欢迎访问我的GitHub 这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 在上一章《Spring Cloud源码分析之Eureka篇第四章:服务注册是如何发起的 》,我们知道了
欢迎访问我的GitHub
这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
概览
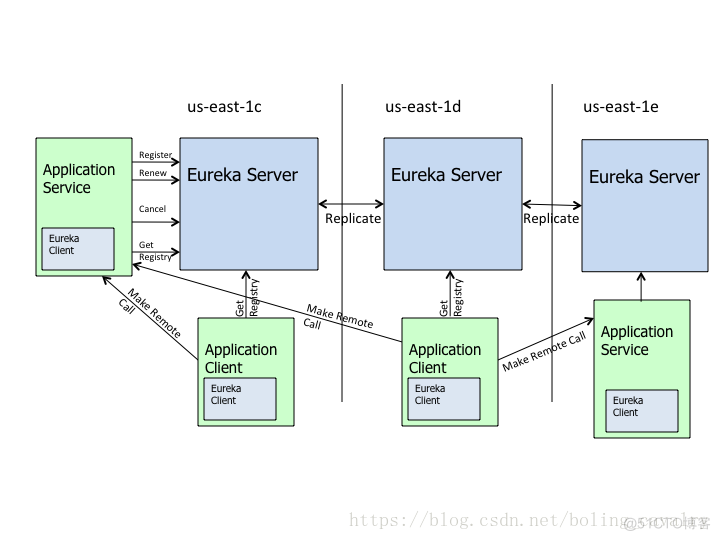
- 以下图片来自Netflix官方,图中显示Eureka Client会向注册中心发起Get Registry请求来获取服务列表,接下来就去看下对应的代码实现;
结论提前知晓
- 看源码易犯困,又难保持注意力集中,因此先抛结论吧,这样不看源码也有收获:
Eureka client从注册中心更新服务列表,然后自身会做缓存;
作为服务消费者,就是从这些缓存信息中获取的服务提供者的信息;
增量更新的服务以30秒为周期循环调用;
增量更新数据在服务端保存时间为3分钟,因此Eureka client取得的数据虽然被称为"增量更新",仍然可能和30秒前取的数据一样,所以Eureka client要自己来处理重复信息;
由3、4两点可以推断出,Eureka client的增量更新,其实获取的是Eureka server最近三分钟内的变更,因此,如果Eureka client有超过三分钟没有做增量更新的话(例如网络问题),那么再调用增量更新接口时,那三分钟内Eureka server的变更就可能获取不到了,这就造成了Eureka server和Eureka client之间的数据不一致,需要有个方案来及时发现这个问题;
正常情况下,Eureka client多次增量更新后,最终的服务列表数据应该Eureka server保持一致,但如果期间发生异常,可能导致和Eureka server的数据不一致,为了暴露这个问题,Eureka server每次返回的增量更新数据中,会带有一致性哈希码,Eureka client用本地服务列表数据算出的一致性哈希码应该和Eureka server返回的一致,若不一致就证明增量更新出了问题导致Eureka client和Eureka server上的服务列表信息不一致了,此时需要全量更新;
Eureka server上的服务列表信息对外提供JSON/XML两种格式下载;
Eureka client使用jersey的SDK,去下载JSON格式的服务列表信息;
关于源码版本
- 本次分析的Spring Cloud版本为Edgware.RELEASE,对应的eureka-client版本为1.7.0;
如何做到周期性执行
- 更新服务列表和服务续约都是周期性循环执行的,这是如何实现的呢,来看initScheduledTasks方法的源码:
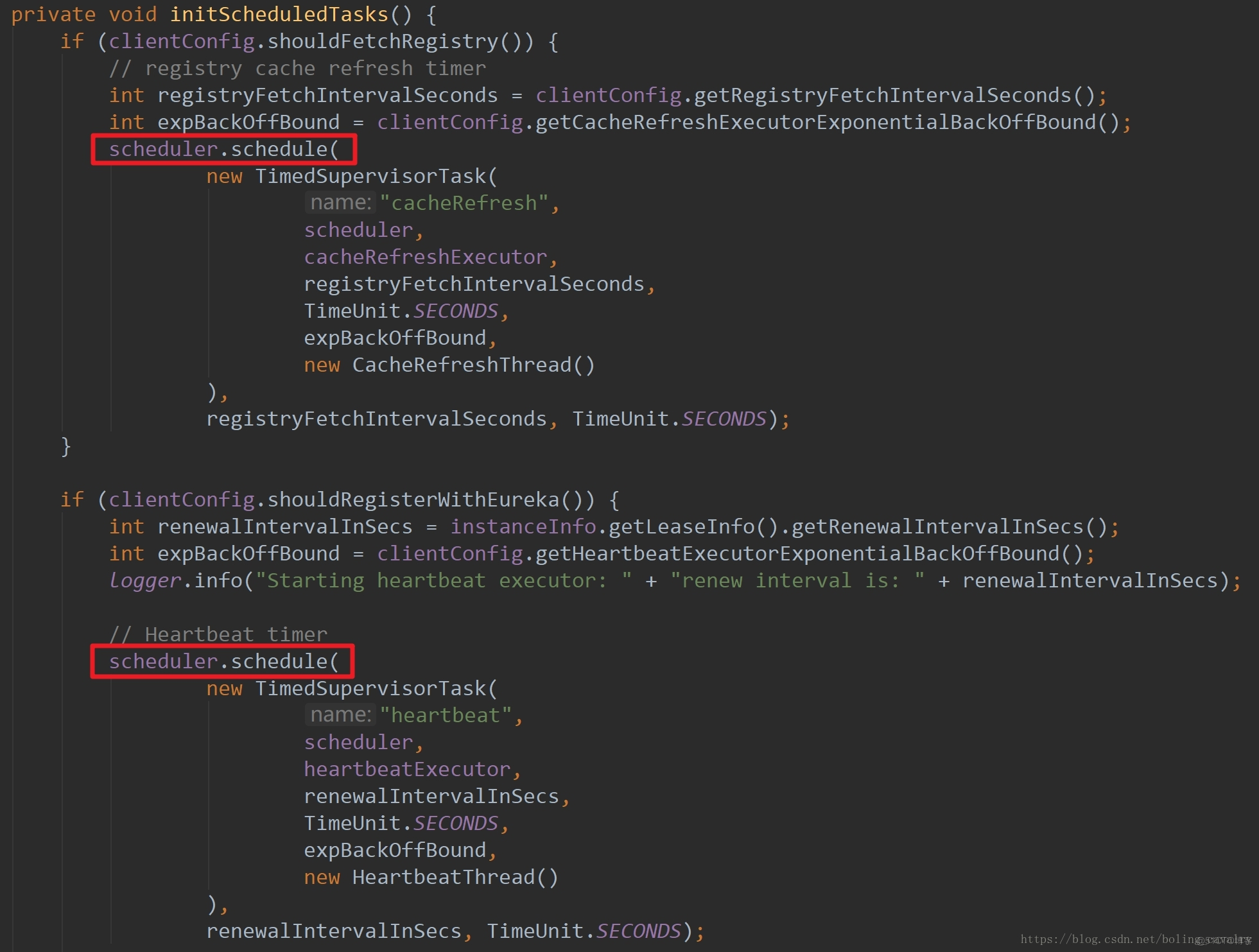
- 如上图两个红框中所示,scheduler.schedule方法其实启动的是一个延时执行的一次性任务,不过TimedSupervisorTask内有乾坤,会在每次执行完任务后再启动一个同样的任务,这样就能实现周期性执行任务了,并且TimedSupervisorTask的功能还不止如此,它还负责任务超时、动态调节周期性间隔、线程池满、未知异常等各种情况的处理,推荐您参考《Eureka的TimedSupervisorTask类(自动调节间隔的周期性任务)》了解更多细节;
来自官方文档的指导信息
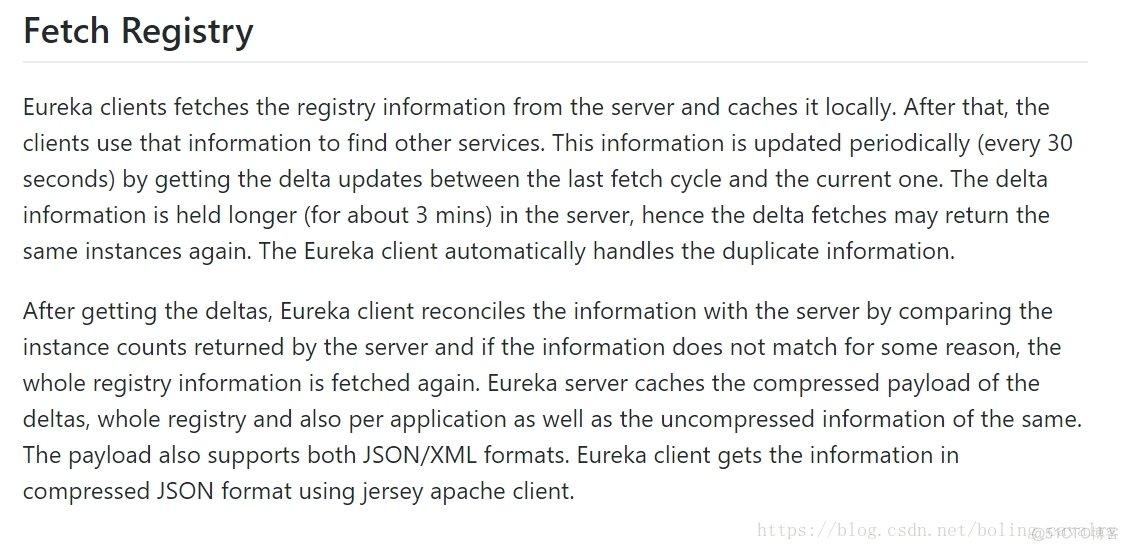
- 对上文,我的理解:
- Eureka client从注册中心更新服务列表,然后自身会做缓存;
- 作为服务消费者,就是从这些缓存信息中获取的服务提供者的信息;
- 增量更新的服务以30秒为周期循环调用;
- 增量更新数据在服务端保存时间为3分钟,因此Eureka client取得的数据虽然被称为"增量更新",仍然可能和30秒前取的数据一样,所以Eureka client要自己来处理重复信息;
- 由3、4两点可以推断出,Eureka client的增量更新,其实获取的是Eureka server最近三分钟内的变更,因此,如果Eureka client有超过三分钟没有做增量更新的话(例如网络问题),那么再调用增量更新接口时,那三分钟内Eureka server的变更就可能获取不到了,这就造成了Eureka server和Eureka client之间的数据不一致,需要有个方案来及时发现这个问题;
