目录
- Starter机制和springboot整合tomcat
- Starter机制
- springboot整合tomcat
- 总结
Starter机制和springboot整合tomcat
Starter机制
先解释一下什么是Starter机制。Starter机制就是maven工程中pom文件引入了某个Starter依赖,就能使用对应的功能 例如 引入web的starter依赖 ,就可以使用有关于web方面的功能。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
那么这个 Starter机制是怎么运作的呢?当我们在项目的pom.xml文件中添加某个Starter依赖时,其实就是简单的添加了很多其他的依赖,比如:
- spring-boot-starter-web:引入了spring-boot-starter、spring-boot-starter-json、spring-boot-starter-tomcat等和Web开发相关的依赖包
- spring-boot-starter-tomcat:引入了tomcat-embed-core、tomcat-embed-el、tomcat-embed-websocket等和Tomcat相关的依赖包
通过springboot自动配置的原理从META-INF/spring.factories中获取到tomcat自动配置类。通过各种条件注解类判断是否满足加载tomcat自动配置类的条件。这样就完成了 Starter机制
如果我们在项目中要用Tomcat,那就依赖spring-boot-starter-web就够了,因为它默认依赖了spring-boot-starter-tomcat,从而依赖了Tomcat,从而Tomcat相关的Bean能生效。
而如果不想用Tomcat,那就得这么写:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
springboot整合tomcat
通过前面SpringBoot的自动配置机制、Starter机制,条件注解分析等,我们拿一个实际的业务案例来串讲一下,那就是SpringBoot和Tomcat的整合。
我们知道,只要我们的项目添加的starter为:spring-boot-starter-web,那么我们启动项目时,SpringBoot就会自动启动一个Tomcat。
那么这是怎么做到的呢?
首先我们可以发现,在spring-boot-starter-web这个starter中,其实间接的引入了spring-bootstarter-tomcat这个starter,这个spring-boot-starter-tomcat又引入了tomcat-embed-core依赖,
所以只要我们项目中依赖了spring-boot-starter-web就相当于依赖了Tomcat。
从这个spring-boot-starter-web依赖中引入了tomcat的依赖

又从tomcat的依赖中引入了tomcat相关的依赖
那么来看下springboot如何启动web容器的。
首先我们知道springboot启动通过SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);,进入run方法,会调到如下代码

