,tophub.today; SCF=ArxHEBnS4gWA2vpCEAZLWdEt3WZ41VwutzJfy5_Y0G5csLa_ffzUixMCM9VGFLlHI_NYhIVN-KhWG3pM1VgAOK8.; login_sid_t=f238365342825b4ed0ec7e03a108002a; cross_origin_o=SSL; _s_tentry=weibo.com; Apache=9854327619564.12.1657262555880; ULV=1657262555884:5:1:1:9854327619564.12.1657262555880:1654528223100; SUBP=0033WrSXqPxfM725Ws9jqgMF55529P9D9WFcW9qsrf3VzYncb2aZUJFP5JpX5o275NHD95QNeoqfS0zRSoe7Ws4Dqcjdi--fiK.Ri--4iK.Xi-iWi--fiKL2i-2X; SSOLoginState=1657262576; SUB=_2A25Pw6GgDeRhGeFM7VcW8ibKyDyIHXVsuJRorDV8PUNbmtAKLUTckW9NQNYH6iWdr1JwBEvZdTe84ORoGdWLbvsu; ALF=1688798575',
'pragma': 'no-cache',
'referer': 'https://weibo.com/',
'sec-ch-ua': '" Not A;Brand";v="99", "Chromium";v="102", "Google Chrome";v="102"',
'sec-ch-ua-mobile': '?0',
'sec-ch-ua-platform': '"Windows"',
'sec-fetch-dest': 'document',
'sec-fetch-mode': 'navigate',
'sec-fetch-site': 'same-site',
'sec-fetch-user': '?1',
'upgrade-insecure-requests': '1',
'user-agent': UserAgent().random,
}
def get_id_uid(name):
"""传入要搜索的内容,返回用户id和文章id"""
name = parse.quote(name)
info = [] # 这里面存放uid和mid形成的元组
table = PrettyTable(["序号", "发布人", "发布时间", "发布主题"])
headers.update({
'path': f'/weibo?q={name}',
"user-agent": UserAgent().random
}) # 防止反爬
resp = requests.get(search_url % name, headers=headers) # 发送请求
resp.encoding = resp.apparent_encoding # 设置编码
html = etree.HTML(resp.text) # 提交给xpath解析
divs = html.xpath('//*[@id="pl_feedlist_index"]/div[2]/div') # 获取到存储内容的div
info = [] # 这里面存放uid和mid形成的元组
table = PrettyTable(["序号", "发布时间", "作者", "主题"]) # 进行美化输出
index = 0
for index, div in enumerate(divs):
try:
mid = div.xpath("./@mid")[0] # 获取mid
# print(mid)
u_url = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div/a/@href")[0] # 先获取链接,再解析数据
uid = re.search("weibo.com/(?P<uid>\d+)\?refer", u_url).group("uid") # 解析出uid
# print(uid)
info.append((mid, uid)) # 添加到列表中
time_ = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[1]/a/text()")[0] # 发布时间
time_ = time_.strip()
time_ = time_.split()[0]
# print(time_)
author = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[2]/@nick-name")[0] # 发布人
author = author.strip()
# print(author)
title = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[2]/a/text()")[0] # 发布主题
title = title.strip()
# print(title)
if not (title.startswith("#") and title.endswith("#")):
# 一般来说,微博里面的主题都是以#开头结尾的,如果不是,说明有点问题,直接抛弃数据
raise AttributeError
if not title or not author:
# 如果数据缺失,直接抛弃数据
raise AttributeError
table.add_row([index + 1, time_, author, title])
except IndexError:
continue
except AttributeError:
index -= 1 # 这步中断,但是索引还是加一了,所以我们应该使得索引减一
continue
print(table)
try:
i = int(input("请输入序号:"))
if not (0 < i <= index + 1): # 如果输入的数据不符合要求,报错
raise AttributeError
return info[i - 1] # 返回对应的mid和uid
except Exception as e:
print("请按照要求输入哦!")
return None
print(get_id_uid("人民日报安倍晋三")) # 这个搜索尽量具体一点,下面,我们就使用人民日报的评论来测试
commit_data = []
arg = ('4788943477806466', '2803301701')
base_url = "https://weibo.com/ajax/statuses/buildComments"
index = 0
def get_first_commit(arg): # 传入文章id和作者id所组成的元组
global index
params_ = {
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': arg[0], # 微博文章的id,可以在搜索页面中获得
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'count': 10, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': arg[1], # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
# print(params_)
resp = requests.get(url=base_url, params=params_, headers=headers)
data = resp.json()
max_id = data["max_id"]
for i in data["data"]:
text = i["text"]
text = re.sub("<.*?>", "", text)
text = text.strip()
if text:
commit_data.append(text)
print(text)
print("-----------------------------------------------------")
print("max_id", max_id)
print(f"爬取完{index}第页评论,休息4秒钟")
print("------------------------------------------------------")
index += 1
time.sleep(4)
return max_id # 返回max_id
max_id = get_first_commit(arg)
print(type(max_id))
def get_other_commit(arg, max_id):
global index
if max_id == 0:
return "大部分内容获取完成!"