- 正常情况下,Eureka client多次增量更新后,最终的服务列表数据应该Eureka server保持一致,但如果期间发生异常,可能导致和Eureka server的数据不一致,为了暴露这个问题,Eureka server每次返回的增量更新数据中,会带有一致性哈希码,Eureka client用本地服务列表数据算出的一致性哈希码应该和Eureka server返回的一致,若不一致就证明增量更新出了问题导致Eureka client和Eureka server上的服务列表信息不一致了,此时需要全量更新;
- Eureka server上的服务列表信息对外提供JSON/XML两种格式下载;
- Eureka client使用jersey的SDK,去下载JSON格式的服务列表信息;准备工作就到此,接下来学习源码,整个过程应围绕上述点八进行,不要过早陷入某些代码细节中;
源码分析
- 如下图红框所示,更新服务列表的逻辑已经封装在CacheRefreshThread类中:
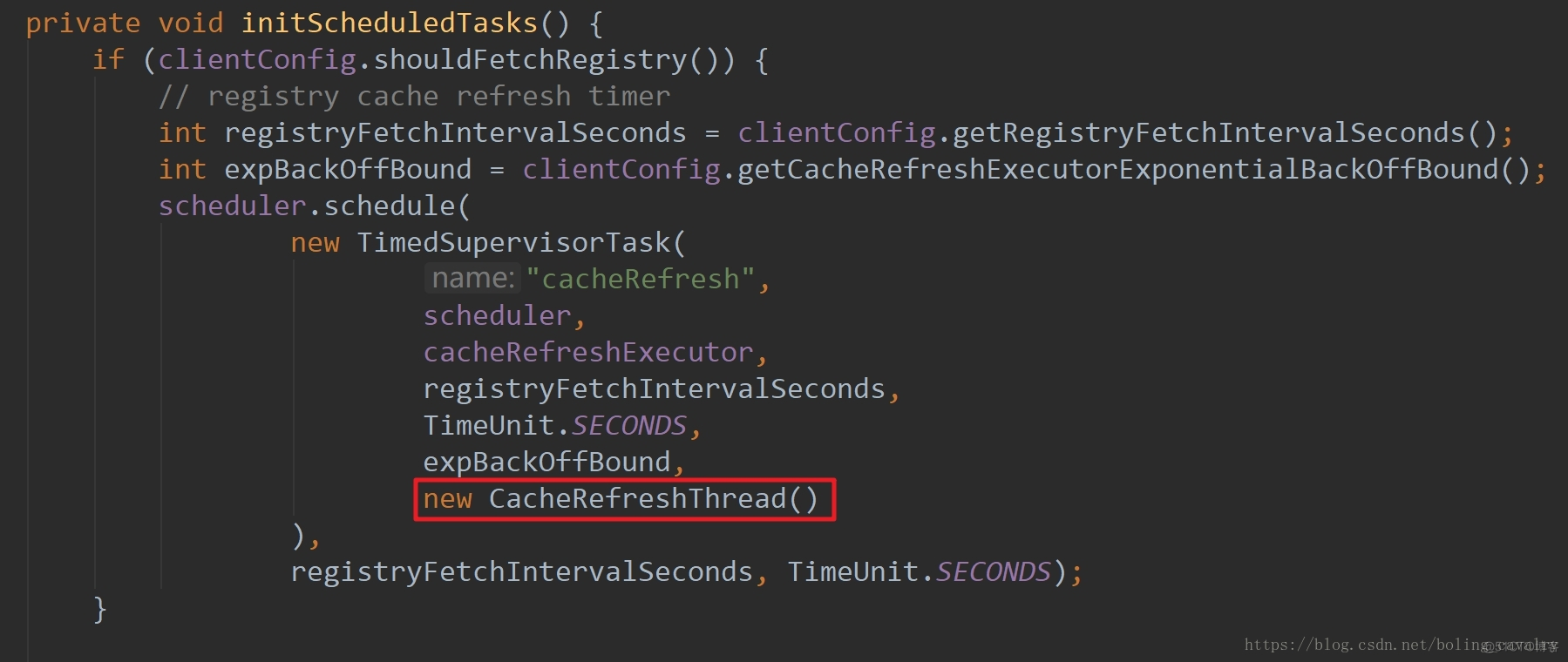
- CacheRefreshThread类中又是调用refreshRegistry方法来实现服务列表更新的,refreshRegistry方法如下:
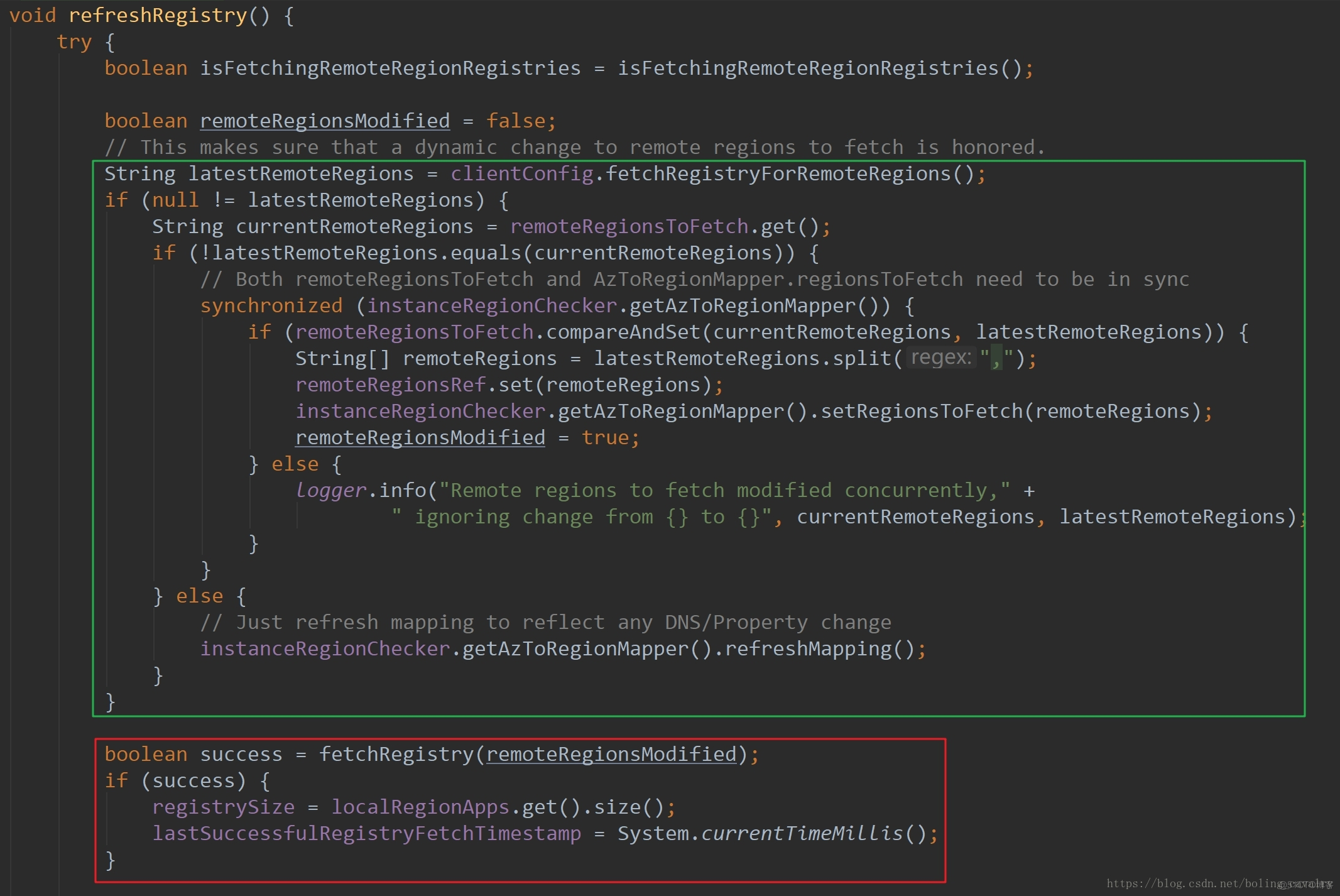
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
//用Stopwatch做耗时分析
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
// 取出本地缓存的,之气获取的服务列表信息
Applications applications = getApplications();
//判断多个条件,确定是否触发全量更新,如下任一个满足都会全量更新:
//1. 是否禁用增量更新;
//2. 是否对某个region特别关注;
//3. 外部调用时是否通过入参指定全量更新;
//4. 本地还未缓存有效的服务列表信息;
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta
{
//这些详细的日志可以看出触发全量更新的原因
logger.info("Disable delta property : {}", clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta());
logger.info("Single vip registry refresh property : {}", clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress());
logger.info("Force full registry fetch : {}", forceFullRegistryFetch);
logger.info("Application is null : {}", (applications == null));
logger.info("Registered Applications size is zero : {}",
(applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0));
logger.info("Application version is -1: {}", (applications.getVersion() == -1));
//全量更新
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
//增量更新
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
//重新计算和设置一致性hash码
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
//日志打印所有应用的所有实例数之和
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + appPathIdentifier + " - was unable to refresh its cache! status = " + e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
//将本地缓存更新的事件广播给所有已注册的监听器,注意该方法已被CloudEurekaClient类重写
onCacheRefreshed();
//检查刚刚更新的缓存中,有来自Eureka server的服务列表,其中包含了当前应用的状态,
