文章目录 Map集合的实现类 HashMap(存储结构:哈希表) HashMap部分源码分析 HashMap源码分析----总结 HashSet与HashMap的关系 Map集合的实现类 HashMa
文章目录
- Map集合的实现类
- HashMap(存储结构:哈希表)
- HashMap部分源码分析
- HashMap源码分析----总结
- HashSet与HashMap的关系
Map集合的实现类
- JDK1.2版本,线程不安全,运行效率快;允许用null作为key或是value。
- JDK1.0版本,线程安全,运行效率慢;不允许nul 1作为key或是value。
- Hashtable的子类,要求key和value都是String。通常用于配置文件的读取。
- 实现了SortedMap接口(是Map的子接口),可以对key自动排序
HashMap(存储结构:哈希表)
代码:
package com.wlw.collection.map;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* HashMap的使用
* 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树(jdk1.8之后))
* key不可重复,values可以重复
*/
public class HashMap_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建集合
HashMap<Student, String> hashMap = new HashMap<Student, String>();
//刚创建hashmap之后,没有添加元素,table = null ,size = 0
Student s1 = new Student("唐三藏",110);
Student s2 = new Student("孙悟空",111);
Student s3 = new Student("猪八戒",112);
Student s4 = new Student("沙和尚",113);
//1.添加
hashMap.put(s1,"东土大唐");
hashMap.put(s2,"花果山");
hashMap.put(s3,"高老庄");
hashMap.put(s4,"流沙河");
//hashMap.put(s4,"天庭"); //覆盖上一个键为s4的value
hashMap.put(new Student("沙和尚",113),"流沙河");
/*
这一句的执行,也会在被放进hashmap集合,这是因为,虽然这个Student对象的内容和s4一样,
但是他们都是new出来的,在堆中都有空间,所以对于HashMap来说他们就是不同的。
为了避免这种情况,我们可以在Student类中重写hashcode()与equals()方法,来判断两个对象是否相等,
重写之后,这个新new出来的就不会被放进hashMap集合中。
*/
System.out.println("元素个数:"+hashMap.size());
System.out.println(hashMap.toString());
//2.删除
/*
hashMap.remove(s1);
System.out.println("删除之后,元素个数:"+hashMap.size());
System.out.println(hashMap.toString());
*/
//3.遍历
//3.1使用 keySet() 返回一个只包含键的set集合
System.out.println("-------------3.1使用 keySet()----------------");
for(Student key : hashMap.keySet()){
System.out.println(key.toString() + "--------->" + hashMap.get(key));
}
//3.2使用 entrySet() 返回一个包含entry的set集合(这个方法遍历效率更高)
System.out.println("-------------3.2使用 entrySet()----------------");
for (Map.Entry<Student,String> entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"--------->"+entry.getValue());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(hashMap.isEmpty());//false
System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue("天庭"));//false
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey(s3)); //true
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey(new Student("孙悟空",111)));//true,因为我们在Student类中重写了hashcode()与equals()方法
}
}
/*
元素个数:4
{Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=111}=花果山, Student{name='唐三藏', stuNo=110}=东土大唐, Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=112}=高老庄, Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=113}=流沙河}
