1 内容介绍
微电网能够协调分布式电源,从而充分发挥分布式发电技术在经济,能源和环境中的优势.针对微电网并网时的优化调度问题,建立了考虑发电成本,电力负荷分配的微电网系统优化模型,并利用改进的多目标粒子群算法,在这两个目标之间进行协调权衡和折中处理,使所有目标函数尽量达到最优.选取微电网案例的日负荷数据进行了优化调度计算,仿真结果表明了所提模型和算法的有效性.
2 部分代码
clc;
clear ;
close all;
tic
%% Problem Definition
%% MOPSO Settings
% number_obj=3;%目标函数为3个
nPop=100; % Population Size种群大小100
nRep=100; % Repository Size存档大小为100
MaxIt=150; % Maximum Number of Iterations原始最大迭代次数100
phi1=2.05;%phi1=phi2=2.05
phi2=2.05;
phi=phi1+phi2;%4.1
chi=2/(phi-2+sqrt(phi^2-4*phi));%0.7298
w=chi; % Inertia Weight惯性权重
wdamp=1; % Inertia Weight Damping Ratio惯性权重阻尼比1
c1=chi*phi1; % Personal Learning Coefficient个体学习因子1.4962
c2=chi*phi2; % Global Learning Coefficient群体学习因子1.4962
nVar=55;%可以理解为粒子的维数,24+24+7
% VarMin=[0 0 0 0.0033];%粒子能取到的最小值
% VarMax=[0.00195 0.0009 0.00365 0.0037]; %粒子能取到的最大值
load data_load
load data_sun
% VarMax=repmat(2.2,1,24);VarMax=[VarMax,repmat(0.1,1,24)];VarMax=[VarMax,data_load(4,1:12)];VarMax=[VarMax,data_load(7,1:12)];
% VarMin=repmat(0,1,24);VarMin=[VarMin,repmat(-0.1,1,24)];VarMin=[VarMin,repmat(0,1,12)];VarMin=[VarMin,repmat(0,1,12)];%可平移负荷设置为节点7
VarMax=repmat(0.1,1,24);VarMax=[VarMax,repmat(0.05,1,24)];VarMax=[VarMax,data_load(7,11:14),data_load(7,19:21)];
VarMin=repmat(-0.1,1,24);VarMin=[VarMin,repmat(-0.05,1,24)];VarMin=[VarMin,repmat(0,1,7)];%可平移负荷设置为节点7
arSize=[1 nVar];%粒子规模为一行nVar
VelMax=(VarMax-VarMin)/5;%粒子速度影响参数原参数除以1
alpha=0.1; % Grid Inflation Parameter网格扩张参数0.1Grid=10; % Number of Grids per each Dimension网络每一维数量1
bta=4; % Leader Selection Pressure Parameter引导选择压力参数4
gamma=2; % Extra (to be deleted) Repository Member Selection Pressure额外(被删除的)存档选择压力2
%% Initialization
load Z_load
load B1
load B2ticle=CreateEmptyParticle(nPop);%产生空粒子群,构造结构体
for i=1:nPop
batteryflag=0;