//当前实例的成员变量lastRemoteInstanceStatus,记录的是最后一次更新的当前应用状态,
//上述两种状态在updateInstanceRemoteStatus方法中作比较 ,如果不一致,就更新lastRemoteInstanceStatus,并且广播对应的事件
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
return true;
}
- 上述代码中已有注释详细说明,就不另外赘述了,接下来细看getAndStoreFullRegistry和getAndUpdateDelta这两个方法,了解全量增量更新的细节;
全量更新本地缓存的服务列表
- getAndStoreFullRegistry方法负责全量更新,代码如下所示,非常简单的逻辑:
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
logger.info("Getting all instance registry info from the eureka server");
Applications apps = null;
//由于并没有配置特别关注的region信息,因此会调用eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications方法从服务端获取服务列表
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
//返回对象就是服务列表
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (apps == null) {
logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");
}
//考虑到多线程同步,只有CAS成功的线程,才会把自己从Eureka server获取的数据来替换本地缓存
else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
//localRegionApps就是本地缓存,是个AtomicReference实例
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));
logger.debug("Got full registry with apps hashcode {}", apps.getAppsHashCode());
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating applications as another thread is updating it already");
}
}
- getAndStoreFullRegistry方法中并无复杂逻辑,只有eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())这段需要展开细看,和Eureka server交互的逻辑都在这里面,方法getApplications的具体实现是在EurekaHttpClientDecorator类:
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(final String... regions) {
return execute(new RequestExecutor<Applications>() {
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) {
return delegate.getApplications(regions);
}
@Override
public RequestType getRequestType() {
//本次向Eureka server请求的类型:获取服务列表
return RequestType.GetApplications;
}
});
}
- EurekaHttpClientDecorator类从名字看是个装饰者模式的实现,看它的其他代码,发现各类远程服务都在此被封装成API了,例如注册的:
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> register(final InstanceInfo info) {
return execute(new RequestExecutor<Void>() {
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) {
