目录
- 简介
- 使用axios
- 配置对象常用的配置项:
- 默认配置
- axios拦截器
- 取消请求
- 总结
简介
本文主要讲解axios的概念和基本使用。
axios时目前最流行的ajax封装库之一,用于很方便地实现ajax请求的发送。
支持的功能:
- 从浏览器发出 XMLHttpRequests请求。
- 从 node.js 发出 http 请求。
- 支持 Promise API。
- 能拦截请求和响应。
- 能转换请求和响应数据。
- 取消请求。
- 实现JSON数据的自动转换。
- 客户端支持防止 XSRF攻击。
先借助json-server创建一个简单的服务,供ajax发送请求,json-server是一个简单的可以接收restful的服务。
github地址:https://github.com/typicode/json-server
第一步:安装:npm install -g json-server
第二步:创建一个名为db.json的文件,把网站的数据复制进去。
{
"posts": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "json-server", "author": "typicode" }
],
"comments": [
{ "id": 1, "body": "some comment", "postId": 1 }
],
"profile": { "name": "typicode" }
}
第三步:启动命令:json-server --watch db.json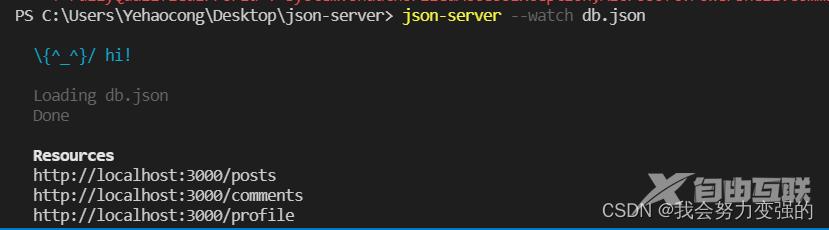
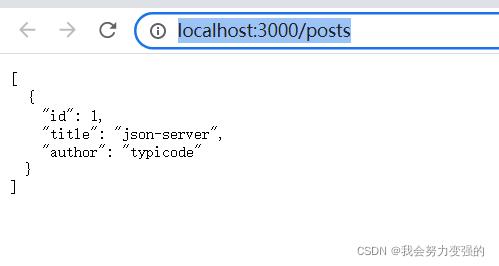
访问http://localhost:3000/posts 下面页面为成功
使用axios
GitHub地址:https://github.com/axios/axios
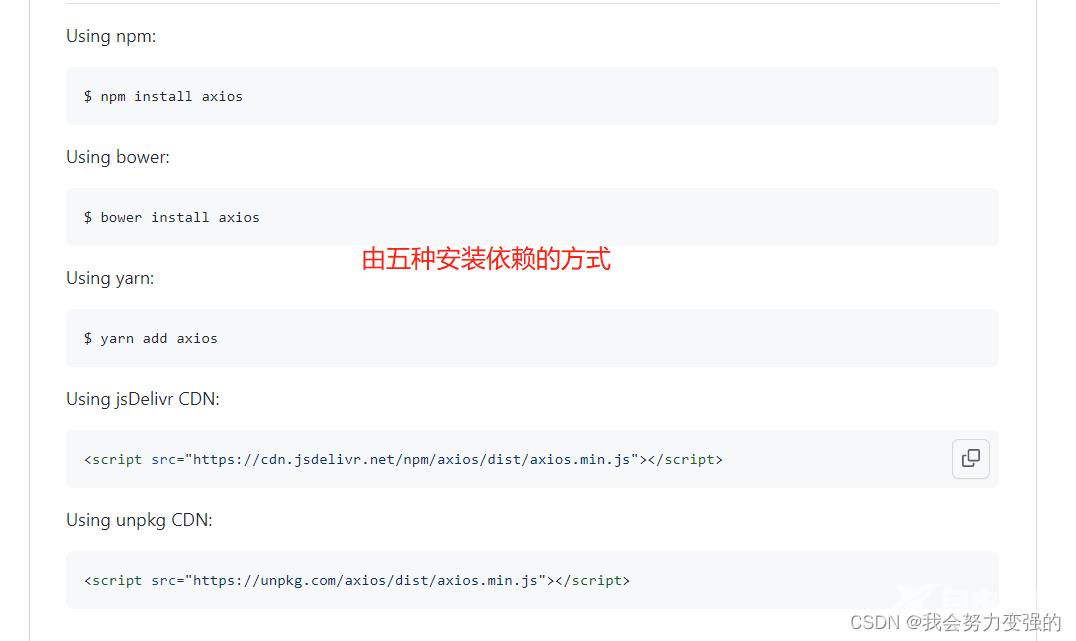
为了方便,我们直接使用第四种。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>axios基本使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn1">发送get请求</button> <br><br>
<button id="btn2">发送post请求</button><br><br>
<button id="btn3">发送put请求</button><br><br>
<button id="btn4">发送delete请求</button>
<hr>
<div>其他发送请求的api:</div><br><br>
<button id="btn5">发送get请求1</button> <br><br>
<button id="btn6">发送post请求1</button><br><br>
<button id="btn7">发送put请求1</button><br><br>
<button id="btn8">发送delete请求1</button>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
//发送get
document.getElementById("btn1").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"GET",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/1"
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送post
document.getElementById("btn2").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"POST",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts",
data:{
title:"axios学习",
author:"Yehaocong"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送put
document.getElementById("btn3").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"PUT",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2",
data:{
title:"axios学习",
author:"Liaoxiaoyan"
}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
