前言
Spring JPA是目前比较常用的ORM解决方案,但是其对于某些场景并不是特别的方便,例如查询部分字段,联表查询,子查询等。
而接下来我会介绍与JPA形成互补,同时也是与JPA兼容得很好的框架QueryDSL。
同时由于目前主流使用Spring Boot,所以本文也会基于Spring Boot来进行演示
如果对于长文无感,但是又希望了解QueryDSL可以直接查看文章最后的总结
环境信息
以下为示例的关键环境信息
- JDK 1.8
- maven 3.6.1
- SpringBoot 2.2.0.RELEASE
- IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.3
- lombok
- mysql-5.7
源码地址
https://github.com/spring-based-solutions/querydsl-jpa-demo
项目整合
pom文件配置
QueryDSL本身定位就是对某些技术的补充或者说是完善,其提供了对JPA、JDBC、JDO等技术的支持。这里引入的是QueryDSL-JPA,需要注意一定要引入querydsl代码生成器插件。
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<querydsl.version>4.2.1</querydsl.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--使用版本较老的mysql驱动包,用于连接mysql-5.7-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.48</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入querydsl-jpa依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-jpa</artifactId>
<version>${querydsl.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<!--引入querydsl代码生成器插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>com.mysema.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>apt-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-apt</artifactId>
<version>${querydsl.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<executions>
<!--设置插件生效的maven生命周期-->
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<!--配置生成文件的目录-->
<outputDirectory>src/generated-sources/java/</outputDirectory>
<processor>com.querydsl.apt.jpa.JPAAnnotationProcessor</processor>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
application配置文件
spring: datasource: ## 数据库相关配置 url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/example?useSSL=false username: root password: root driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 指定驱动类 jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update # 自动创建表以及更新表结构,生产环境慎用 show-sql: true # 打印执行的SQL
配置类
由于QueryDSL不提供starter,所以需要自行准备一个配置类,代码如下所示
import com.querydsl.jpa.impl.JPAQueryFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
/**
* QueryDSL配置类
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
@Configuration
public class QuerydslConfig {
@Autowired
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Bean
public JPAQueryFactory queryFactory(){
return new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
}
}
启动类
启动类很简单,只需要使用@SpringBootApplication即可
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class QuerydslJpaDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(QuerydslJpaDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