return delegate.register(info);
}
@Override
public RequestType getRequestType() {
return RequestType.Register;
}
});
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> sendHeartBeat(final String appName,
final String id,
final InstanceInfo info,
final InstanceStatus overriddenStatus) {
return execute(new RequestExecutor<InstanceInfo>() {
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) {
return delegate.sendHeartBeat(appName, id, info, overriddenStatus);
}
@Override
public RequestType getRequestType() {
return RequestType.SendHeartBeat;
}
});
}
- 再继续追踪 delegate.register(info),进入了AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类,这里面是各种网络请求的具体实现,EurekaHttpClientDecorator类中的getApplications、register、sendHeartBeat等方法对应的网络请求响应逻辑在AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient中都有具体实现,篇幅所限我们只关注getApplications:
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(String... regions) {
//取全量数据的path是""apps"
return getApplicationsInternal("apps/", regions);
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getDelta(String... regions) {
//取增量数据的path是""apps/delta"
return getApplicationsInternal("apps/delta", regions);
}
//具体的请求响应处理都在此方法中
private EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplicationsInternal(String urlPath, String[] regions) {
ClientResponse response = null;
String regionsParamValue = null;
try {
//jersey、resource这些关键词都预示着这是个restful请求
WebResource webResource = jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath);
if (regions != null && regions.length > 0) {
regionsParamValue = StringUtil.join(regions);
webResource = webResource.queryParam("regions", regionsParamValue);
}
Builder requestBuilder = webResource.getRequestBuilder();
addExtraHeaders(requestBuilder);
//发起网络请求,将响应封装成ClientResponse实例
response = requestBuilder.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE).get(ClientResponse.class);
Applications applications = null;
if (response.getStatus() == Status.OK.getStatusCode() && response.hasEntity()) {
