概述
本文开始分析 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 中另一个比较重要的处理方法postProcessMergedBeanDefinition,它被调用的时机是在 Spring 通过反射创建 Bean 实例对象之后、属性装配之前。它的作用,是将类中标记了相关注解的注入点解析出来。
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法分析
进入postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法的源码。
// org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
非常简洁,只有两行代码,分别调用了两个方法,我们逐个分析。
findAutowiringMetadata
先进入findAutowiringMetadata方法。
// org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadataprivate InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
从方法的名称中可以看出,它用来从类中找到自动注入元信息,最后返回一个 InjectionMetadata 类型的结果。
首先,会从缓存injectionMetadataCache中,查找注入元信息,如果获取到的注入元信息不需要被刷新,则直接返回。如果需要刷新,则通过buildAutowiringMetadata方法,构建元信息,并放入缓存中,再在方法末尾返回。
在这里,如果缓存中获取到的注入元信息为空,也属于需要刷新的情况。
接下来我们看buildAutowiringMetadata方法是如何构建这些元信息的。
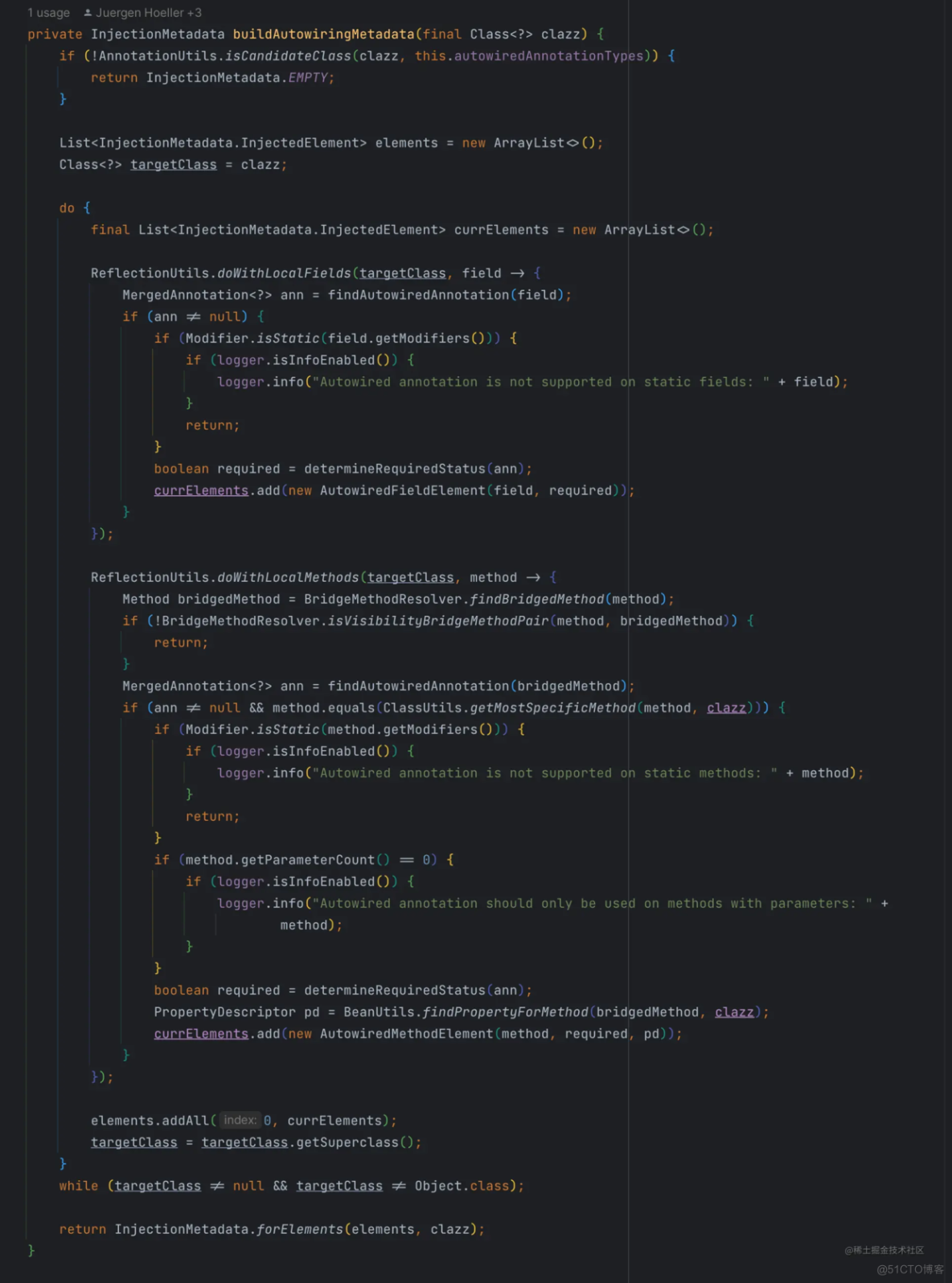
这个方法比较长,我们逐步来分析。
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
首先会判断当前的类型是不是 Java 内部的类型,如果是的话,则直接返回空的信息。
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
// 循环语句块
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
接着声明了一个 InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement 类型的空列表,以及一个表示类型的targetClass变量,初始值为方法参数传入的clazz。然后,在targetClass不为空且不是 Object 类型的情况下,执行do-while循环中的逻辑。
下面我们看do-while语句块中的内容。
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
在循环语句块中,首先会遍历所有的被标记了@AutoWired、@Value、@Inject注解的字属性字段封装为 AutowiredFieldElement 对象,并添加到事先声明好的currElements集合中。需要注意的是,这里会跳过静态字段,因此静态字段是无法通过这几个注解进行注入的。
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
接着,再将添加了这些注解的非晶态方法,封装成 AutowiredMethodElement 对象,添加到currElements集合中。
elements.addAll(0, currElements);targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
在循环体的最后,将currElements中的内容都添加到elements集合中,然后将targetClass指向其父类。
