目录
- 一、背景
- 二、源码分析
- 2.1 问题1:为什么需要 NonNul 检查 ?
- 2.1.1 怎么检查的?
- 2.1.2 为什么要做这个检查呢?
- 2.2 问题2: 为什么不根据当前系统类型来获取分隔符?
- 三、Zoom Out
- 3.1 代码健壮性
- 3.2 代码严谨性
- 3.3 如何写注释
- 四、总结
一、背景
最近用到了 org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils#getName 这个方法,该方法可以传入文件路径,获取文件名。 简单看了下源码,虽然并不复杂,但和自己设想略有区别,值得学习,本文简单分析下。
二、源码分析
org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils#getName
/**
* Gets the name minus the path from a full fileName.
* <p>
* This method will handle a file in either Unix or Windows format.
* The text after the last forward or backslash is returned.
*
<pre>
* a/b/c.txt --> c.txt
* a.txt --> a.txt
* a/b/c --> c
* a/b/c/ --> ""
* </pre>
* <p>
* The output will be the same irrespective of the machine that the code is running on.
*
* @param fileName the fileName to query, null returns null
* @return the name of the file without the path, or an empty string if none exists.
* Null bytes inside string will be removed
*/
public static String getName(final String fileName) {
// 传入 null 直接返回 null
if (fileName == null) {
return null;
}
// NonNul 检查
requireNonNullChars(fileName);
// 查找最后一个分隔符
final int index = indexOfLastSeparator(fileName);
// 从最后一个分隔符窃到最后
return fileName.substring(index + 1);
}
2.1 问题1:为什么需要 NonNul 检查 ?
2.1.1 怎么检查的?
org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils#requireNonNullChars
/**
* Checks the input for null bytes, a sign of unsanitized data being passed to to file level functions.
*
* This may be used for poison byte attacks.
*
* @param path the path to check
*/
private static void requireNonNullChars(final String path) {
if (path.indexOf(0) >= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Null byte present in file/path name. There are no "
+ "known legitimate use cases for such data, but several injection attacks may use it");
}
}
java.lang.String#indexOf(int) 源码:
/**
* Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of
* the specified character. If a character with value
* {@code ch} occurs in the character sequence represented by
* this {@code String} object, then the index (in Unicode
* code units) of the first such occurrence is returned. For
* values of {@code ch} in the range from 0 to 0xFFFF
* (inclusive), this is the smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.charAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
* </pre></blockquote>
* is true. For other values of {@code ch}, it is the
* smallest value <i>k</i> such that:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.codePointAt(<i>k</i>) == ch
* </pre></blockquote>
* is true. In either case, if no such character occurs in this
* string, then {@code -1} is returned.
*
* @param ch a character (Unicode code point).
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
* character sequence represented by this object, or
* {@code -1} if the character does not occur.
*/
public int indexOf(int ch) {
return indexOf(ch, 0);
}
可知,indexOf(0) 目的是查找 ASCII 码为 0 的字符的位置,如果找到则抛出 IllegalArgumentException异常。 搜索 ASCII 对照表,得知 ASCII 值为 0 代表控制字符 NUT,并不是常规的文件名所应该包含的字符。