//取得全部应用信息
applications = response.getEntity(Applications.class);
}
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus(), Applications.class)
.headers(headersOf(response))
.entity(applications)
.build();
} finally {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Jersey HTTP GET {}/{}?{}; statusCode={}",
serviceUrl, urlPath,
regionsParamValue == null ? "" : "regions=" + regionsParamValue,
response == null ? "N/A" : response.getStatus()
);
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
}
}
获取服务列表信息的增量更新
- 获取服务列表信息的增量更新是通过getAndUpdateDelta方法完成的,具体分析请看下面的中文注释:
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
Applications delta = null;
//增量信息是通过eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta方法完成的
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
//delta中保存了Eureka server返回的增量更新
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
if (delta == null) {
logger.warn("The server does not allow the delta revision to be applied because it is not safe. "
+ "Hence got the full registry.");
//如果增量信息为空,就直接发起一次全量更新
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
}
//考虑到多线程同步问题,这里通过CAS来确保请求发起到现在是线程安全的,
//如果这期间fetchRegistryGeneration变了,就表示其他线程也做了类似操作,因此放弃本次响应的数据
else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());
String reconcileHashCode = "";
if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
//用Eureka返回的增量数据和本地数据做合并操作,这个方法稍后会细说
updateDelta(delta);
//用合并了增量数据之后的本地数据来生成一致性哈希码
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
logger.warn("Cannot acquire update lock, aborting getAndUpdateDelta");
}
//Eureka server在返回增量更新数据时,也会返回服务端的一致性哈希码,
//理论上每次本地缓存数据经历了多次增量更新后,计算出的一致性哈希码应该是和服务端一致的,
//如果发现不一致,就证明本地缓存的服务列表信息和Eureka server不一致了,需要做一次全量更新
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
//一致性哈希码不同,就在reconcileAndLogDifference方法中做全量更新
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating application delta as another thread is updating it already");
logger.debug("Ignoring delta update with apps hashcode {}, as another thread is updating it already", delta.getAppsHashCode());