-------------3.1使用 keySet()----------------
Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=111}--------->花果山
Student{name='唐三藏', stuNo=110}--------->东土大唐
Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=112}--------->高老庄
Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=113}--------->流沙河
-------------3.2使用 entrySet()----------------
Student{name='孙悟空', stuNo=111}--------->花果山
Student{name='唐三藏', stuNo=110}--------->东土大唐
Student{name='猪八戒', stuNo=112}--------->高老庄
Student{name='沙和尚', stuNo=113}--------->流沙河
false
false
true
true
*/package com.wlw.collection.map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int stuNo;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int stuNo) {
this.name = name;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(int stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", stuNo=" + stuNo +
'}';
}
//重写equals
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return stuNo == student.stuNo &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
//重写hashcode
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, stuNo);
}
}
HashMap部分源码分析
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 初始容量大小 16static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //hashmap数组最大容量2^30
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;//加载因子,元素个数大于75% 则扩容
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //jdk 1.8 当链表长度>8,并且数组长度>64时,将该链表转换成红黑树
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;//jdk 1.8 当链表的元素个数小于6,则变成链表
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;//jdk 1.8 数组长度
transient Node<K,V>[] table; //哈希表中的数组
size;//元素个数
//无参构造
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // 加载因子
}
//刚创建hashmap之后,没有添加元素,table = null ,size = 0
//put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) { // 比较key
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length; // n = 16,添加第一个元素时,数组长度变为16
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//添加
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) //如果元素个数大于了数组长度的0.75,就扩容
resize(); //扩容大小*2
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
HashMap源码分析----总结
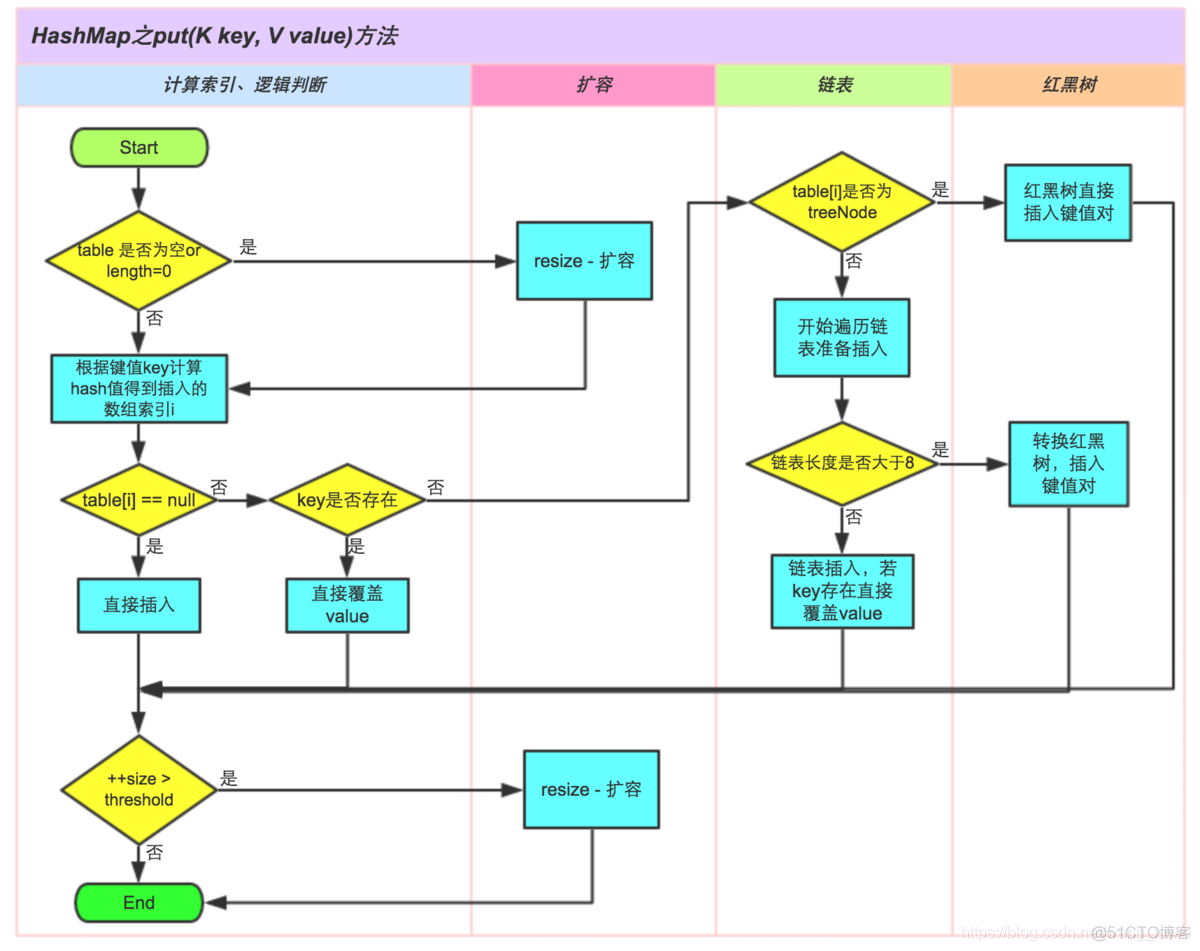

HashSet与HashMap的关系
HashSet的部分源码:(分析可知,HashSet 里用的就是 HashMap,他们两是同一结构哈希表)
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;//无参构造
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
//add()方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