这里结合循环体的while条件,可以知道,这个循环体要执行的工作是,以方法参数传入的类型开始遍历它的父类,一直到 Object 类之前,将这些类中声明的所有带注入相关注解的非静态的属性和方法都封装成 InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement 对象(属性对应 AutowiredFieldElement,方法对应 AutowiredMethodElement),然后统一放到elements集合中。
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);方法的最后,将elements集合和类型信息封装成 InjectionMetadata 返回。
checkConfigMembers
回到postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,在得到 InjectionMetadata 类型的注解信息metadata后,会调用它的checkConfigMembers方法。
// org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InjectionMetadata#checkConfigMemberspublic void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Set<InjectedElement> checkedElements = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.injectedElements.size());
for (InjectedElement element : this.injectedElements) {
Member member = element.getMember();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedConfigMember(member)) {
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedConfigMember(member);
checkedElements.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered injected element on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
this.checkedElements = checkedElements;
}
这个方法中,会对injectedElements成员变量集合进行遍历,这里 InjectionMetadata 的injectedElements的成员变量,其实就是上一部中创建 InjectionMetadata 对象时,传入的elements参数,也就是解析出的带注入注解的属性和方法封装后的对象集合。
循环中会判断当前遍历到的element,在 BeanDefinition 中是不是外部管理的配置成员,这里的成员指的就是属性或者方法,如果不是的话,则将其注册为外部管理的配置成员,也就是添加到 BeanDefinition 的externallyManagedConfigMembers集合中,然后再将element对象添加到事先声明好的 InjectedElement 集合checkedElements中。
方法的最后,将checkedElements集合赋值给 InjectionMetadata 的checkedElements成员变量。
总结
本文介绍了 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 后处理器中的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,它的作用是在当前处理的类型中解析出需要注入的属性和方法。
下一篇讲分析 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 最后一个比较重要的处理方法postProcessProperties。