particle(i).Velocity=0;
while batteryflag==0
particle(i).Position=unifrnd(VarMin,VarMax,VarSize);%产生Varsize个的从VarMin到VarMax的“均匀分布”(并不是一般地均匀)随机数或者产生1行3列的矩阵
% particle(i).Cost=CostFunction(particle(i).Position);%得到对应粒子目标函数的值;——应该在这个位置将变动的粒子的值重新赋给负荷矩阵,
batteryflag=battery_flag(particle(i).Position);
end
[particle(i).Cost,B1]=parameter_load3(B1,B2,particle(i).Position,data_load,data_sun);
particle(i).Best.Position=particle(i).Position;
particle(i).Best.Cost=particle(i).Cost;
ticle=DetermineDomination(particle);%决定主导元素的赋值true或false即1或0,即判断支配性
rep=GetNonDominatedParticles(particle);% 得到非支配粒子
rep_costs=GetCosts(rep);%GetCosts(rep)作用是将rep这个结构体中的的Cost元素取出来形成矩阵
G=CreateHypercubes(rep_costs,nGrid,alpha);
for i=1:numel(rep)
[rep(i).GridIndex rep(i).GridSubIndex]=GetGridIndex(rep(i),G);
end
end
compare_result=abs(compare(1)-compare(2))/compare(2);
record(it)=compare(1);
if it>MaxIt;
break
end
it=it+1;
end
%% Results
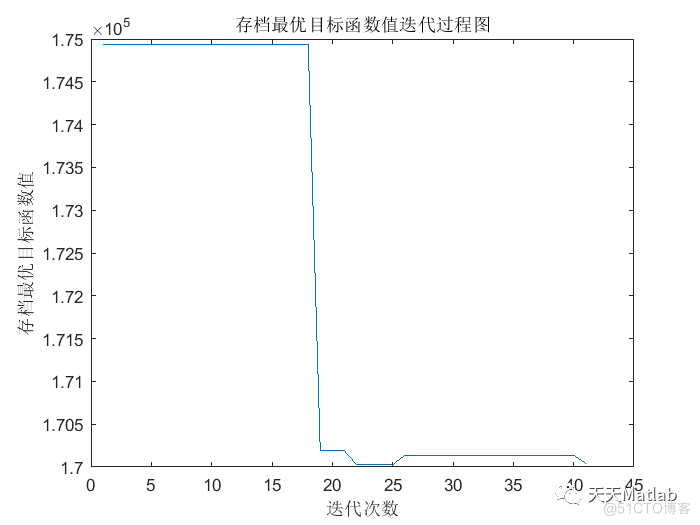
figure
plot(record);
xlabel('迭代次数');ylabel('存档最优目标函数值');
title('存档最优目标函数值迭代过程图');
hold on
%测试rep中粒子位置是否符合储能限制条件
for i=1:100
rep_flag(i)=battery_flag(rep(i).Position);
end
costs=GetCosts(particle);
rep_costs=GetCosts(rep);
[final final_num]=min(integrate);
best_position=rep(final_num).Best.Position;
% plot3(best_position(1),best_position(2),best_position(3),'rP','MarkerSize',12);
% hold on
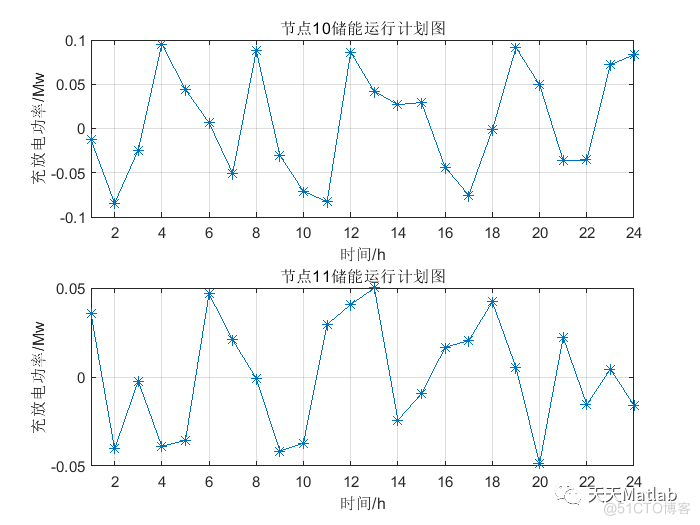
figure;
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(best_position(1,1:24),'-*');
title('节点10储能运行计划图')
xlabel('时间/h');ylabel('充放电功率/Mw');
grid on
xlim([1 24]);
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(best_position(1,25:48),'-*');
grid on
xlim([1 24]);
title('节点11储能运行计划图')
xlabel('时间/h');ylabel('充放电功率/Mw');
% figure
