从完成一个简单的『手写数字识别任务』开始,快速了解飞桨框架 API 的使用方法。
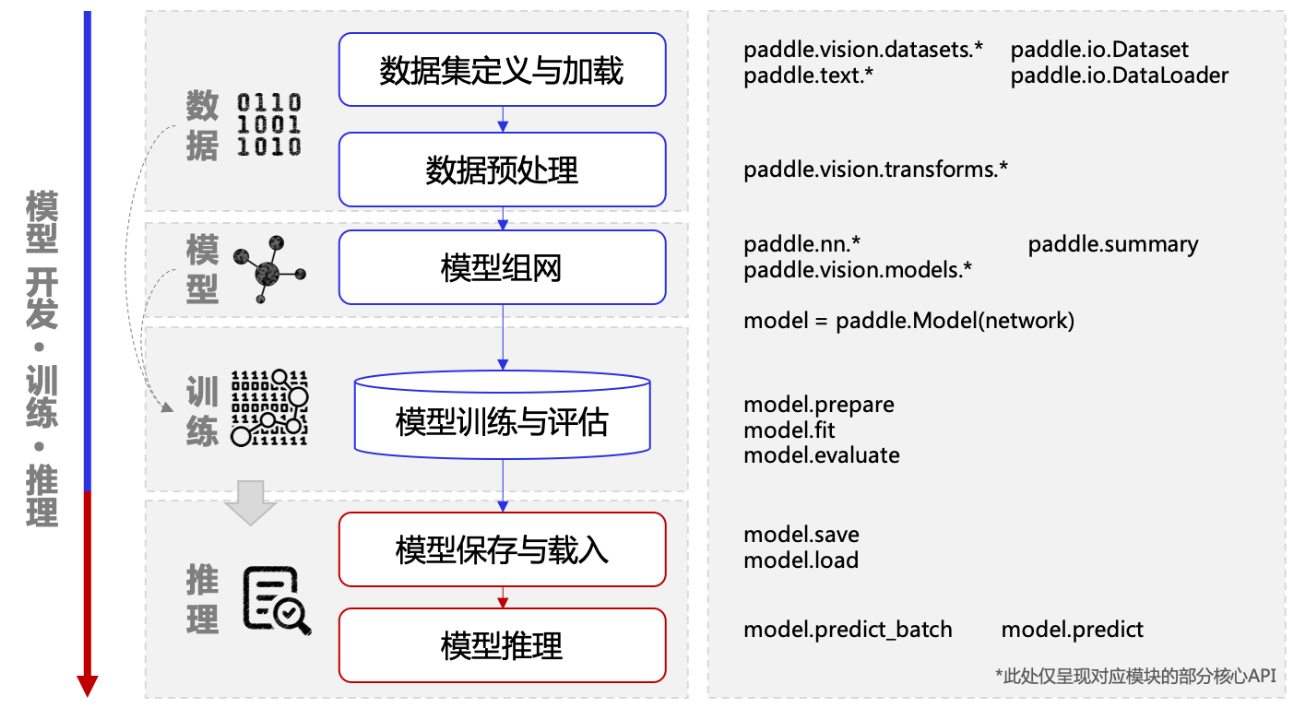
模型开发
『手写数字识别』是深度学习里的 Hello World 任务,用于对 0 ~ 9 的十类数字进行分类,即输入手写数字的图片,可识别出这个图片中的数字。
本任务用到的数据集为 MNIST 手写数字数据集,用于训练和测试模型。该数据集包含 60000 张训练图片、 10000 张测试图片、以及对应的分类标签文件,每张图片上是一个 0 ~ 9 的手写数字,分辨率为 28 * 28。
直接去飞桨AI Studio首页创建项目——添加数据集
导入要用到的包
import paddle import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import cv2 import paddle.vision.transforms as T加载数据集
飞桨在 paddle.vision.datasets 下内置了计算机视觉(Computer Vision,CV)领域常见的数据集,如 MNIST、Cifar10、Cifar100、FashionMNIST 和 VOC2012 等。在本任务中,先后加载了 MNIST 训练集(mode='train')和测试集(mode='test'),训练集用于训练模型,测试集用于评估模型效果。
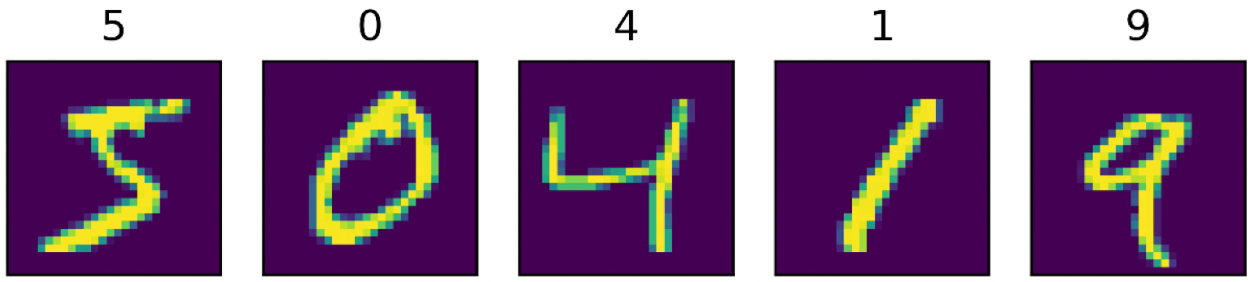
transform = T.Normalize(mean=[127.5], std=[127.5]) train_dataset = paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='train', transform=transform) eval_dataset = paddle.vision.datasets.MNIST(mode='test',transform=transform) # 打印数据集里图片数量 print('训练集样本量:{}, 验证集样本量{}'.format(len(train_dataset),len(eval_dataset))) #显示样本 cv2.imwrite("C:/1.PNG", train_dataset[0][0]) plt.figure() plt.imshow(train_dataset[0][0].reshape([28,28]),cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.show()模型组网
飞桨的模型组网有多种方式,既可以直接使用飞桨内置的模型,也可以自定义组网。『手写数字识别任务』比较简单,普通的神经网络就能达到很高的精度。
可以使用飞桨内置的 LeNet 作为模型。飞桨在 paddle.vision.models 下内置了 CV 领域的一些经典模型,LeNet 就是其中之一,调用很方便,只需一行代码即可完成 LeNet 的网络构建和初始化。num_classes 字段中定义分类的类别数,因为需要对 0 ~ 9 的十类数字进行分类,所以设置为 10。
# 模型组网并初始化网络 lenet = paddle.vision.models.LeNet(num_classes=10) # 可视化模型组网结构和参数 paddle.summary(lenet,(1, 1, 28, 28))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param # =========================================================================== Conv2D-1 [[1, 1, 28, 28]] [1, 6, 28, 28] 60 ReLU-1 [[1, 6, 28, 28]] [1, 6, 28, 28] 0 MaxPool2D-1 [[1, 6, 28, 28]] [1, 6, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-2 [[1, 6, 14, 14]] [1, 16, 10, 10] 2,416 ReLU-2 [[1, 16, 10, 10]] [1, 16, 10, 10] 0 MaxPool2D-2 [[1, 16, 10, 10]] [1, 16, 5, 5] 0 Linear-1 [[1, 400]] [1, 120] 48,120 Linear-2 [[1, 120]] [1, 84] 10,164 Linear-3 [[1, 84]] [1, 10] 850 =========================================================================== Total