1. 背景 此处将单记录一下 global 、 filters和cardinality的聚合操作。 2、解释 1、global global聚合是全局聚合,是对所有的文档进行聚合,而不受查询条件的限制。 global 聚合器只能作为顶级
1. 背景
此处将单记录一下 global 、 filters和cardinality的聚合操作。
2、解释
1、global
global聚合是全局聚合,是对所有的文档进行聚合,而不受查询条件的限制。
global 聚合器只能作为顶级聚合器,因为将一个 global 聚合器嵌入另一个桶聚合器是没有意义的。
比如: 我们有50个文档,通过查询条件筛选之后存在10个文档,此时我想统计总共有多少个文档。是50个,因为global统计不受查询条件的限制。
2、filters
定义一个多桶聚合,其中每个桶都与一个过滤器相关联。每个桶都会收集与其关联的过滤器匹配的所有文档。
比如: 我们总共有50个文档,通过查询条件筛选之后存在10个文档,此时我想统计 这10个文档中,出现info词语的文档有多少个,出现warn词语的文档有多少个。
3、cardinality
类似于 SQL中的 COUNT(DISTINCT(字段)),不过这个是近似统计,是基于 HyperLogLog++ 来实现的。
3、需求
我们有一组日志,每条日志都存在id和message2个字段。此时根据message字段过滤出存在info warn的日志,然后进行统计:
4、前置条件
4.1 创建mapping
PUT /index_api_log { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 1 }, "mappings": { "properties": { "message":{ "type": "text" }, "id": { "type": "long" } } } }4.2 准备数据
PUT /index_api_log/_bulk {"index":{"_id":1}} {"message": "this is info message-01","id":1} {"index":{"_id":2}} {"message": "this is info message-02","id":2} {"index":{"_id":3}} {"message": "this is warn message-01","id":3} {"index":{"_id":4}} {"message": "this is error message","id":4} {"index":{"_id":5}} {"message": "this is info and warn message","id":5}5、实现3的需求
5.1 dsl
POST /index_api_log/_search { "size": 0, "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "message": "info warn" } } ] } }, "aggregations": { "agg_01": { "filters": { "filters": { "info": { "match": { "message": "info" } }, "warn": { "match": { "message": "warn" } } }, "other_bucket": true, "other_bucket_key": "other" } }, "agg_02":{ "global": {}, "aggs": { "total": { "cardinality": { "field": "id", "precision_threshold": 30000 } } } } } }5.2 java 代码