params = {
'flow': 0, # 根据什么获取,0为热度,1为发布时间
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': arg[0], # 微博文章的id
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'max_id': max_id, # 用来控制页数的,这个可以在上一个数据包的响应的max_id
'count': 20, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': arg[1], # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
resp = requests.get(url=base_url, params=params, headers=headers)
data = resp.json()
max_id = data["max_id"]
commit = data["data"]
if commit:
for i in commit:
text = i["text"]
text = re.sub("<.*?>", "", text)
text = text.strip()
if text:
commit_data.append(text)
print(text)
print("-----------------------------------------------------")
print("max_id", max_id)
print(f"爬取完{index}第页评论,休息4秒钟")
print("------------------------------------------------------")
index += 1
time.sleep(4)
return get_other_commit(arg, max_id)
return "大部分内容获取完成!"
print(get_other_commit(arg, max_id))
with open("./commit.txt", "a+", encoding="utf-8") as f:
string = "\n".join(commit_data) # 列表数据的拼接
f.write(string) # 写入文件中,先进行存储,防止出现意外
import jieba
data = open("./commit.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 获取我们刚才获取到的数据
# print(jieba.cut(data)) # 对数据进行分词,得到一个生成器
stop_word = open("./stoplist.txt", encoding='utf8').read().split() # 导入停词表,进行数据的清洗
# print(stop_word)
word_list = [w for w in jieba.cut(data)]
# print(word_list)
from wordcloud import WordCloud
font = "./font.ttf" # 导入字体
wc = WordCloud(font_path=font,
width = 1000,
height = 700,
background_color='white',
max_words=100,
stopwords=stop_word # 加载停用词
)
wc.generate(" ".join(word_list)) # 加载词云文本
img = wc.to_image()
img.show()
import requests, time, re # 发送请求,接收JSON数据,正则解析
from prettytable import PrettyTable # 美化展示
from fake_useragent import UserAgent # 随机请求头
from lxml import etree # 进行xpath解析
from urllib import parse # 将中文转换为url编码
from wordcloud import WordCloud # 导入词云库生成词云
import jieba # 导入jieba库分词
search_url = "https://s.weibo.com/weibo?q=%s" # 搜索要使用的url
base_url = "https://weibo.com/ajax/statuses/buildComments" # 获取评论需要使用的url
# 微博有cookie反爬,如果要使用其搜索功能的话,最好添加cookie
headers = {
'authority': 's.weibo.com',
'method': 'GET',
'scheme': 'https',
'accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9',
'accept-encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'accept-language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8',
'cache-control': 'no-cache',
'cookie': 'SINAGLOBAL=6849256018210.763.1640318151683; UOR=,,tophub.today; SCF=ArxHEBnS4gWA2vpCEdEt3WZ41VwutzJfy5_Y0G5csLa_ffzUixMCM9VGFLlHI_NYhIVN-KhWG3pM1VgAOK8.; login_sid_t=f238365342825b4ed0ec7e03a108002a; cross_origin_proto=SSL; _s_tentry=weibo.com; Apache=9854327619564.12.1657262555880; ULV=1657262555884:5:1:1:9854327619564.12.1657262555880:1654528223100; SUBP=0033WrSXqPxfM725Ws9jqgMF55529P9D9WFcW9qsrf3VzYncb2aZUJFP5JpX5o275NHD95QNeoqfS0zRSoe7Ws4Dqcjdi--fiKnRiK.Ri--4iK.Xi-iWi--fiKL2i-2X; SSOLoginState=1657262576; SUB=_2A25Pw6GgDeRhGeFM7VcW8ibKyDyIHXVsuJRorDV8PUNbmtAKLUTckW9NQNYH6iWdr1JwBEvZdTe84ORoGdWLbvsu; ALF=1688798575',
'pragma': 'no-cache',
'referer': 'https://weibo.com/',
'sec-ch-ua': '" Not A;Brand";v="99", "Chromium";v="102", "Google Chrome";v="102"',
'sec-ch-ua-mobile': '?0',
'sec-ch-ua-platform': '"Windows"',
'sec-fetch-dest': 'document',
'sec-fetch-mode': 'navigate',
'sec-fetch-site': 'same-site',
'sec-fetch-user': '?1',
'upgrade-insecure-requests': '1',
'user-agent': UserAgent().random,
}
commit_data = [] # 存储获取到的数据
index = 0 # 记录爬取评论页数,打印日志
def get_id_uid(name):
"""传入要搜索的内容"""
name = parse.quote(name)
info = [] # 这里面存放uid和mid形成的元组
table = PrettyTable(["序号", "发布人", "发布时间", "发布主题"])
headers.update({
'path': f'/weibo?q={name}',
"user-agent": UserAgent().random
}) # 防止反爬
resp = requests.get(search_url % name, headers=headers) # 发送请求
resp.encoding = resp.apparent_encoding # 设置编码
html = etree.HTML(resp.text) # 提交给xpath解析
divs = html.xpath('//*[@id="pl_feedlist_index"]/div[2]/div') # 获取到存储内容的div
info = [] # 这里面存放uid和mid形成的元组
table = PrettyTable(["序号", "发布时间", "作者", "主题"]) # 进行美化输出