document.getElementById("btn4").onclick = function(){
axios({
method:"DELETE",
url:"http://localhost:3000/posts/2",
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//其他发送请求的api
document.getElementById("btn5").onclick = function(){
//发送get,使用get,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时config配置对象
axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送post
document.getElementById("btn6").onclick = function(){
//发送post请求,第一个参数时url,第二个参数时请求体,第三个参数时config配置对象
axios.post("http://localhost:3000/posts",
{title:"axios学习2",
author:"Yehaocong2"})
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//发送put,
document.getElementById("btn7").onclick = function(){
//发送put,接收三个参数,url 请求体 、 config配置对象
axios.put("http://localhost:3000/posts/2",{title:"axios学习",
author:"Liaoxiaoyan"})
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
document.getElementById("btn8").onclick = function(){
//发送delete请求,接收2个参数, url config配置对象
axios.delete("http://localhost:3000/posts/3")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
};
//这个与axios({})基本相同
// axios.request({
// })
</script>
</html>
请求的响应结果结构分析:

配置对象常用的配置项:
{
// 路径url
url: '/user',
// 请求方法,默认get
method: 'get',
//基础url,最终请求的url是 baseURL+url拼接,所以再全局设置默认,可以使得发送请求时的url变得简洁
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
//设置请求头
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
//设置请求url的query参数,可以使得url简洁。
//比如url是https://some-domain.com/api/user 然后params如下设置,那么最终的url是:
//https://some-domain.com/api/user?ID=12345&name=Jack
params: {
ID: 12345,
name:"Jack"
},
//设置请求体
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
//设置请求的另外一种格式,不过这个是直接设置字符串的
data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte',
//请求超时,单位毫秒,默认0,不超时。
timeout: 1000,
//响应数据类型,默认json
responseType: 'json',
//响应数据的编码规则,默认utf-8
responseEncoding: 'utf8',
//响应体的最大长度
maxContentLength: 2000,
// 请求体的最大长度
maxBodyLength: 2000,
//设置响应状态码为多少时是成功,调用resolve,否则调用reject失败
//默认是大于等于200,小于300
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300;
},
默认配置
可以设置全局默认配置,是为了避免多种重复配置在不同请求中重复,比如baseURL、timeout等,这里设置baseURL。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>默认配置</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