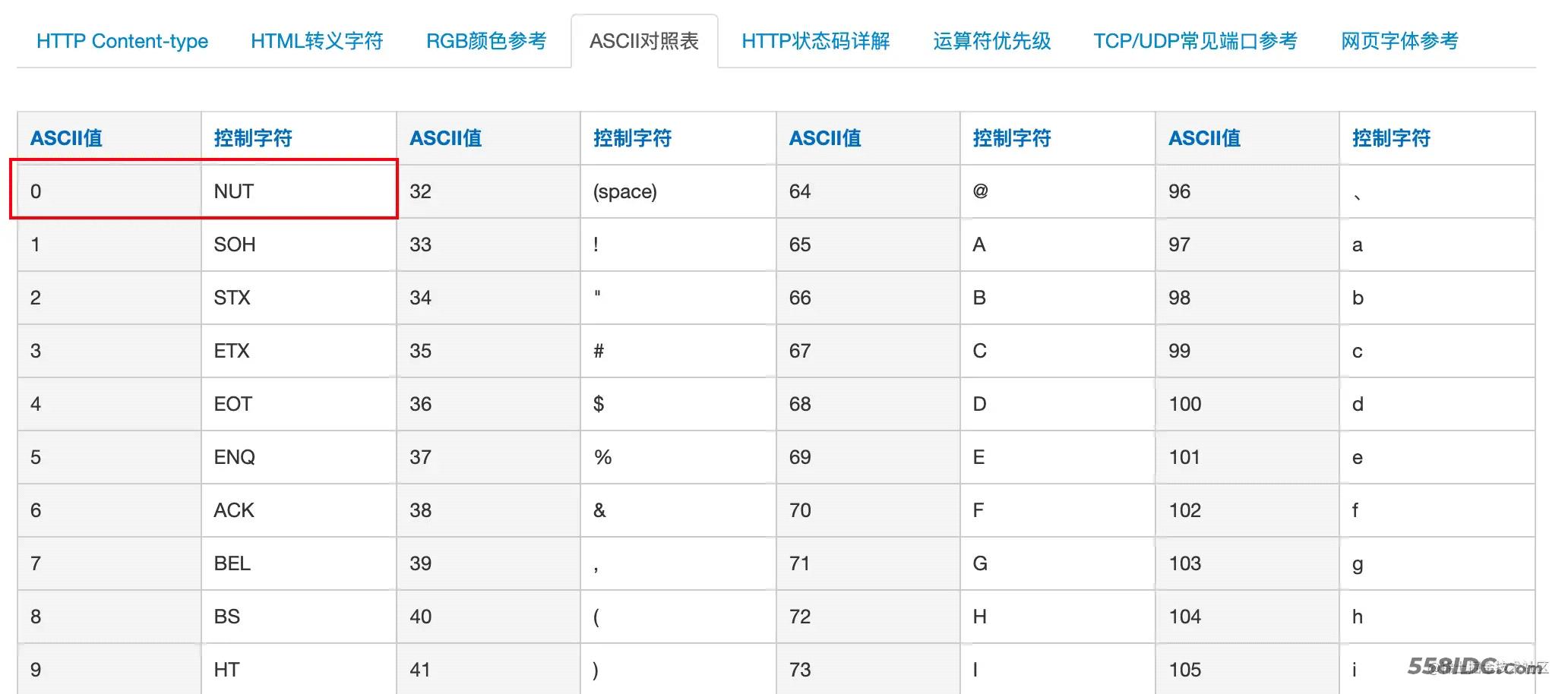
2.1.2 为什么要做这个检查呢?
null 字节是一个值为 0 的字节,如十六进制中的 0x00。 存在与 null 字节有关的安全漏洞。 因为 C 语言中使用 null 字节作为字符串终结符,而其他语言(Java,PHP等)没有这个字符串终结符; 例如,Java Web 项目只允许用户上传 .jpg 格式的图片,但利用这个漏洞就可以上传 .jsp 文件。 如用户上传 hack.jsp<NUL>.jpg 文件, Java 会认为符合 .jpg 格式,实际调用 C 语言系统函数写入磁盘时讲 当做字符串分隔符,结果将文件保存为 hack.jsp。 有些编程语言不允许在文件名中使用 ·· <NUL>,如果你使用的编程语言没有对此处理,就需要自己去处理。 因此,这个检查很有必要。
代码示例:
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils;
public class FilenameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename= "hack.jsp\0.jpg";
System.out.println( FilenameUtils.getName(filename));
}
}
报错信息:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Null byte present in file/path name. There are no known legitimate use cases for such data, but several injection attacks may use it
at org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils.requireNonNullChars(FilenameUtils.java:998)
at org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils.getName(FilenameUtils.java:984)
at org.example.FilenameDemo.main(FilenameDemo.java:8)
如果去掉校验:
package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils;
public class FilenameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename= "hack.jsp\0.jpg";
// 不添加校验
String name = getName(filename);
// 获取拓展名
String extension = FilenameUtils.getExtension(name);
System.out.println(extension);
}
public static String getName(final String fileName) {
if (fileName == null) {
return null;
}
final int index = FilenameUtils.indexOfLastSeparator(fileName);
return fileName.substring(index + 1);
}
}
Java 的确会将拓展名识别为 jpg
jpg
JDK 8 及其以上版本试图创建 hack.jsp\0.jpg 的文件时,底层也会做类似的校验,无法创建成功。
大家感兴趣可以试试使用 C 语言写入名为 hack.jsp\0.jpg 的文件,最终很可能文件名为 hack.jsp。
2.2 问题2: 为什么不根据当前系统类型来获取分隔符?
查找最后一个分隔符 org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils#indexOfLastSeparator
/**
* Returns the index of the last directory separator character.
* <p>
* This method will handle a file in either Unix or Windows format.
* The position of the last forward or backslash is returned.
* <p>
* The output will be the same irrespective of the machine that the code is running on.
*
* @param fileName the fileName to find the last path separator in, null returns -1
* @return the index of the last separator character, or -1 if there
* is no such character
*/
public static int indexOfLastSeparator(final String fileName) {
if (fileName == null) {
return NOT_FOUND;
}
final int lastUnixPos = fileName.lastIndexOf(UNIX_SEPARATOR);
final int lastWindowsPos = fileName.lastIndexOf(WINDOWS_SEPARATOR);
return Math.max(lastUnixPos, lastWindowsPos);
}
该方法的语义是获取文件名,那么从函数的语义层面上来说,不管是啥系统的文件分隔符都必须要保证得到正确的文件名。 试想一下,在 Windows 系统上调用该函数,传入一个 Unix 文件路径,得不到正确的文件名合理吗? 函数设计本身就应该考虑兼容性。 因此不能获取当前系统的分隔符来截取文件名。 源码中分别获取 Window 和 Unix 分隔符,有哪个用哪个,显然更加合理。
三、Zoom Out
3.1 代码健壮性
我们日常编码时,要做防御性编程,对于错误的、非法的输入都要做好预防。
3.2 代码严谨性
我们写代码一定不要想当然。 我们先想清楚这个函数究竟要实现怎样的功能,而且不是做一个 “CV 工程师”,无脑“拷贝”代码。 同时,我们也应该写好单测,充分考虑各种异常 Case ,保证正常和异常的 Case 都覆盖到。
3.3 如何写注释
org.apache.commons.io.FilenameUtils#requireNonNullChars 函数注释部分就给出了这么设计的原因:This may be used for poison byte attacks.
