安卓中实现异步任务(2)——使用AsyncTask实现 问题背景 上次的文章大致介绍了几种安卓汇总实现异步任务的方法,讲得比较简要,有朋友问到具体的实现方式,现在开始分列几篇文章
安卓中实现异步任务(2)——使用AsyncTask实现
问题背景
上次的文章大致介绍了几种安卓汇总实现异步任务的方法,讲得比较简要,有朋友问到具体的实现方式,现在开始分列几篇文章详细介绍这几种异步的具体实现。这篇讲得是基于asyncTask实现,持续更新。
实现demo
(1)实现我们的AsyncTask子类
import android.content.Context; import android.os.AsyncTask; import android.util.Log; import android.widget.ProgressBar; import android.widget.TextView; import android.widget.Toast; public class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<Integer,Integer,Integer> { private final String TAG = "AsyncTask"; private TextView textView; private ProgressBar progressBar; private Context context; public MyAsyncTask(TextView textView, ProgressBar progressBar, Context context) { this.textView = textView; this.progressBar = progressBar; this.context = context; } @Override protected void onPreExecute() { super.onPreExecute(); Log.d(TAG,"onPreExecute(): " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } @Override protected Integer doInBackground(Integer... ints) { Integer count = ints[0]; while (count < 10 && !isCancelled()){ // isCancelled()表示判断当前任务是否被取消,防止在取消异步任务的时候循环不能及时停下 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } count++; Log.d(TAG,"doInBackground(): "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() +" "+count); publishProgress(count); } return count; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(Integer i) { Log.d(TAG,"onPostExecute(): "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); textView.setText(i + ""); } @Override protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) { Log.d(TAG,"onProgressUpdate(): " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); textView.setText(values[0]+""); progressBar.setProgress(values[0]); } @Override protected void onCancelled() { Log.d(TAG,"nCancelled(): "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); super.onCancelled(); Toast.makeText(context,"任务取消成功", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }(2)新建我们的activity,对应layout布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".thread.AsyncTaskActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:hint="0" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <ProgressBar style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" android:id="@+id/progressBar" android:progress="0" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:text="启动任务" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentStart="true" android:onClick="doTaskClick" /> <Button android:text="取消任务" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:onClick="cancelTaskClick" /> </RelativeLayout> </LinearLayout>(3)对应我们activity的代码如下:
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.ProgressBar; import android.widget.TextView; public class AsyncTaskActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private TextView textView; private ProgressBar progressBar; private MyAsyncTask myAsyncTask; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_async_task); textView= findViewById(R.id.textView); progressBar= findViewById(R.id.progressBar); } public void doTaskClick(View view){ myAsyncTask = new MyAsyncTask(textView, progressBar,this); // 执行异步任务,传入初始参数 myAsyncTask.execute(1); } public void cancelTaskClick(View view){ // 取消异步任务 myAsyncTask.cancel(true); } }执行结果如下:
安卓中实现异步任务(2)——使用AsyncTask实现
