#include stdio.h struct student { long num ; float score ; struct student * next ; }; void main (){ struct student a , b , c , * head ; a . num = 10101 ; a . score = 89.5 ; b . num = 10103 ; b . score = 90.5 ; c . num = 10107 ; c . score =
struct student {
long num;
float score;
struct student *next;
};
void main(){
struct student a,b,c,*head;
a.num = 10101;
a.score = 89.5;
b.num = 10103;
b.score = 90.5;
c.num = 10107;
c.score = 85;
head = &a;
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
c.next = NULL;
do {
printf("%1d %5.1f\n", head->num, head->score);
head = head->next;
} while( head );
}

答案
#include <stdio.h>#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define
struct student *creat();
void print(struct student *head);
struct student {
int num;
float score;
struct student *next;
};
int n;
void main(){
struct student *stu;
stu = creat();
print( stu );
printf("\n\n");
system("pause");
}
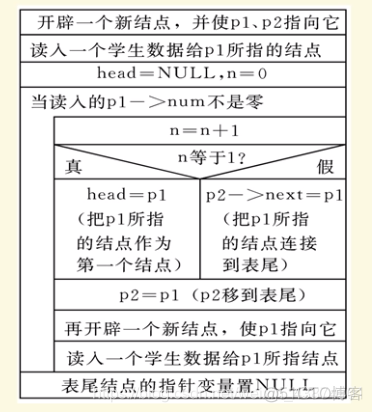
struct student *creat() {
struct student *head;
struct student *p1, *p2;
p1 = p2 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN);
printf("Please enter the num : ");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("Please enter the score : ");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
head = NULL;
n=0;
while(0 != p1->num) {
n++;
if(1 == n) {
head = p1;
}
else {
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct student *)malloc(LEN);
printf("\nPlease enter the num: ");
scanf("%d", &p1->num);
printf("\nPlease enter the score: ");
scanf("%f", &p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct student *head) {
struct student *p;
printf("\nThere are %d recoreds!\n",n);
p=head;
if( head ) {
do {
printf(" %d %f\n",p->num,p->score);
p = p->next;
} while( p );
}
}
练习题
#include <stdio.h>struct STU {char name[20];int num;int score;};
void main(){
struct STU s[5] = {{"Wa",2011,703},{"Zhangsan",2012,580},{"Lisi",2013,680},{"Zhangsan",2012,550},{"Zhangsan",2012,537}},
*p[5],*t;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)p[i] = &s[i];
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=i+1;j<5;j++)
if(p[i]->score>p[j]->score)
{t=p[i];p[i]=p[j];p[j]=t;}
printf("%d%5d\n",s[0].score,p[0]->score);
}
703 537