实体类
主要有讲师和课程,每个课程都有一个讲师,每个讲师有多个课程,即讲师与课程的关系为一对多
课程
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
/**
* 课程,一个课程对应一个讲师
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
@Data
@Entity
public class Course {
/**
* 课程ID
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
/**
* 课程名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 对应讲师的ID
*/
private Long lecturerId;
}
讲师
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
/**
* 讲师,一个讲师有多个课程
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
@Data
@Entity
public class Lecturer {
/**
* 讲师ID
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
/**
* 讲师名字
*/
private String name;
/**
* 性别,true(1)为男性,false(0)为女性
*/
private Boolean sex;
}
Repository接口
如果要使用QuerDSL需要Repository接口除了继承JpaRepository接口(此接口为Spring-JPA提供的接口)外,还需要继承QuerydslPredicateExecutor接口。关键示例如下:
课程Repository
import com.example.querydsl.jpa.entity.Course;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.querydsl.QuerydslPredicateExecutor;
/**
* 课程Repository
*
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
public interface CourseRepository extends
JpaRepository<Course, Integer>,
QuerydslPredicateExecutor<Course> {
}
讲师Repository
import com.example.querydsl.jpa.entity.Lecturer;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.querydsl.QuerydslPredicateExecutor;
/**
* 讲师Repository
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
public interface LecturerRepository extends
JpaRepository<Lecturer,Integer>,
QuerydslPredicateExecutor<Lecturer> {
}
代码生成
前面配置QueryDSL代码生成器就是用于这一步,==每次实体类有变更最好重复执行本步骤重新生成新的代码==。由于个人习惯使用IDEA,所以以IDEA作为演示。
双击下图内容即可生成代码了,
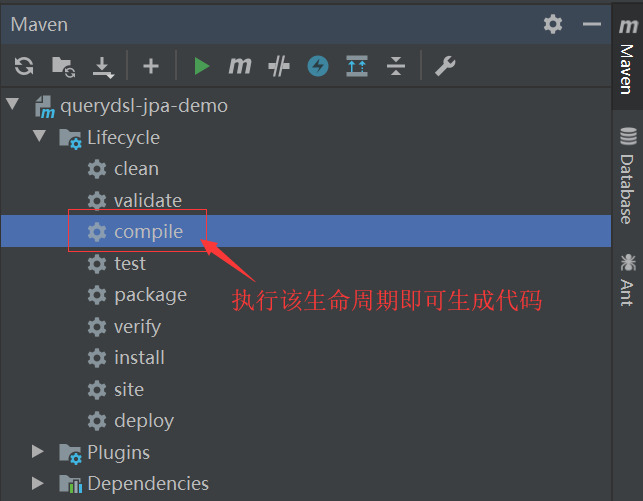
然后就会在src/generated-sources目录可以看到生成的代码,包名与实体包名一致,但是类名为Q开头的文件
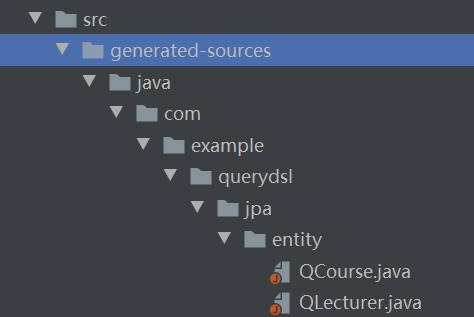
上一步的截图我们可以看到其实生成的代码被IDEA识别为普通文件了,所以我们需要标记src/generated-sources/java目录的用途,如下图所示
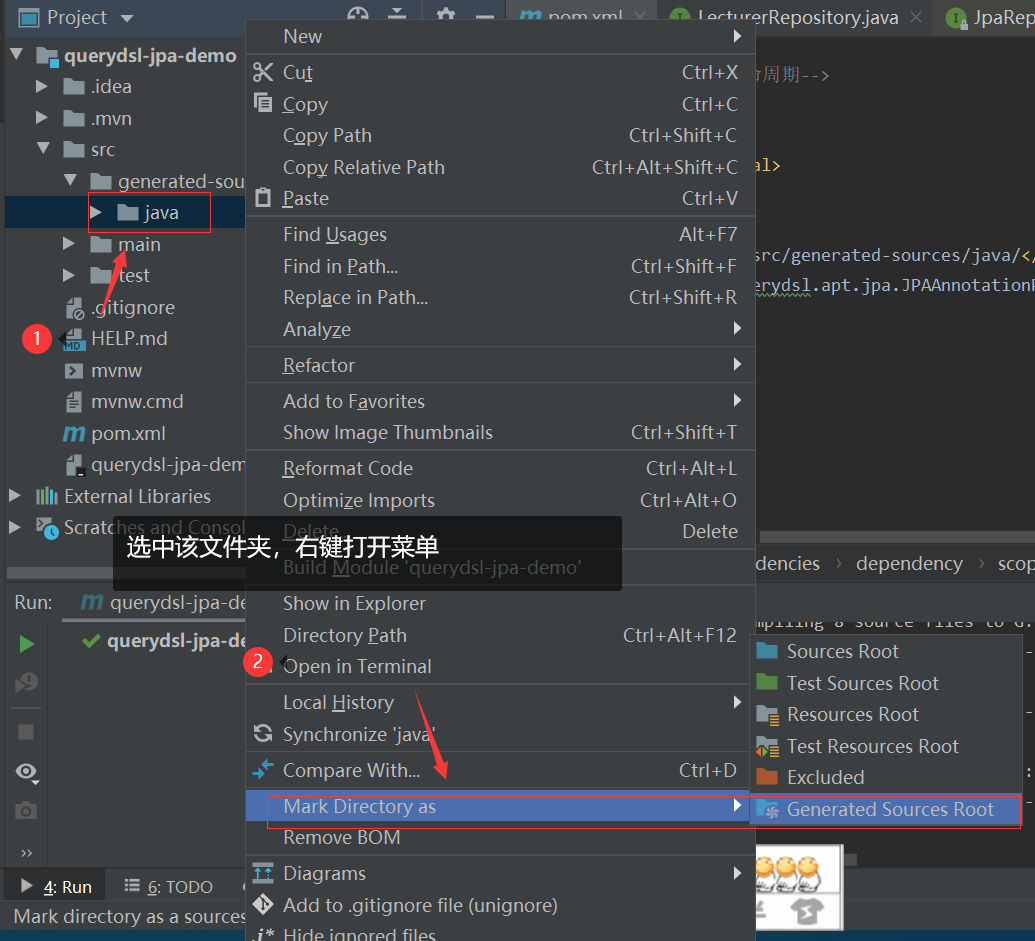
标记后,效果如下,可以看到代码被正确识别了
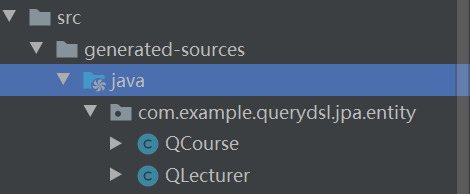
到了这一步其实已经完成整合了,下面就开始验证是否正确整合以及展示QueryDSL的优势了
验证整合与演示
下面我会使用单元测试来验证QueryDSL是否正确整合以及演示一下QueryDSL的优势
单元测试类
这里主要是单元测试类的关键内容,需要注意@BeforeEach是Junit5的注解,表示每个单元测试用例执行前会执行的方法其实对应Junit4的@Before
/**
* @SpringBootTest 默认不支持事务且自动回滚
* 使用@Transactional 开启事务,
* 使用@Rollback(false) 关闭自动回滚
* @author Null
* @date 2019-10-24
*/
@SpringBootTest
class QuerydslJpaDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CourseRepository courseRepository;
@Autowired
private LecturerRepository lecturerRepository;
@Autowired
private JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