问题背景
上篇文章大致介绍了几种安卓汇总实现异步任务的方法,讲得比较简要,有朋友问到具体的实现方式,现在开始分列几篇文章详细介绍这几种异步的具体实现。这篇讲得是基于asyncTask实现,持续更新。
实现demo
(1)实现我们的AsyncTask子类
import android.content.Context; import android.os.AsyncTask; import android.util.Log; import android.widget.ProgressBar; import android.widget.TextView; import android.widget.Toast; public class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<Integer,Integer,Integer> { private final String TAG = "AsyncTask"; private TextView textView; private ProgressBar progressBar; private Context context; public MyAsyncTask(TextView textView, ProgressBar progressBar, Context context) { this.textView = textView; this.progressBar = progressBar; this.context = context; } @Override protected void onPreExecute() { super.onPreExecute(); Log.d(TAG,"onPreExecute(): " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } @Override protected Integer doInBackground(Integer... ints) { Integer count = ints[0]; while (count < 10 && !isCancelled()){ // isCancelled()表示判断当前任务是否被取消,防止在取消异步任务的时候循环不能及时停下 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } count++; Log.d(TAG,"doInBackground(): "+ Thread.currentThread().getName() +" "+count); publishProgress(count); } return count; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(Integer i) { Log.d(TAG,"onPostExecute(): "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); textView.setText(i + ""); } @Override protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) { Log.d(TAG,"onProgressUpdate(): " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); textView.setText(values[0]+""); progressBar.setProgress(values[0]); } @Override protected void onCancelled() { Log.d(TAG,"nCancelled(): "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); super.onCancelled(); Toast.makeText(context,"任务取消成功", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }(2)新建我们的activity,对应layout布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".thread.AsyncTaskActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:hint="0" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <ProgressBar style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" android:id="@+id/progressBar" android:progress="0" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:text="启动任务" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentStart="true" android:onClick="doTaskClick" /> <Button android:text="取消任务" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:onClick="cancelTaskClick" /> </RelativeLayout> </LinearLayout>(3)对应我们activity的代码如下:
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.ProgressBar; import android.widget.TextView; public class AsyncTaskActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private TextView textView; private ProgressBar progressBar; private MyAsyncTask myAsyncTask; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_async_task); textView= findViewById(R.id.textView); progressBar= findViewById(R.id.progressBar); } public void doTaskClick(View view){ myAsyncTask = new MyAsyncTask(textView, progressBar,this); // 执行异步任务,传入初始参数 myAsyncTask.execute(1); } public void cancelTaskClick(View view){ // 取消异步任务 myAsyncTask.cancel(true); } }执行结果如下:
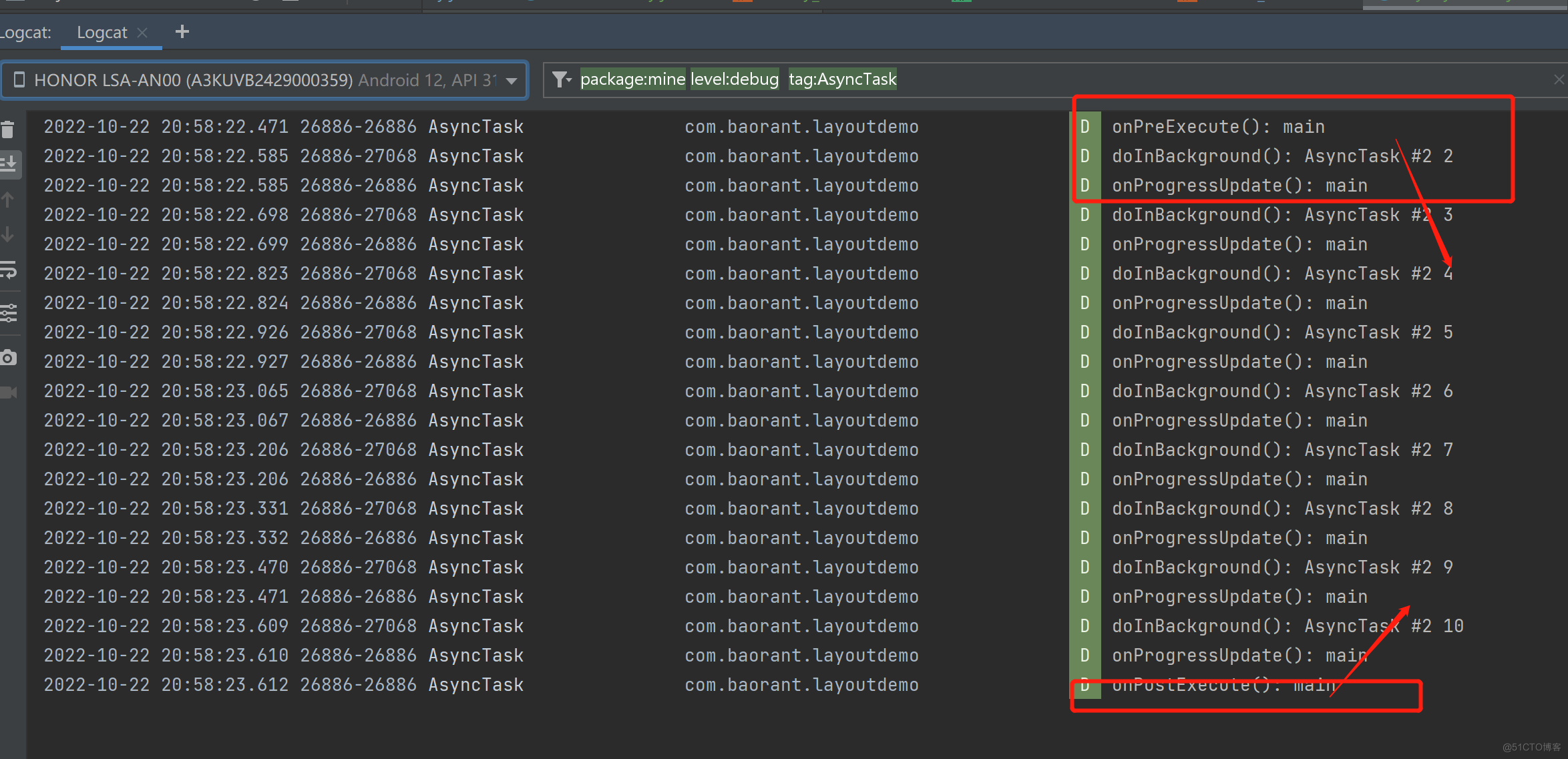 根据log,我们可以很清楚的看到asyncTask对应各方法所在的线程以及执行时机;
根据log,我们可以很清楚的看到asyncTask对应各方法所在的线程以及执行时机;
关键代码分析
持续更新。。。