params: 61,610 Trainable params: 61,610 Non-trainable params: 0 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Input size (MB): 0.00 Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.11 Params size (MB): 0.24 Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.35 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- {'total_params': 61610, 'trainable_params': 61610}
也可以自己随便搭建一个:
network = paddle.nn.Sequential(
paddle.nn.Conv2D(1,10,5),
paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(3,2),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(10,20,5),
paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(3,2),
paddle.nn.Flatten(),
paddle.nn.Linear(180,64),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Linear(64,10)
)
model = paddle.Model(network)
model.summary((1,1,28,28)) # 可以搭建一层就看看网络结构
模型训练
模型训练
模型训练需完成如下步骤:
-
使用 paddle.Model 封装模型。 将网络结构组合成可快速使用 飞桨高层 API 进行训练、评估、推理的实例,方便后续操作。
-
使用 paddle.Model.prepare 完成训练的配置准备工作。 包括损失函数、优化器和评价指标等。飞桨在 paddle.optimizer 下提供了优化器算法相关 API,在 paddle.nn Loss层 提供了损失函数相关 API,在 paddle.metric 下提供了评价指标相关 API。
-
使用 paddle.Model.fit 配置循环参数并启动训练。 配置参数包括指定训练的数据源
train_dataset、训练的批大小batch_size、训练轮数epochs等,执行后将自动完成模型的训练循环。
因为是分类任务,这里损失函数使用常见的 CrossEntropyLoss (交叉熵损失函数),优化器使用 Adam,评价指标使用 Accuracy 来计算模型在训练集上的精度。
# 封装模型,便于进行后续的训练、评估和推理 model = paddle.Model(lenet) # 模型训练的配置准备,准备损失函数,优化器和评价指标 model.prepare(paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=model.parameters()), paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), paddle.metric.Accuracy()) # 开始训练 model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=5, batch_size=64, verbose=1)模型评估、验证
模型训练完成之后,调用 paddle.Model.evaluate ,使用预先定义的测试数据集,来评估训练好的模型效果,评估完成后将输出模型在测试集上的损失函数值 loss 和精度 acc。
result = model.evaluate(eval_dataset,verbose=1) print(result) res = model.predict(eval_dataset,verbose=1) def show_img(img,predict): plt.figure() plt.title("predict:{}".format(predict)) plt.imshow(img.reshape([28,28]),cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.show() indexs = [1,26,56,111] for idx in indexs: show_img(eval_dataset[idx][0], res[0][idx].argmax())模型保存
模型训练完成后,通常需要将训练好的模型参数和优化器等信息,持久化保存到参数文件中,便于后续执行推理验证。