}
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getDelta(final String... regions) {
return execute(new RequestExecutor<Applications>() {
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) {
return delegate.getDelta(regions);
}
@Override
public RequestType getRequestType() {
return RequestType.GetDelta;
}
});
}
- 再看AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类中的getDelta方法,居然和全量获取服务列表数据调用了相同的方法getApplicationsInternal,只是ur参数不一样而已;
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getDelta(String... regions) {
return getApplicationsInternal("apps/delta", regions);
}
private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {
int deltaCount = 0;
//遍历所有服务
for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
//遍历当前服务的所有实例
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
//取出缓存的所有服务列表,用于合并
Applications applications = getApplications();
String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance);
//判断正在处理的实例和当前应用是否在同一个region
if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) {
//如果不是同一个region,接下来合并的数据就换成专门为其他region准备的缓存
Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion);
if (null == remoteApps) {
remoteApps = new Applications();
remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps);
}
applications = remoteApps;
}
++deltaCount;
if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { //对新增的实例的处理
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion);
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
} else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { //对修改实例的处理
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
} else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) { //对删除实例的处理
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).removeInstance(instance);
}
}
}
logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount);
getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());
//整理数据,使得后续使用过程中,这些应用的实例总是以相同顺序返回
getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
//和当前应用不在同一个region的应用,其实例数据也要整理
for (Applications applications : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {
applications.setVersion(delta.getVersion());
applications.shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
}
}
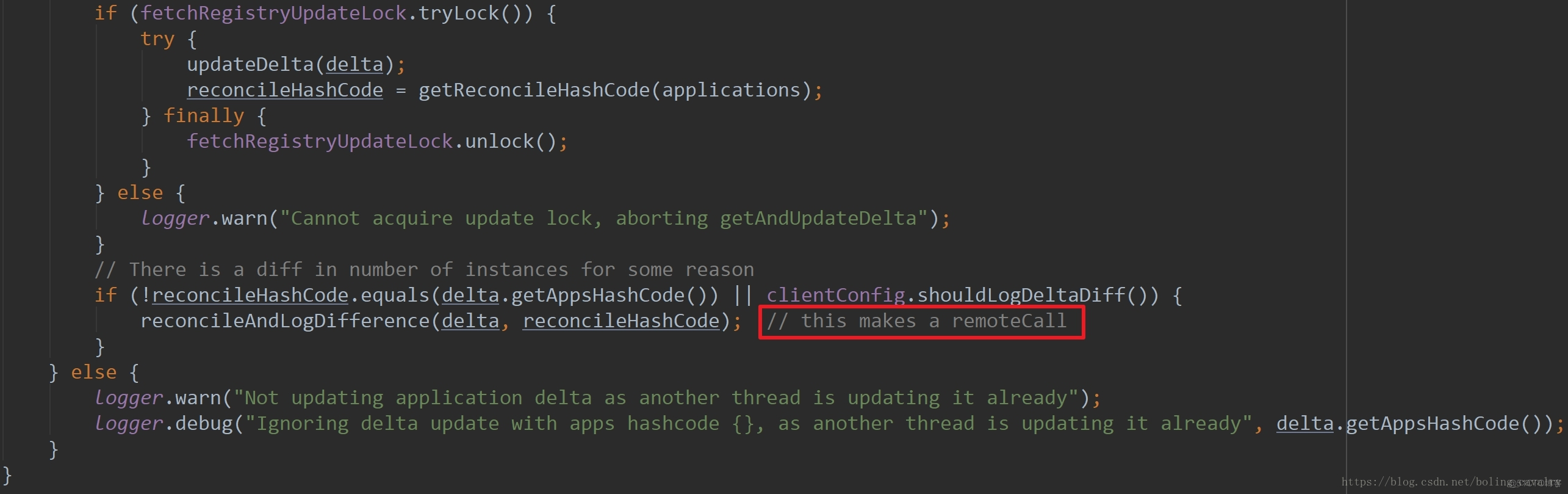
- 上图红框中提醒:此处会发生一次远程调用,这说明发现Eureka server和Eureka client保存的服务列表数据不一致时会向Eureka server发起一次请求,打开reconcileAndLogDifference方法看详情:
private void reconcileAndLogDifference(Applications delta, String reconcileHashCode) throws Throwable {
logger.debug("The Reconcile hashcodes do not match, client : {}, server : {}. Getting the full registry",
reconcileHashCode, delta.getAppsHashCode());
RECONCILE_HASH_CODES_MISMATCH.increment();
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
//从Eureka server获取全量数据
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
Applications serverApps = httpResponse.getEntity();
if (serverApps == null) {
logger.warn("Cannot fetch full registry from the server; reconciliation failure");
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
try {
Map<String, List<String>> reconcileDiffMap = getApplications().getReconcileMapDiff(serverApps);
StringBuilder reconcileBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> mapEntry : reconcileDiffMap.entrySet()) {
reconcileBuilder.append(mapEntry.getKey()).append(": ");
for (String displayString : mapEntry.getValue()) {
reconcileBuilder.append(displayString);
}
reconcileBuilder.append('\n');
}
String reconcileString = reconcileBuilder.toString();
logger.debug("The reconcile string is {}", reconcileString);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Could not calculate reconcile string ", e);
}
}
//CAS成功就把全量数据更新到本地缓存中
if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(serverApps));
getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());
logger.debug(
"The Reconcile hashcodes after complete sync up, client : {}, server : {}.",
getApplications().getReconcileHashCode(),
delta.getAppsHashCode());
} else {