/**
* 初始化数据
*/
@BeforeEach
public void initData(){
// 清空数据表
courseRepository.deleteAll();
lecturerRepository.deleteAll();
// 初始化讲师
Lecturer tom=new Lecturer();
tom.setName("Tom");
tom.setSex(true);
lecturerRepository.save(tom);
Lecturer marry=new Lecturer();
marry.setName("Marry");
marry.setSex(false);
lecturerRepository.save(marry);
// 初始化课程
Course chinese=new Course();
chinese.setName("Chinese");
chinese.setLecturerId(tom.getId());
courseRepository.save(chinese);
Course physics=new Course();
physics.setName("Physics");
physics.setLecturerId(tom.getId());
courseRepository.save(physics);
Course english=new Course();
english.setName("English");
english.setLecturerId(marry.getId());
courseRepository.save(english);
}
...省略各个用例
}
单表模糊查询
/**
* 根据课程名称模糊查询课程
*/
@Test
public void testSelectCourseByNameLike() {
// 组装查询条件
QCourse qCourse = QCourse.course;
// %要自行组装
BooleanExpression expression = qCourse.name.like("P%");
System.out.println(courseRepository.findAll(expression));
}
联表查询
/**
* 根据讲师姓名查课程
*/
@Test
public void testSelectCourseByLecturerName(){
QCourse qCourse = QCourse.course;
QLecturer qLecturer = QLecturer.lecturer;
// 这里包含了组装查询条件和执行查询的逻辑,组装好条件后记得执行fetch()
List<Course> courses=queryFactory.select(qCourse)
.from(qCourse)
.leftJoin(qLecturer)
.on(qCourse.lecturerId.eq(qLecturer.id))
.where(qLecturer.name.eq("Tom"))
.fetch();
System.out.println(courses);
}
更新
/**
* 根据姓名更新讲师性别<br/>
* 使用@Transactional开启事务<br/>
* 使用@Rollback(false)关闭自动回滚<br/>
*/
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void testUpdateLecturerSexByName(){
QLecturer qLecturer = QLecturer.lecturer;
// 更新Tom的性别为女性,返回的是影响记录条数
long num=queryFactory.update(qLecturer)
.set(qLecturer.sex,false)
.where(qLecturer.name.eq("Tom"))
.execute();
// 这里输出被更新的记录数
System.out.println(num);
}
删除
/**
* 根据根据性别删除讲师
*/
@Test
@Transactional
@Rollback(false)
public void testDeleteLecturerBySex(){
QLecturer qLecturer = QLecturer.lecturer;
// 删除性别为男性的讲师
long num=queryFactory.delete(qLecturer)
.where(qLecturer.sex.eq(true))
.execute();
// 输出被删除的记录数
System.out.println(num);
}
用例分析
从用例中可以看出其实QueryDSL的API更加切合原生的SQL,基本上从代码上就可以看出你希望执行的SQL了。
细心的朋友会发现QueryDSL是没有insert方法,因为JPA提供的save()方法已经足够处理了。
同时要记得要组装好你的SQL后别忘记调用fetch()或者execute()方法。
总结
Spring Boot JPA整合QueryDSL的关键步骤
- 引入依赖和插件
- 编写配置类
- 使用插件生成代码
- 标记生成文件为代码
- Repository继承QuerydslPredicateExecutor
QueryDSL的API类似原生SQL,API风格类似StringBuilder的API(Fluent API风格)。但是不提供insert对应的操作。
QueryDSL对于复杂的SQL的支持十分友好,算是对于JPA对这块需求的补充和完善。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
