目录 概述 场景引入 MapProxy使用 MapProxy源码解析 总结 概述 Hutool是一个小而全的Java工具类库,通过静态方法封装,降低相关API的学习成本,提高工作效率,使Java拥有函数式语言般的优雅
目录
- 概述
- 场景引入
- MapProxy使用
- MapProxy源码解析
- 总结
概述
Hutool是一个小而全的Java工具类库,通过静态方法封装,降低相关API的学习成本,提高工作效率,使Java拥有函数式语言般的优雅,让Java语言也可以“甜甜的”。
目前公司项目中主要采用Hutool作为项目的工具包,相对于google的guava, hutool的工具类采用中文注释,更加符合国人使用。所谓知己知彼,我们需要了解Hutool都具有什么样的功能,才能够最大化发挥它的价值。
本文主要就hutool 5.8.8版本中MapProxy的使用。
场景引入
其实Map在get的时候是比较危险的,你可能不知道它是什么类型,需要进行强制,举个例子如下:
@Test
public void testMapProxy1() {
Map<String, Object> userMap = MapUtil.newHashMap(16);
userMap.put("username", "alvin");
userMap.put("age", 20);
// 使用map的时候, 需要进行强转,一旦类型错误,会报错
String age = (String)userMap.get("age");
}
运行结果:
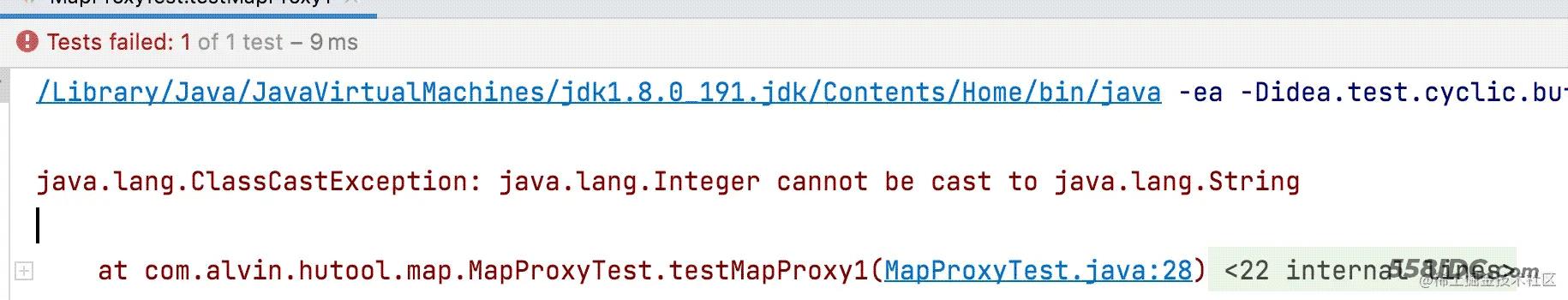
那有什么更好的解决方案吗?Hutool提供了一种解决方案给我们。
MapProxy使用
依赖引入
<dependency> <groupId>cn.hutool</groupId> <artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId> <version>5.8.8</version> </dependency>
定义一个可访问接口
interface MapUser {
String getUsername();
Integer getAge();
MapUser setAge(Integer age);
}
通过MapProxy访问
@Test
public void testMapProxy2() {
Map<String, Object> userMap = MapUtil.newHashMap(16);
userMap.put("username", "alvin");
userMap.put("age", 20);
MapProxy mapProxy = MapProxy.create(userMap);
Integer age = mapProxy.getInt("age", 18);
Assert.assertTrue(age == 20);
// 通过代理的方式
MapUser mapUser = mapProxy.toProxyBean(MapUser.class);
// 后续访问会变的更加安全
Assert.assertTrue(mapUser.getAge() == 20);
mapUser.setAge(30);
Assert.assertTrue(mapUser.getAge() == 30);
}
MapProxy源码解析
Map代理,提供各种getXXX方法,并提供默认值支持,它的类结构图如下:

- 实现了OptNullBasicTypeFromObjectGetter接口, 提供了基本类型的get, 在不提供默认值的情况下, 如果值不存在或获取错误,返回null, 比如:
mapProxy.getInt("age", 18)。 - 实现了InvocationHandler接口,支持jdk的动态代理,生成代理对象。
public <T> T toProxyBean(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoaderUtil.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass}, this);
}
- toProxyBean方法就是生成代理对象,最终会调用代理类的invoke方法,这里的代理类就是MapProxy本身。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
final Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 如果调用方法参数为空
if (ArrayUtil.isEmpty(parameterTypes)) {
final Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
// 方法返回值不是void
if (void.class != returnType) {
// 匹配Getter
final String methodName = method.getName();
String fieldName = null;
if (methodName.startsWith("get")) {
// 匹配getXXX
fieldName = StrUtil.removePreAndLowerFirst(methodName, 3);
} else if (BooleanUtil.isBoolean(returnType) && methodName.startsWith("is")) {
// 匹配isXXX
fieldName = StrUtil.removePreAndLowerFirst(methodName, 2);
}else if ("hashCode".equals(methodName)) {
return this.hashCode();
} else if ("toString".equals(methodName)) {
return this.toString();
}
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(fieldName)) {
if (false == this.containsKey(fieldName)) {
// 驼峰不存在转下划线尝试
fieldName = StrUtil.toUnderlineCase(fieldName);
}
return Convert.convert(method.getGenericReturnType(), this.get(fieldName));
}
}
// 如果方法参数不为空
} else if (1 == parameterTypes.length) {
// 匹配Setter
final String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.startsWith("set")) {
final String fieldName = StrUtil.removePreAndLowerFirst(methodName, 3);
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(fieldName)) {
this.put(fieldName, args[0]);
final Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
// 判断返回类型是不是代理类的实例
if(returnType.isInstance(proxy)){
return proxy;
}
}
} else if ("equals".equals(methodName)) {
return this.equals(args[0]);
}
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(method.toGenericString());
}
总结
本文主要讲解了Hutool中的MapProxy类的使用,希望对大家有帮助
以上就是Hutool开发利器MapProxy类使用技巧详解的详细内容,更多关于Hutool开发MapProxy类的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