% temp=data_load(7,1:12)-best_position(1,49:60);
% load7=[temp(1,5:12)+data_load(7,1:8),best_position(1,49:60),temp(1,1:4)+data_load(7,21:24)];
% plot(data_load(7,1:24));hold on
% plot(load7,'-*');hold on;
% xlim([1 24]);
% legend('平移前','平移后')
% title('负荷7平移前与平移后日负荷曲线')
% xlabel('时间/h');ylabel('功率/Mw');
% grid on
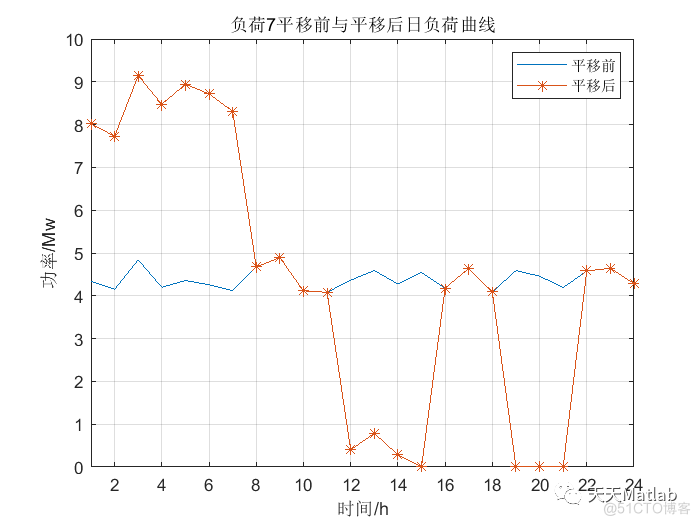
figure
temp1=data_load(7,11:14)-best_position(1,49:52);
temp2=data_load(7,19:21)-best_position(1,53:55);
% temp=[temp1,temp2];
load7=[temp1+data_load(7,1:4),temp2+data_load(7,5:7),data_load(7,8:11),best_position(1,49:52),data_load(7,16:18),best_position(1,53:55),data_load(7,22:24)];
plot(data_load(7,1:24));hold on
plot(load7,'-*');hold on;
xlim([1 24]);
legend('平移前','平移后')
title('负荷7平移前与平移后日负荷曲线')
xlabel('时间/h');ylabel('功率/Mw');
grid on
check=zeros(100,1);
for number=1:100
check(number)=particle(number).Dominated;
end
num_position=find(check==0);
num=numel(num_position);
clear i;
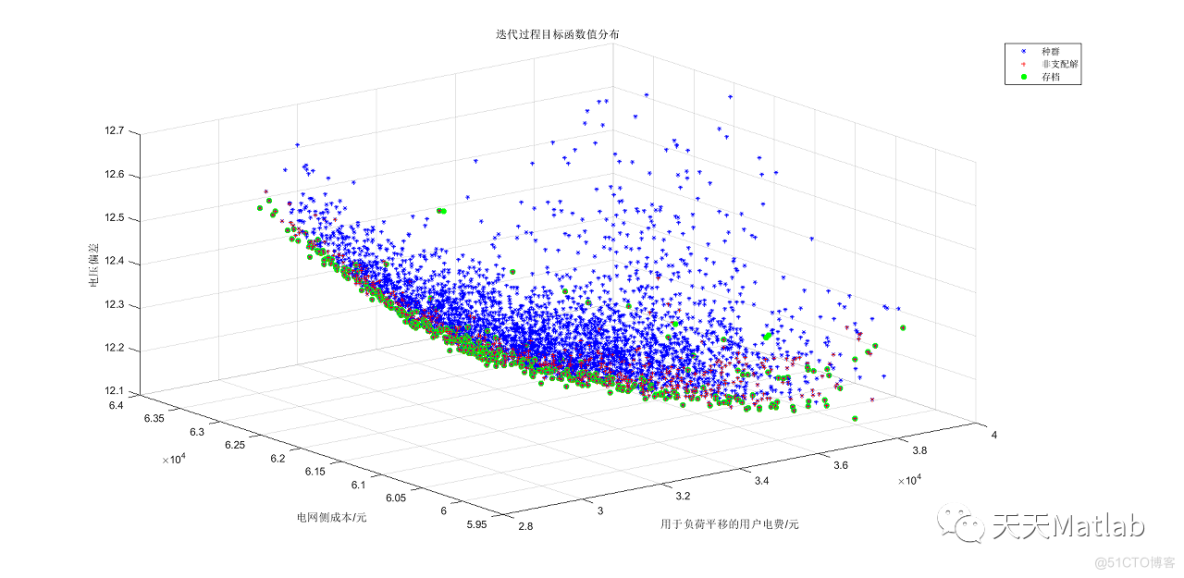
figure;
best_cost=rep(final_num).Best.Cost;
plot3(best_cost(1),best_cost(2),best_cost(3),'rP','MarkerSize',16)
hold on
plot3(costs(1,:),costs(2,:),costs(3,:),'b.');
hold on;
plot3(rep_costs(1,:),rep_costs(2,:),rep_costs(3,:),'gx');
% legend('Best Repository','Main Population','Repository');
legend('存档最优值','主要种群值','存档值');
xlabel('用于负荷平移的用户电费/元');ylabel('电网侧成本/元');zlabel('电压偏移');
grid on;
title('种群和存档最优解对应目标函数的值')
if it>MaxIt
disp(['迭代次数达到限制最大值100,','跳出迭代']);
end
disp(['最优解为:',num2str(best_position)]);
disp(['最优值为:',num2str(best_cost)]);
toc
3 运行结果
4 参考文献
[1]单新文, 唐灏, 范磊,等. 基于改进粒子群算法的微电网多目标优化调度研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2021.
[2]王金全, 黄丽, 杨毅. 基于多目标粒子群算法的微电网优化调度[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2014, 30(1):6.