axios.defaults.baseURL="http://localhost:3000";
//因为上面配置了baseURL,所以我们之后的请求只需要配置url不用像之前那样的全路径
axios.get("/posts/1")
.then(response=>{
console.log(response);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
axios拦截器
实质就是函数。
分为两种类型:
- 请求拦截器:用于拦截请求,自定义做一个逻辑后再把请求发送,可以用于配置公用的逻辑,就不用每个请求都配一遍。
- 响应拦截器:用于拦截响应,做一些处理后再出发响应回调。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>axios拦截器</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
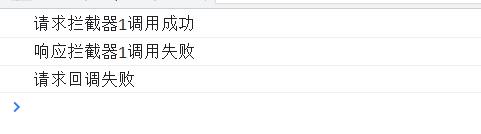
//这个是设置请求拦截器的api,传入两个回调,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调。
axios.interceptors.request.use(
function(config){
console.log("请求拦截器1调用成功");
return config;
},
function(error){
console.log("请求拦截器1调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
//这个是设置响应拦截器的api,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调
axios.interceptors.response.use(
function(response){
console.log("响应拦截器1调用成功");
return response;
},
function(error){
console.log("响应拦截器1调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
)
axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1")
.then(function(response){
//
console.log("请求回调成功");
}).catch(function(error){
console.log("请求回调失败");
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
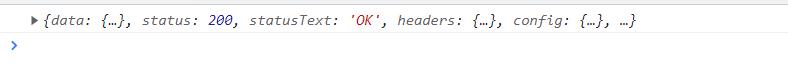
效果:
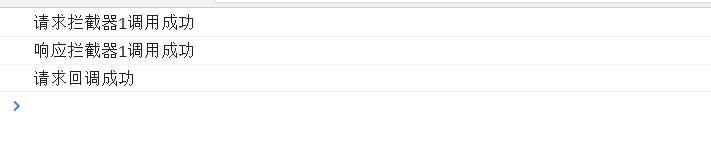
要理解这些个拦截器需要由一定的es6 Promise基础,出现上面效果的原因是,发送请求前,请求被请求拦截器拦截了,并且请求拦截器返回了一个非Promise实例的对象config,所以下一个拦截器是调用成功回调的,所以就打印响应拦截器成功,然后响应拦截器成功的回调返回的是非Promise实例的对象response,所以最终的请求回调是调用成功的回调,所以返回请求调用成功。
尝试以下再请求拦截器的成功回调中,返回reject状态的Promise。
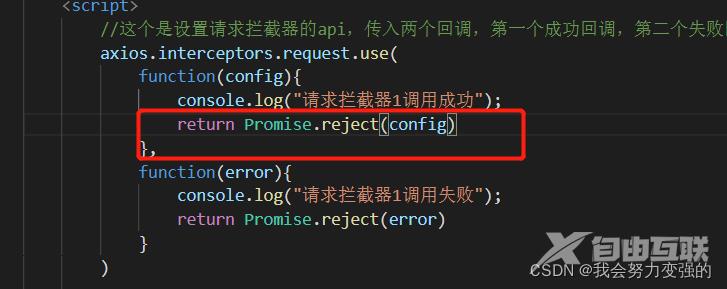
效果:
出现上面效果的原因是,请求拦截器的成功回调中最后返回了reject状态的Promise实例对象,被判断为失败,到了回调链的下一回调,也就是响应拦截器的回调时,调用的时失败的回调,失败的回调中又返回了reject状态的Promise实例对象,所以到了真正请求的回调页调用了失败回调。
上面的效果与Promise如出一辙。
多个拦截器的效果:加了一个请求拦截器一个响应拦截器:

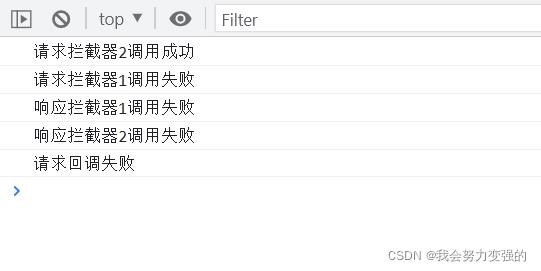
可以看到请求拦截器类似栈,后进先出,响应拦截器类似队列,先进先出。
可以在请求拦截器中对config进行调整,比如添加一个超时什么的,可以在响应拦截器中对response返回值进行调整,比如我返回到回调函数中只想要响应体部分。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>axios拦截器</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
//这个是设置请求拦截器的api,传入两个回调,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调。