index = 0
for index, div in enumerate(divs):
try:
mid = div.xpath("./@mid")[0] # 获取mid
# print(mid)
u_url = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div/a/@href")[0] # 先获取链接,再解析数据
uid = re.search("weibo.com/(?P<uid>\d+)\?refer", u_url).group("uid") # 解析出uid
# print(uid)
info.append((mid, uid)) # 添加到列表中
time_ = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[1]/a/text()")[0] # 发布时间
time_ = time_.strip()
time_ = time_.split()[0]
# print(time_)
author = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[2]/@nick-name")[0] # 发布人
author = author.strip()
# print(author)
title = div.xpath("./div[@class='card']/div[1]/div[2]/p[2]/a/text()")[0] # 发布主题
title = title.strip()
# print(title)
if not (title.startswith("#") and title.endswith("#")):
# 一般来说,微博里面的主题都是以#开头结尾的,如果不是,说明有点问题,直接抛弃数据
raise AttributeError
if not title or not author:
# 如果数据缺失,直接抛弃数据
raise AttributeError
table.add_row([index + 1, time_, author, title])
except IndexError:
continue
except AttributeError:
index -= 1
continue
print(table)
try:
i = int(input("请输入序号:"))
if not (0 < i <= index + 1): # 如果输入的数据不符合要求,报错
raise AttributeError
return info[i - 1] # 返回对应的mid和uid
except Exception as e:
print("请按照要求输入哦!")
return None
def get_first_commit(arg): # 传入文章id和作者id所组成的元组
global index
params_ = {
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': arg[0], # 微博文章的id,可以在搜索页面中获得
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'count': 10, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': arg[1], # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
# print(params_)
resp = requests.get(url=base_url, params=params_, headers=headers)
data = resp.json()
max_id = data["max_id"]
for i in data["data"]:
text = i["text"]
text = re.sub("<.*?>", "", text)
text = text.strip()
if text:
commit_data.append(text)
print(text)
print("-----------------------------------------------------")
print("max_id", max_id)
print(f"爬取完{index}第页评论,休息4秒钟")
print("------------------------------------------------------")
index += 1
time.sleep(4)
return max_id # 返回max_id
def get_other_commit(arg, max_id):
global index
if max_id == 0:
return "大部分内容获取完成!"
params = {
'flow': 0, # 根据什么获取,0为热度,1为发布时间
'is_reload': 1, # 是否重新加载数据到页面
'id': arg[0], # 微博文章的id
'is_show_bulletin': 2,
'is_mix': 0,
'max_id': max_id, # 用来控制页数的,这个可以在上一个数据包的响应的max_id
'count': 20, # 推测是获取每页评论条数
'uid': arg[1], # 发布这篇微博的用户id
}
resp = requests.get(url=base_url, params=params, headers=headers)
data = resp.json()
max_id = data["max_id"]
commit = data["data"]
if commit:
for i in commit:
text = i["text"]
text = re.sub("<.*?>", "", text)
text = text.strip()
if text:
commit_data.append(text)
print(text)
print("-----------------------------------------------------")
print("max_id", max_id)
print(f"爬取完{index}第页评论,休息4秒钟")
print("------------------------------------------------------")
index += 1
time.sleep(4)
return get_other_commit(arg, max_id)
return "大部分内容获取完成!"
def get_img():
data = open("./commit.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 获取我们刚才获取到的数据
# print(jieba.cut(data)) # 对数据进行分词,得到一个生成器
stop_word = set(open("./stoplist.txt", encoding='utf-8').read().split()) # 导入停词表,进行数据的清洗,这个可以直接在百度上搜索下载
# print(stop_word)
word_list = [w for w in jieba.cut(data)]
# print(word_list)
font = "./font.ttf" # 导入字体
wc = WordCloud(font_path=font,
width=1000,
height=700,
background_color='white',
max_words=100,
stopwords=stop_word, # 加载停用词
).generate(" ".join(word_list)) # 加载词云文本
wc.to_file("./ret.png")
def main():
name = input("请输入内容:")
arg = get_id_uid(name)
if arg:
print(get_other_commit(arg, get_first_commit(arg)))
with open("./commit.txt", "a+", encoding="utf-8") as f:
string = "\n".join(commit_data)
f.write(string)
choice = input("是否生成词云:[yes/no]")
if choice == "yes":
get_img()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# get_img()
所有源代码及其文件,都在这里:https://github.com/liuzhongkun1/spider_/tree/master/%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/%E5%BE%AE%E5%8D%9A%E8%AF%84%E8%AE%BA