这个run方法中的有一个refreshContext(context);方法。refreshContext(context);方法经过一系列调用到ServletWebServerApplicationContext的onRefresh()方法
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 启动Tomcat
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
重点就是createWebServer();方法。这个方法中就启动了tomcat
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//ServletWebServerFactory 一个接口 实现类有TomcatServletWebServerFactory 等等容器工厂
//通过getWebServerFactory() 获取到对应容器的创建工厂
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
//通过实现类的getWebServer来启动对应的容器
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
createWebServer();中核心代码是ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();和this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());。我们一步步分析这两个方法。
首先ServletWebServerFactory 是一个接口,它的实现类有
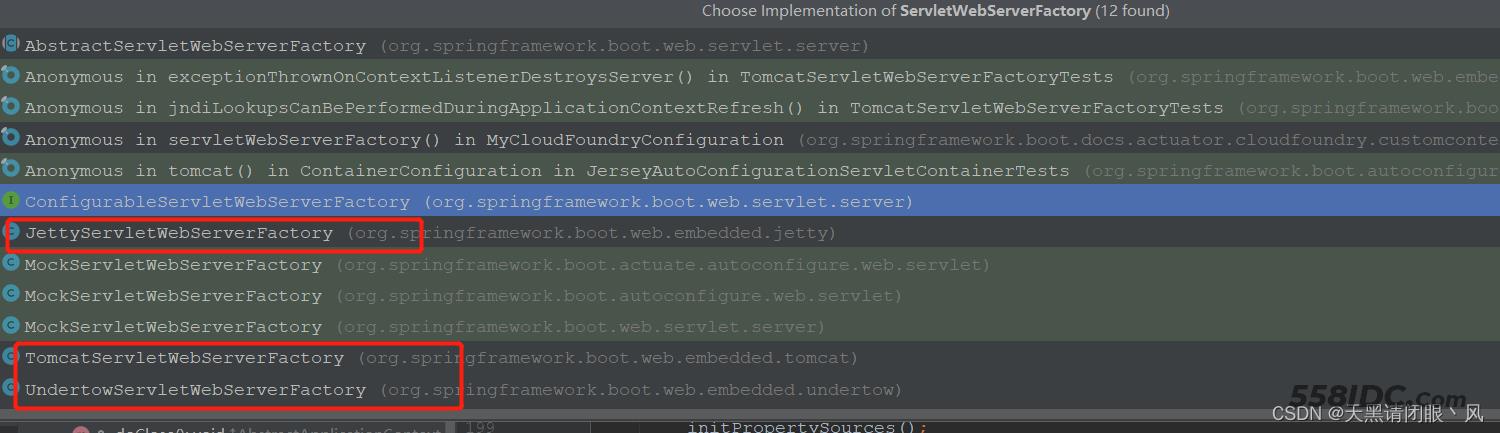
那么它会用到哪个实现类呢?这个就和ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();方法有关
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
//获取到ServletWebServerFactory 所有实现类的bean的名称 也就是springboot中配置了哪些容器 如tomcat jetty等
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
//如果没有bean 表示没有配置容器
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
//如果bean大于1 表示配置了多个容器
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
//最终返回唯一的容器工厂 比如配置了tomcat 那么就返回了TomcatServletWebServerFactory
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
这个方法中,先获取所有ServletWebServerFactory类型的beanName,如果为空或者大于一个,就会抛异常,也就是说如果配置了tomcat又配置jetty,就会有两个ServletWebServerFactory类型的beanName,那么就会抛出异常。
判断通过后,通过beanName和类型从bean工厂中获取到唯一的ServletWebServerFactory,然后返回。重点就是ServletWebServerFactory类型的bean是什么时候配置进去的。这个就是涉及到web的自动配置类。
在MATE-INF/spring.factories中有一个ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration的自动配置类。
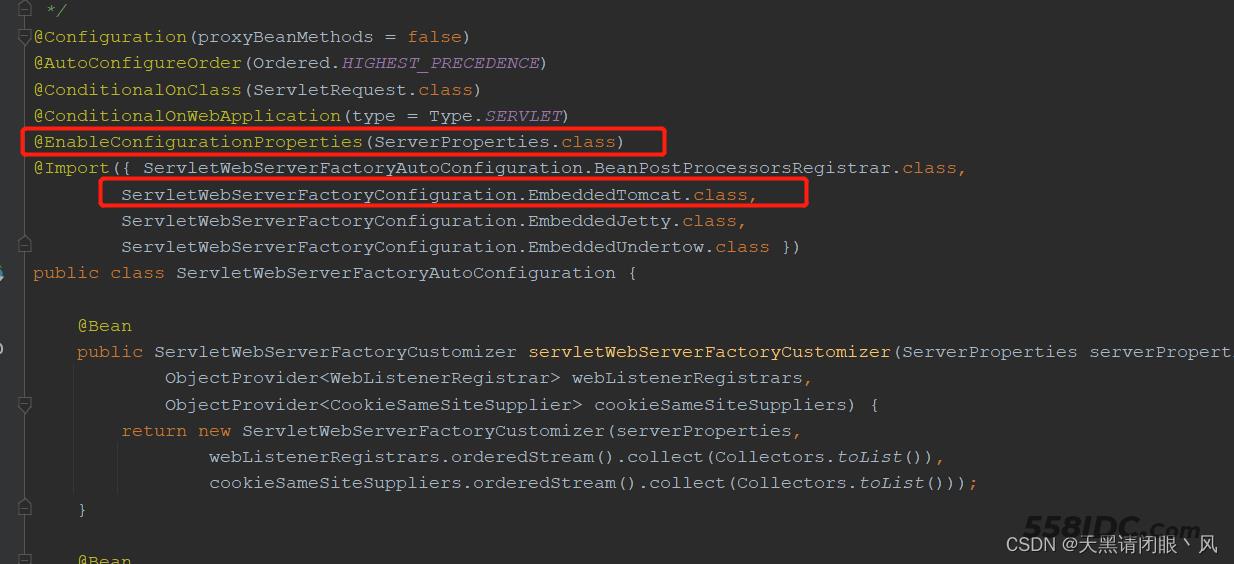
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)注解会去加载ServerProperties
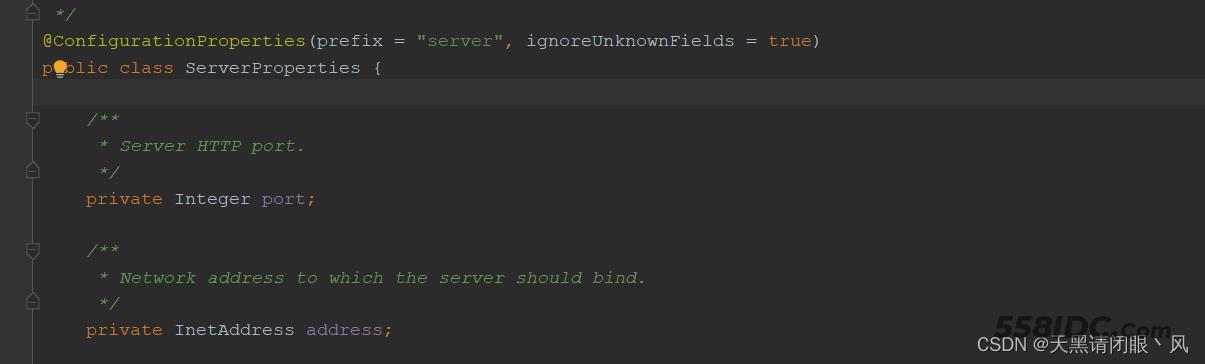
@ConfigurationProperties注解会从配置文件中读取对应的信息到ServerProperties的属性上,所以我们在配置文件定义端口号,地址等等就会被识别。
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration的自动配置类通过@Import注解导入了ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,

EmbeddedTomcat.class定义了TomcatServletWebServerFactory,所以回到之前的getWebServerFactory(),拿到的就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory。然后调用factory.getWebServer来启动容器。实际上就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer方法
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
for (LifecycleListener listener : this.serverLifecycleListeners) {
tomcat.getServer().addLifecycleListener(listener);
}
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
这个方法一目了然,就是new Tomcat(),然后启动。
这大致就是springboot整合tomcat的流程。如果整合的是jetty,那么拿到的ServletWebServerFactory类型就是JettyServletWebServerFactory,过程是一样的。
总结
springboot整合tomcat的过程中,首先通过依赖导入了tomcat的相关依赖。通过ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration自动配置类,加载EmbeddedTomcat,也就是加载了TomcatServletWebServerFactory。通过TomcatServletWebServerFactory的getWebServer方法启动tomcat。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot Starter机制及整合tomcat的实现详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot Starter机制内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
