集合
概念:对象的容器,实现了对对象常用的操作
与数组的区别:
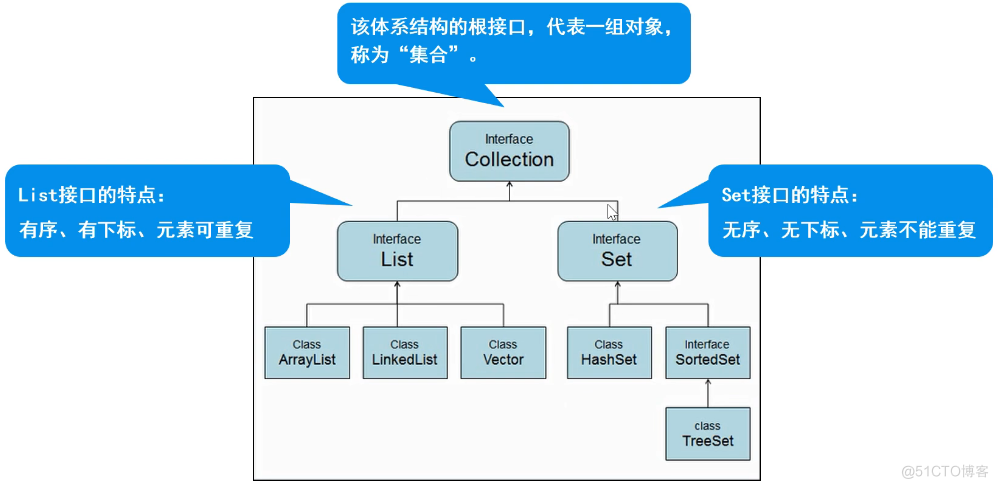
Collection:
特点:代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复。
创建集合 Collection collection = new ArrayList();
常用方法:
collection.remove();collection.clear();
for(Object object : collection){ }
while(it.hasNext()){
String object = (String)it.next();
}
collection.contains();判断字符串中是否包含指定的字符或字符串 collection.isEmpty(); 是否为空
List
特点:有序、有下标、元素可重复
创建集合对象 List list = new ArrayList<>( );
常用方法:
当删除数字与索引矛盾时 对数字强转
list.remove((Object) 10) 或 list.remove(new Integer(10))
sout(list.get(i));
}
for(Object list: collection){ }
while(it.hasNext()){
String object = (String)it.next(); //强转
// 可以使用it.remove(); 进行移除元素
// collection.remove(); 不能用collection其他方法 会报并发修改异常
}
while(li.hasNext()){
System.out.println(li.nextIndex() + ":" + li.next()); //从前往后遍历
}
while(li.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(li.previousIndex() + ":" + li.previous()); //从后往前遍历
}
List实现类
ArrayList
数组结构实现,必须要连续空间,查询快、增删慢
jdk1.2版本,运行效率块、线程不安全
LinkedList
双向链表结构实现,无需连续空间,增删快,查询慢
ArrayList
创建集合 ArrayList<> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
3.判断
arrayList.contains(); 和 arrayList.isEmpty();
4.查找
arrayList.indexof();
LinkedList
创建链表集合LinkedList<> li = new LinkedList<>();
常用方法与List一致
泛型
- 本质是参数化类型,把类型作为参数传递
- 常见形式有泛型类、泛型接口、泛型方法
- 语法 T成为类型占位符,表示一种引用类型,可以写多个逗号隔开
- 好处 1. 提高代码重用性 2. 防止类型转换异常,提高代码安全性
泛型类
// 写一个泛型类public class MyGeneric<T>{
//使用泛型T
//1 创建变量
T t;
//2 泛型作为方法的参数
public void show(T t){
sout(t);
}
//3 泛型作为方法的返回值
public T getT(){
return t;
}
}// 使用泛型类
public class TestGeneric{
public static void main(String[] args){
//使用泛型类创建对象
// 注意: 1. 泛型只能使用引用类型
//
MyGeneric<String> myGeneric = new MyGeneric<String>();
myGeneric.t = "hello";
myGeneric.show("hello world!");
String string = myGeneric.getT();
MyGeneric<Integer> myGeneric2 = new MyGeneric<Integer>();
myGeneric2.t = 100;
myGeneric2.show(200);
Integer integer = myGeneric2.getT();
}
}
Set集合
特点:无序、无下标、元素不可重复
方法:全部继承自Collection中的方法
增、删、遍历、判断与collection一致
HashSet
存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
存储过程(重复依据)
新建集合 HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<String>();
添加元素 hashSet.add( );
删除元素 hashSet.remove( );
遍历操作
1. 增强for for( type type : hashSet)
2. 迭代器 Iterator<String> it = hashSet.iterator( );
判断 hashSet.contains( ); hashSet.isEmpty();
TreeSet
特点
- 基于排列顺序实现元素不重复
- 实现SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排序
- 元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则
- 通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素
存储结构:红黑树
创建集合 TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>()
添加元素 treeSet.add();
删除元素 treeSet.remove();
遍历 1. 增强for 2. 迭代器
判断 treeSet.contains();
补充:TreeSet集合的使用
Comparator 实现定制比较(比较器)
Comparable 可比较的
Map
Map接口的特点
HashMap
存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
使用key可使hashcode和equals作为重复
增、删、遍历、判断与上述一致
Hashtable
线程安全,运行效率慢;不允许null作为key或是value
Properties
hashtable的子类,要求key和value都是string,通常用于配置文件的读取
TreeMap
实现了SortedMap接口(是map的子接口),可以对key自动排序