注释不应该“喃喃自语”讲一些显而易见的废话。 对于容易让人困惑的设计,一定要通过注释讲清楚设计原因。
此外,结合工作经验,推荐一些其他注释技巧: (1)对于稍微复杂或者重要的设计,可以通过注释给出核心的设计思路; 如: java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor#execute
/**
* Executes the given task sometime in the future. The task
* may execute in a new thread or in an existing pooled thread.
*
* If the task cannot be submitted for execution, either because this
* executor has been shutdown or because its capacity has been reached,
* the task is handled by the current {@link RejectedExecutionHandler}.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @throws RejectedExecutionException at discretion of
* {@code RejectedExecutionHandler}, if the task
* cannot be accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code command} is null
*/
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
(2)对于关联的代码,可以使用 @see 或者 {@link } 的方式,在代码中提供关联代码的快捷跳转方式。
/**
* Sets the core number of threads. This overrides any value set
* in the constructor. If the new value is smaller than the
* current value, excess existing threads will be terminated when
* they next become idle. If larger, new threads will, if needed,
* be started to execute any queued tasks.
*
* @param corePoolSize the new core size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code corePoolSize < 0}
* or {@code corePoolSize} is greater than the {@linkplain
* #getMaximumPoolSize() maximum pool size}
* @see #getCorePoolSize
*/
public void setCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int delta = corePoolSize - this.corePoolSize;
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
if (workerCountOf(ctl.get()) > corePoolSize)
interruptIdleWorkers();
else if (delta > 0) {
// We don't really know how many new threads are "needed".
// As a heuristic, prestart enough new workers (up to new
// core size) to handle the current number of tasks in
// queue, but stop if queue becomes empty while doing so.
int k = Math.min(delta, workQueue.size());
while (k-- > 0 && addWorker(null, true)) {
if (workQueue.isEmpty())
break;
}
}
}
(2)在日常业务开发中,非常推荐讲相关的文档、配置页面链接也放到注释中,极大方便后期维护。 如:
/**
* 某某功能
*
* 相关文档:
* <a href="https://blog.csdn.net/w605283073" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >设计文档</a>
* <a href="https://blog.csdn.net/w605283073" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >三方API地址</a>
*/
public void demo(){
// 省略
}
(4)对于工具类可以考虑讲给出常见的输入对应的输出。 如 org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils#center(java.lang.String, int, char)
/**
* <p>Centers a String in a larger String of size {@code size}.
* Uses a supplied character as the value to pad the String with.</p>
*
* <p>If the size is less than the String length, the String is returned.
* A {@code null} String returns {@code null}.
* A negative size is treated as zero.</p>
*
* <pre>
* StringUtils.center(null, *, *) = null
* StringUtils.center("", 4, ' ') = " "
* StringUtils.center("ab", -1, ' ') = "ab"
* StringUtils.center("ab", 4, ' ') = " ab "
* StringUtils.center("abcd", 2, ' ') = "abcd"
* StringUtils.center("a", 4, ' ') = " a "
* StringUtils.center("a", 4, 'y') = "yayy"
* </pre>
*
* @param str the String to center, may be null
* @param size the int size of new String, negative treated as zero
* @param padChar the character to pad the new String with
* @return centered String, {@code null} if null String input
* @since 2.0
*/
public static String center(String str, final int size, final char padChar) {
if (str == null || size <= 0) {
return str;
}
final int strLen = str.length();
final int pads = size - strLen;
if (pads <= 0) {
return str;
}
str = leftPad(str, strLen + pads / 2, padChar);
str = rightPad(str, size, padChar);
return str;
}
(5) 对于废弃的方法,一定要注明废弃的原因,给出替代方案。 如:java.security.Signature#setParameter(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object)
/**
* 省略部分
*
* @see #getParameter
*
* @deprecated Use
* {@link #setParameter(java.security.spec.AlgorithmParameterSpec)
* setParameter}.
*/
@Deprecated
public final void setParameter(String param, Object value)
throws InvalidParameterException {
engineSetParameter(param, value);
}
四、总结
很多优秀的开源项目的代码设计都非常严谨,往往简单的代码中也蕴藏着缜密的思考。 我们有时间可以看看一些优秀的开源项目,可以从简单的入手,可以先想想如果自己写大概该如何实现,然后和作者的实现思路对比,会有更大收获。 平时看源码时,不仅要知道源码长这样,更要了解为什么这么设计。
以上就是FilenameUtils.getName 函数源码分析的详细内容,更多关于FilenameUtils.getName 函数的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