@Test @DisplayName("global and filters and cardinality 聚合") public void test01() throws IOException { SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(searchRequest -> searchRequest.index("index_api_log") // 查询 message 中存在 info 和 warn 的日志 .query(query -> query.bool(bool -> bool.must(must -> must.match(match -> match.field("message").query("info warn"))))) // 查询的结果不返回 .size(0) // 第一个聚合 .aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.filters(filters -> filters.filters(f -> f.array( Arrays.asList( // 在上一步query的结果中,将 message中包含info的进行聚合 Query.of(q -> q.match(m -> m.field("message").query("info"))), // 在上一步query的结果中,将 message中包含warn的进行聚合 Query.of(q -> q.match(m -> m.field("message").query("warn"))) ) ) ) // 如果上一步的查询中,存在非 info 和 warn的则是否聚合到 other 桶中 .otherBucket(true) // 给 other 桶取一个名字 .otherBucketKey("other") ) ) // 第二个聚合 .aggregations("agg_02", agg -> agg // 此处的 global 聚合只能放在顶部 .global(global -> global) // 子聚合,数据来源于所有的文档,不受上一步query结果的限制 .aggregations("total", subAgg -> // 类似于SQL中的 count(distinct(字段)),是一个近似统计 subAgg.cardinality(cardinality -> // 统计的字段 cardinality.field("id") // 精度,默认值是30000,最大值也是40000,不超过这个值的聚合近似准确值 .precisionThreshold(30000) ) ) ) ); System.out.println("request: " + request); SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class); System.out.println("response: " + response); }5.3 运行结果
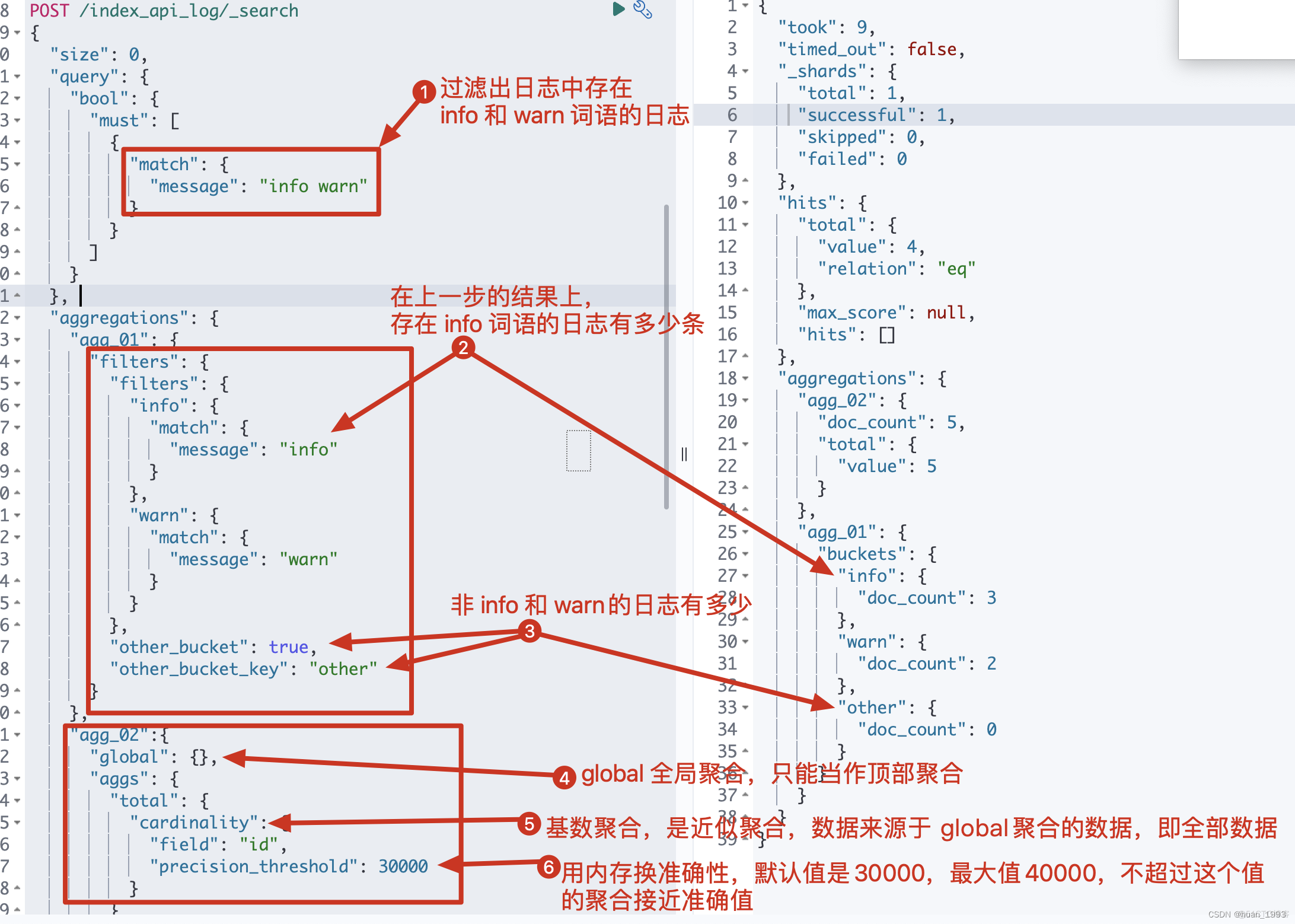
6、实现代码
https://gitee.com/huan1993/spring-cloud-parent/blob/master/es/es8-api/src/main/java/com/huan/es8/aggregations/bucket/GlobalAndFiltersAggs.java
7、参考文档
1、https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-aggregations-bucket-global-aggregation.html