axios.interceptors.request.use(
function(config){
console.log("请求拦截器1调用成功");
return config;
},
function(error){
console.log("请求拦截器1调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
axios.interceptors.request.use(
function(config){
//设置请求超时时间
config.timeout = 5000;
console.log("请求拦截器2调用成功");
return config;
},
function(error){
console.log("请求拦截器2调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
//这个是设置响应拦截器的api,第一个成功回调,第二个失败回调
axios.interceptors.response.use(
function(response){
console.log("响应拦截器1调用成功");
console.log(response);
//返回到请求回调时,只要data数据
return response.data;
},
function(error){
console.log("响应拦截器1调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
)
axios.interceptors.response.use(
function(response){
console.log("响应拦截器2调用成功");
return response;
},
function(error){
console.log("响应拦截器2调用失败");
return Promise.reject(error);
}
)
axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1")
.then(function(response){
//
console.log("请求回调成功");
console.log(response);
}).catch(function(error){
console.log("请求回调失败");
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:
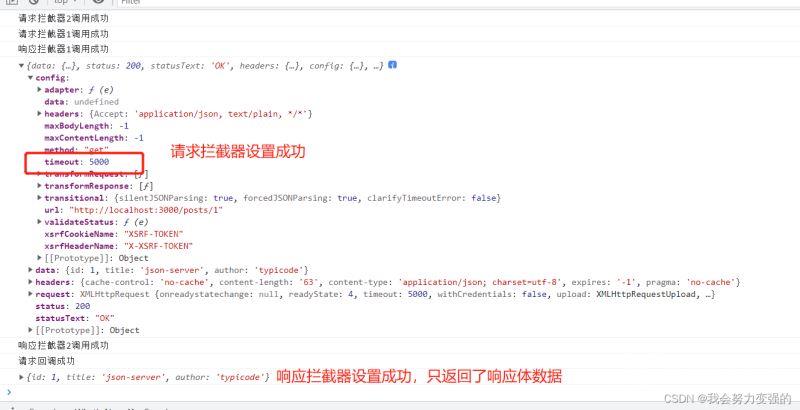
取消请求
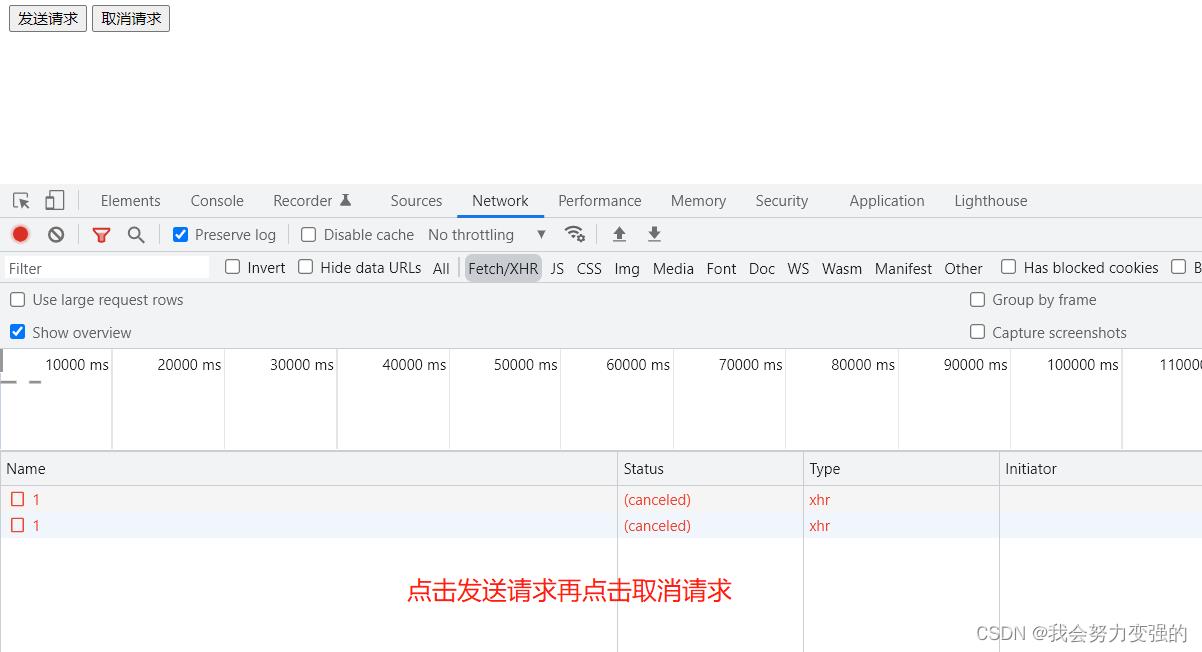
取消请求就是发送了请求后,等待一段时间得不到回应,可以取消他。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>axios取消请求</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn1">发送请求</button>
<button id="btn2">取消请求</button>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
//第一步:定义一个全局的cancel变量,初始值是null
let cancel = null;
document.getElementById("btn1").onclick = function(){
axios.get("http://localhost:3000/posts/1",
{
//第二步:在请求的配置对象中,配置cancelToken属性值,并把函数的c参数赋值给全局变量cancel
cancelToken:new axios.CancelToken(function(c){
cancel = c;
})
})
.then(function(response){
//
console.log(response);
}).catch(function(error){
console.log("请求回调失败");
})
}
document.getElementById("btn2").onclick = function(){
//第三步:调用cancel函数就是取消请求接收
cancel();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
需要把服务器的响应时间调到3秒,不然太快的话,演示不了取消请求。。
json-server --watch db.json -d 3000
总结
到此这篇关于axios概念介绍和基本使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关axios介绍和使用内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