在飞桨中可通过调用 paddle.Model.save 保存模型。代码示例如下,其中 output 为模型保存的文件夹名称,minst 为保存的模型文件名称。
# 保存模型,文件夹会自动创建 model.save('./output/mnist')
以上代码执行后会在output目录下保存两个文件,mnist.pdopt为优化器的参数,mnist.pdparams为模型的参数。
output ├── mnist.pdopt # 优化器的参数 └── mnist.pdparams # 模型的参数
如果是
model.save('snap/mnist',training=False)
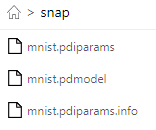
选择前两个进行部署
模型部署 环境配置- 下载安装C++预测库,
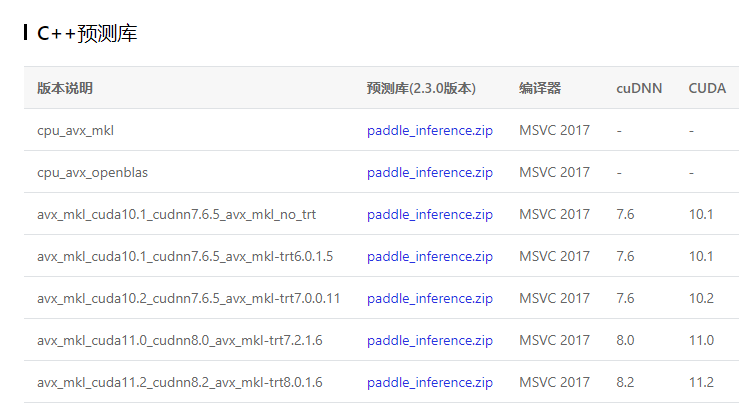
- 下载opencv
- 下载tensorrt的对应版本(可以不用)
- 下载安装cuda以及cudnn(如果和上面给的版本不一样,还要自己编译太麻烦,不如就选10.2)
- 属性页配置
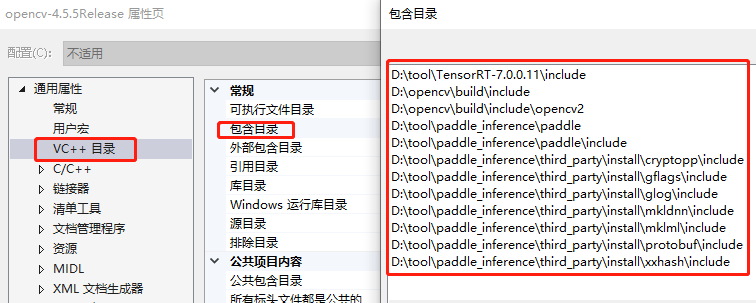
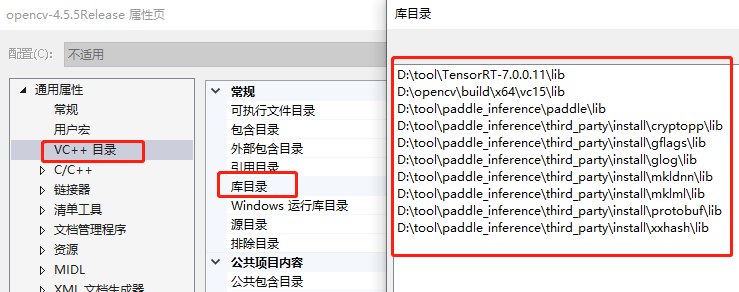
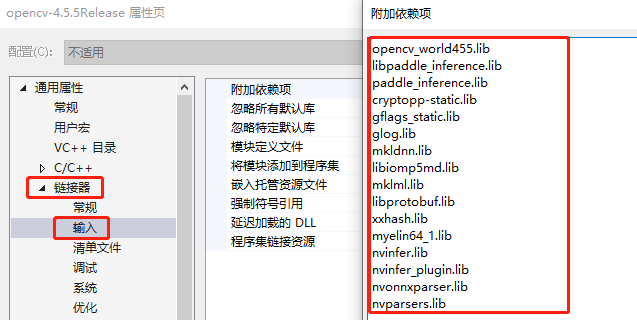
gitee链接包含模型文件
"Paddle.h"
#pragma once #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <paddle_inference_api.h> #include <numeric> using namespace cv; using namespace std; class Paddle { private: paddle_infer::Config config; public: bool loadModel(string& model_dir, string& model_file, string& params_file, int threads); void softmax(const vector<float>& input, vector<float>& result); void preprocess(Mat& src, Mat& dst, float meanValue, float stdValue); void gpuInference(Mat& srcImage, int srcWidth, int srcHeight, int matType, float meanValue, float stdValue, int& labelIndex, double& probability); };
"Paddle.cpp"
#include "Paddle.h" //加载模型 bool Paddle::loadModel(string& model_dir, string& model_file, string& params_file, int threads) { // Config默认是使用CPU预测,可以设置开启MKLDNN加速、设置CPU的线程数、开启IR优化、开启内存优化。 if (model_dir == "") { config.SetModel(model_file, params_file); // Load combined model } else { config.SetModel(model_dir); // Load no-combined model } config.EnableMKLDNN(); config.EnableUseGpu(1000, 0); //config.SetCpuMathLibraryNumThreads(threads); config.SwitchIrOptim(); config.EnableMemoryOptim(); return true; } void Paddle::softmax(const vector<float>& input, vector<float>& result) { result.clear(); float max = *std::max_element(input.begin(), input.end()); subtract(input, max, result); exp(result, result); float total = sum(result)[0]; divide(result, total, result); } //预处理 void Paddle::preprocess(Mat& src, Mat& dst, float meanValue, float stdValue) { Scalar