logger.warn("Not setting the applications map as another thread has advanced the update generation");
}
}
广播:更新缓存
- 更新缓存的广播是在onCacheRefreshed方法中执行的,该方法在扩展类CloudEurekaClient中被覆盖:
@Override
protected void onCacheRefreshed() {
if (this.cacheRefreshedCount != null) {
long newCount = this.cacheRefreshedCount.incrementAndGet();
log.trace("onCacheRefreshed called with count: " + newCount);
//spring容器内的广播
this.publisher.publishEvent(new HeartbeatEvent(this, newCount));
}
}
- 上述代码显示,这是个spring容器内的广播,this.publisher的类型是ApplicationEventPublisher,如果您对spring的广播机制有兴趣,可以参考文章《spring4.1.8扩展实战之三:广播与监听》;
广播:本地状态变化
- 从Eureka server中取得的服务列表,自然也包括当前应用自己的信息,这个信息会保存在成员变量lastRemoteInstanceStatus中,每次更新了缓存后,都会用缓存中的信息和lastRemoteInstanceStatus对比,如果不一致,就表示在Eureka server端记录的当前应用状态发生了变化,此时就广播一次;
private synchronized void updateInstanceRemoteStatus() {
// Determine this instance's status for this app and set to UNKNOWN if not found
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus currentRemoteInstanceStatus = null;
if (instanceInfo.getAppName() != null) {
Application app = getApplication(instanceInfo.getAppName());
if (app != null) {
InstanceInfo remoteInstanceInfo = app.getByInstanceId(instanceInfo.getId());
if (remoteInstanceInfo != null) {
currentRemoteInstanceStatus = remoteInstanceInfo.getStatus();
}
}
}
if (currentRemoteInstanceStatus == null) {
currentRemoteInstanceStatus = InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN;
}
// Notify if status changed
if (lastRemoteInstanceStatus != currentRemoteInstanceStatus) {
//这里发起广播
onRemoteStatusChanged(lastRemoteInstanceStatus, currentRemoteInstanceStatus);
lastRemoteInstanceStatus = currentRemoteInstanceStatus;
}
}
小结
- 至此,更新服务列表的源码学习就完成了,除了原理的学习,还另有两大收获:
- 第一,官方文档对整个过程做了准确的总结,围绕着这些总结去看代码,能够事半功倍,重要是整个过程都保持的正确的方向,不会由于细节的干扰而偏离主线;
- 第二,Eureka的注册中心设计,尽管多个client轮询请求会增加服务器压力,但使用增量更新再加上Server自身缓存3分钟数据的方式,可以有效的减少数据量和相关的计算,再加上一致性哈希码来弥补增量更新的弊端,在性能和完整性方面都有了保证,另外增量更新不需要client的时间戳,这样既节省性能又简化了实现逻辑,这种设计方式值得我们学习;
欢迎关注51CTO博客:程序员欣宸
学习路上,你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴...






