vector是连续存储结构,支持随机的高效的随机和在尾部进行插入、删除操作,其它位置的插入、删除操作相对来说效率较低。 vector相当于一个数组,但它的数组空间大小需要写一程序来
vector是连续存储结构,支持随机的高效的随机和在尾部进行插入、删除操作,其它位置的插入、删除操作相对来说效率较低。
vector相当于一个数组,但它的数组空间大小需要写一程序来实现。
它的内存分配原理大概可分为下面几步:
1)首先分配一块内存空间进行存储;
2)当所需存储的数据超过分配的空间时,再重新分配一块空间;
3)将旧元素复制到新空间;
4)释放旧空间。
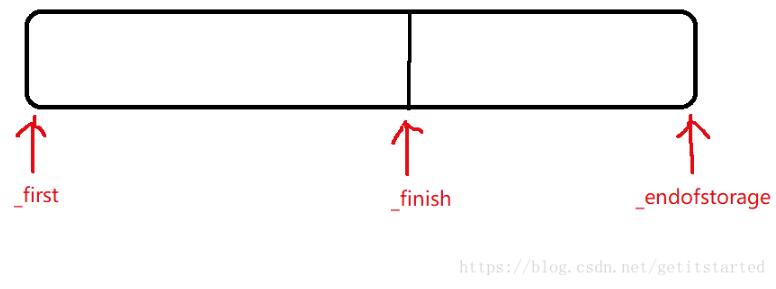
实现代码如下:
vector.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int DataType;
class Vector
{
public:
Vector()
:_first(NULL),
_finish(NULL),
_endofstorage(NULL)
{}
Vector(const Vector& v){
if (v.Size() > 0){
_first = new DataType(v.Size());
memcpy(_first, v._first, sizeof (DataType)*v.Size());
}
if (_first > 0){
_finish = _first + v.Size();
_endofstorage = _first + v.Size();
}
_first = _finish = _endofstorage = NULL;
}
Vector& operator=(const Vector& v){
if (this != &v){
/*swap(_first, v._first);
swap(_finish, v._finish);
swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);*/
DataType* tmp = new DataType(v.Size());
memcpy(tmp, _first, sizeof(DataType)*v.Size());
delete _first;
_first = tmp;
_finish = _first + v.Size();
_endofstorage = _first + v.Size();
}
return *this;
}
~Vector(){
delete[] _first;
_first = _finish = _endofstorage = NULL;
}
void Print(){
DataType* cur = _first;
while (cur != _first){
cout << "*cur" << endl;
cur++;
}
cout << endl;
}
size_t Size() const{
return _finish - _first;
}
size_t Capacity() const{
return _endofstorage - _first;
}
void Expand(size_t n){
if (n > Capacity()){
DataType* tmp = new DataType(n);
size_t size = Size();
memcpy(tmp, _first, sizeof(DataType)*size);
delete[] _first;
_first = tmp;
_finish = _first + size;
_endofstorage = _first + n;
}
}
void PushBack(DataType x){
if (_finish == _endofstorage){
size_t capacity = Capacity() > 0 ? Capacity() * 2 : 3;
Expand(capacity);
/*if (Capacity() == 0){
Expand(3);
}
else{
Expand(Capacity() * 2);
}*/
}
*_finish = x;
++_finish;
}
void PopBack(){
assert(_finish > _first);
--_finish;
}
void Reserve(size_t n){
if (n > Capacity()){
Expand(n);
}
}
void Insert(size_t pos, DataType x){
assert(pos < Size());
if (_finish = _endofstorage){
size_t capacity = Capacity() > 0 ? Capacity() * 2 : 3;
Expand(capacity);
}
int tmp = Size() - 1;
while (tmp >= (int)pos){
_first[tmp + 1] = _first[tmp];
--tmp;
}
_first[pos] = x;
++_finish;
}
void Erase(size_t pos){
assert(pos < Size());
size_t cur = pos;
while (cur < Size()-1){
_first[cur] = _first[cur] + 1;
++cur;
}
--_finish;
}
size_t Find(DataType x){
DataType *cur = _first;
while (cur != _finish){
if (*cur == x){
return cur - _first;
}
++cur;
}
return -1;
}
private:
DataType* _first;
DataType* _finish;
DataType* _endofstorage;
};
test.cpp
#include"vector.h"
void Tset(){
Vector v;
v.PushBack(1);
v.PushBack(2);
v.PushBack(3);
v.PushBack(4);
v.PopBack();
v.Print();
size_t pos = v.Find(1);
printf("pos->data:expcet 1,axtual %lu", pos);
Vector v1;
v1.Insert(1, 0);
v1.Print();
Vector v2;
v2.Erase(3);
v2.Print();
}
int main(){
Tset();
return 0;
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