mean(meanValue); Scalar std(stdValue); src.convertTo(src, CV_32F, 1.0 / 255.0); subtract(src, mean, src); divide(src, std, src); dst = src.clone(); } //单张图像前向传播 void Paddle::gpuInference(Mat& srcImage, int srcWidth, int srcHeight, int matType, float meanValue, float stdValue, int& labelIndex, double& probability) { clock_t start, end; Mat dstImage(srcWidth, srcHeight,CV_32FC1); //预处理 int buffer_size = srcWidth * srcHeight; preprocess(srcImage, dstImage, meanValue, stdValue); std::vector<float> input_buffer; input_buffer.assign((float*)dstImage.datastart, (float*)dstImage.dataend); input_buffer.resize(buffer_size); // 创建Predictor std::shared_ptr<paddle_infer::Predictor> predictor = paddle_infer::CreatePredictor(config); // 设置输入 auto input_names = predictor->GetInputNames(); auto input_t = predictor->GetInputHandle(input_names[0]); std::vector<int> input_shape = { 1, 1, srcWidth, srcHeight }; input_t->Reshape(input_shape); input_t->CopyFromCpu(input_buffer.data()); start = clock(); predictor->Run(); end = clock(); // 后处理 auto output_names = predictor->GetOutputNames(); auto output_t = predictor->GetOutputHandle(output_names[0]); std::vector<int> output_shape = output_t->shape(); int out_num = std::accumulate(output_shape.begin(), output_shape.end(), 1, std::multiplies<int>()); std::vector<float> out_data; out_data.resize(out_num); output_t->CopyToCpu(out_data.data());
Point maxLoc; double maxValue = 0; vector<float> output; softmax(out_data, output); minMaxLoc(output, 0, &maxValue, 0, &maxLoc); labelIndex = maxLoc.x; probability = maxValue; cout << labelIndex << ":" << probability; double time = end - start; cout << "spend time:" << time << endl; }
调用
#include "Paddle.h" int main() { Paddle p; string model_dir = ""; string model_file = "F:/C++Projects/paddle/mnist.pdmodel"; string params_file = "F:/C++Projects/paddle/mnist.pdiparams"; p.loadModel(model_dir, model_file, params_file, 1); Mat src = imread("D:/Backup/桌面/6.png", 0); resize(src, src, Size(28, 28)); bitwise_not(src, src);//变成黑底白字 int labelIndex = 0; double probability = 0.0; p.gpuInference(src, 28, 28, CV_8UC1, 0.5, 0.5, labelIndex, probability); }
结果: