一、Nacos服务心跳
1.1、客户端心跳
Nacos Client会维护一个定时任务通过持续调用服务端的接口更新心跳时间,保证自己处于存活状态,防止服务端将服务剔除,Nacos默认5秒向服务端发送一次,通过请求服务端接口**/instance/beat**发送心跳。
客户端服务在注册服务
根据nacos-discovery的META-INF目录下的spring.factories配置来完成相关类的自动装配。

- NacosServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration用来注册管理这几个bean。
-
NacosServiceRegistry:完成服务注册,实现ServiceRegistry。
-
NacosRegistration:用来注册时存储nacos服务端的相关信息。
-
NacosAutoServiceRegistration 继承spring中的AbstractAutoServiceRegistration,AbstractAutoServiceRegistration实现ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent>,通过事件监听来发起服务注册,到时候会调用NacosServiceRegistry.register(registration)
在NacosServiceRegistry.registry方法中,调用了nacos client sdk中的namingService.registerInstance完成服务注册。
public class NacosServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry<Registration> { @Override public void register(Registration registration) { if (StringUtils.isEmpty(registration.getServiceId())) { log.warn("No service to register for nacos client..."); return; } NamingService namingService = namingService(); String serviceId = registration.getServiceId(); String group = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getGroup(); Instance instance = getNacosInstanceFromRegistration(registration); try { namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance); log.info("nacos registry, {} {} {}:{} register finished", group, serviceId, instance.getIp(), instance.getPort()); } catch (Exception e) { if (nacosDiscoveryProperties.isFailFast()) { log.error("nacos registry, {} register failed...{},", serviceId, registration.toString(), e); rethrowRuntimeException(e); } else { log.warn("Failfast is false. {} register failed...{},", serviceId, registration.toString(), e); } } } }继续看namingService.registerInstance的实现主要就两件事
-
1、beatReactor.addBeatInfo创建心跳信息实现健康检查,Nacos Server必须要确保注册的服务实例是健康的,而心跳检测就是服务监控检测的方式。
-
2、serverProxy.registerService 服务注册。
看下BeatInfo这个类
- 给周期任务设定时间beatInfo.setPeriod(instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval())
接下来我们看下addBeatInfo方法,该方法内部主要是将BeatTask任务加入到线程池ScheduledExecutorService当中。
public class BeatReactor implements Closeable { private final ScheduledExecutorService executorService; private final NamingProxy serverProxy; public BeatReactor(NamingProxy serverProxy, int threadCount) { this.serverProxy = serverProxy; //实例化客户端心跳机制线程池 this.executorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(threadCount, new ThreadFactory() { @Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { Thread thread = new Thread(r); thread.setDaemon(true); thread.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.naming.beat.sender"); return thread; } }); } public void addBeatInfo(String serviceName, BeatInfo beatInfo) { NAMING_LOGGER.info("[BEAT] adding beat: {} to beat map.", beatInfo); String key = buildKey(serviceName, beatInfo.getIp(), beatInfo.getPort()); BeatInfo existBeat = null; //fix #1733 if ((existBeat = dom2Beat.remove(key)) != null) { existBeat.setStopped(true); } dom2Beat.put(key, beatInfo); //将心跳任务添加到线程池中,发起一个心跳检测任务 executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), beatInfo.getPeriod(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); MetricsMonitor.getDom2BeatSizeMonitor().set(dom2Beat.size()); } }重点部分就是看BeatTask
BeatTask继承Runnable,run方法就是我们的重点,该方法调用了NamingProxy的sendBeat方法,服务端请求地址为**/instance/beat**的方法。
public class BeatReactor implements Closeable { private final ScheduledExecutorService executorService; private final NamingProxy serverProxy; class BeatTask implements Runnable { BeatInfo beatInfo; public BeatTask(BeatInfo beatInfo) { this.beatInfo = beatInfo; } @Override public void run() { if (beatInfo.isStopped()) { return; } //心跳周期执行时间 long nextTime = beatInfo.getPeriod(); try { //向Nacos Server服务端发送心跳请求 JsonNode result = serverProxy.sendBeat(beatInfo, BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled); long interval = result.get("clientBeatInterval").asLong(); boolean lightBeatEnabled = false; if (result.has(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED)) { lightBeatEnabled = result.get(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED).asBoolean(); } BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled = lightBeatEnabled; if (interval > 0) { nextTime = interval; } int code = NamingResponseCode.OK; if (result.has(CommonParams.CODE)) { code = result.get(CommonParams.CODE).asInt(); } //如果返回资源未找到,则立即重新注册服务 if (code == NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND) { Instance instance = new Instance(); instance.setPort(beatInfo.getPort()); instance.setIp(beatInfo.getIp()); instance.setWeight(beatInfo.getWeight()); instance.setMetadata(beatInfo.getMetadata()); instance.setClusterName(beatInfo.getCluster()); instance.setServiceName(beatInfo.getServiceName()); instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId()); instance.setEphemeral(true); try { //发送http请求,向Nacos Server服务端注册服务 serverProxy.registerService(beatInfo.getServiceName(), NamingUtils.getGroupName(beatInfo.getServiceName()), instance); } catch (Exception ignore) { } } } catch (NacosException ex) { NAMING_LOGGER.error("[CLIENT-BEAT] failed to send beat: {}, code: {}, msg: {}", JacksonUtils.toJson(beatInfo), ex.getErrCode(), ex.getErrMsg()); } catch (Exception unknownEx) { NAMING_LOGGER.error("[CLIENT-BEAT] failed to send beat: {}, unknown exception msg: {}", JacksonUtils.toJson(beatInfo), unknownEx.getMessage(), unknownEx); } finally { //定时去运行,发送心跳请求 executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), nextTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } } } public class NamingProxy implements Closeable { //向Nacos Server服务端发送心跳请求 public JsonNode sendBeat(BeatInfo beatInfo, boolean lightBeatEnabled) throws NacosException { if (NAMING_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { NAMING_LOGGER.debug("[BEAT] {} sending beat to server: {}", namespaceId, beatInfo.toString()); } Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>(8); Map<String, String> bodyMap = new HashMap<String, String>(2); if (!lightBeatEnabled) { bodyMap.put("beat", JacksonUtils.toJson(beatInfo)); } params.put(CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, namespaceId); params.put(CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME, beatInfo.getServiceName()); params.put(CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, beatInfo.getCluster()); params.put("ip", beatInfo.getIp()); params.put("port", String.valueOf(beatInfo.getPort())); String result = reqApi(UtilAndComs.nacosUrlBase + "/instance/beat", params, bodyMap, HttpMethod.PUT); return JacksonUtils.toObj(result); } //发送http请求,向Nacos Server服务端注册服务 public void registerService(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException { NAMING_LOGGER.info("[REGISTER-SERVICE] {} registering service {} with instance: {}", namespaceId, serviceName, instance); final Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>(16); params.put(CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, namespaceId); params.put(CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME, serviceName); params.put(CommonParams.GROUP_NAME, groupName); params.put(CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, instance.getClusterName()); params.put("ip", instance.getIp()); params.put("port", String.valueOf(instance.getPort())); params.put("weight", String.valueOf(instance.getWeight())); params.put("enable", String.valueOf(instance.isEnabled())); params.put("healthy", String.valueOf(instance.isHealthy())); params.put("ephemeral", String.valueOf(instance.isEphemeral())); params.put("metadata", JacksonUtils.toJson(instance.getMetadata())); reqApi(UtilAndComs.nacosUrlInstance, params, HttpMethod.POST); } }心跳实际就是通过schedule定时向server发送数据包,然后启动一个线程检测服务端的返回,如果在指定时间没有返回则认为服务端出了问题,服务端也会根据发来的心跳包不断更新服务的状态。
1.2、服务端心跳
接下来我们把目光放到服务端,找到InstanceController的beat方法,如果是参数beat信息的话,说明是第一次发起心跳,则会带有服务实例信息,因为发起心跳成功则服务端会返回下次不要带beat信息的参数,这样客户端第二次就不会携带beat信息了。如果发现没有该服务,又没带beat信息,说明这个服务可能被移除过了,直接返回没找到。如果没有服务,但是发现有beat信息,那就从beat中获取服务实例信息,进行注册:
看InstanceController的beat方法
@RestController @RequestMapping(UtilsAndCommons.NACOS_NAMING_CONTEXT + "/instance") public class InstanceController { @CanDistro @PutMapping("/beat") @Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE) public ObjectNode beat(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode(); //设置心跳间隔 result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, switchDomain.getClientBeatInterval()); String beat = WebUtils.optional(request, "beat", StringUtils.EMPTY); RsInfo clientBeat = null; //判断有无心跳内容 //如果存在心跳内容则不是轻量级心跳就转化为RsInfo if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beat)) { clientBeat = JacksonUtils.toObj(beat, RsInfo.class); } String clusterName = WebUtils .optional(request, CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME); String ip = WebUtils.optional(request, "ip", StringUtils.EMPTY); int port = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "port", "0")); if (clientBeat != null) { if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(clientBeat.getCluster())) { clusterName = clientBeat.getCluster(); } else { // fix #2533 clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName); } ip = clientBeat.getIp(); port = clientBeat.getPort(); } String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID); String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME); NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName); Loggers.SRV_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] full arguments: beat: {}, serviceName: {}", clientBeat, serviceName); //获取对应的实例的信息 Instance instance = serviceManager.getInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, clusterName, ip, port); //如果实例不存在 if (instance == null) { //并且心跳内容也不存在 if (clientBeat == null) { result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND); //返回RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND给客户端,客户端会发起服务注册 return result; } Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("[CLIENT-BEAT] The instance has been removed for health mechanism, " + "perform data compensation operations, beat: {}, serviceName: {}", clientBeat, serviceName); //根据心跳内容创建一个实例信息 instance = new Instance(); instance.setPort(clientBeat.getPort()); instance.setIp(clientBeat.getIp()); instance.setWeight(clientBeat.getWeight()); instance.setMetadata(clientBeat.getMetadata()); instance.setClusterName(clusterName); instance.setServiceName(serviceName); instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId()); instance.setEphemeral(clientBeat.isEphemeral()); //注册实例 serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance); } //获取服务的信息 Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName); if (service == null) { throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, "service not found: " + serviceName + "@" + namespaceId); } //不存在心跳内容的话,要创建一个进行处理 if (clientBeat == null) { clientBeat = new RsInfo(); clientBeat.setIp(ip); clientBeat.setPort(port); clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName); } service.processClientBeat(clientBeat); result.put(CommonParams.CODE, NamingResponseCode.OK); //5秒间隔 if (instance.containsMetadata(PreservedMetadataKeys.HEART_BEAT_INTERVAL)) { result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval()); } //告诉客户端不需要带上心跳信息了,变成轻量级心跳了 result.put(SwitchEntry.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED, switchDomain.isLightBeatEnabled()); return result; } }接下来看一下processClientBeat方法,该方法将ClientBeatProcessor放入到线程池中,接下来我们看下重点看下run方法,
public class Service extends com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.pojo.Service implements Record, RecordListener<Instances> { public void processClientBeat(final RsInfo rsInfo) { ClientBeatProcessor clientBeatProcessor = new ClientBeatProcessor(); clientBeatProcessor.setService(this); //将服务提供者的心跳信息设置进去 clientBeatProcessor.setRsInfo(rsInfo); //放入线程池 HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(clientBeatProcessor); } } public class HealthCheckReactor { public static ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleNow(Runnable task) { return GlobalExecutor.scheduleNamingHealth(task, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } }该方法内部主要就是更新对应实例下心跳时间,并且发送服务变更事件。
public class ClientBeatProcessor implements Runnable { private RsInfo rsInfo; private Service service; @Override public void run() { Service service = this.service; if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] processing beat: {}", rsInfo.toString()); } String ip = rsInfo.getIp(); String clusterName = rsInfo.getCluster(); int port = rsInfo.getPort(); //获取对应集群下的所有实例信息 Cluster cluster = service.getClusterMap().get(clusterName); List<Instance> instances = cluster.allIPs(true); for (Instance instance : instances) { //更新对应实例下最近一次心跳信息 if (instance.getIp().equals(ip) && instance.getPort() == port) { if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] refresh beat: {}", rsInfo.toString()); } //更新该实例最后一次心跳更新时间 instance.setLastBeat(System.currentTimeMillis()); if (!instance.isMarked()) { if (!instance.isHealthy()) { //如果之前该实例是不健康的,会被设置为健康 instance.setHealthy(true); Loggers.EVT_LOG .info("service: {} {POS} {IP-ENABLED} valid: {}:{}@{}, region: {}, msg: client beat ok", cluster.getService().getName(), ip, port, cluster.getName(), UtilsAndCommons.LOCALHOST_SITE); //发送服务变更事件 getPushService().serviceChanged(service); } } } } } } @Component public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { @Autowired private SwitchDomain switchDomain; private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void serviceChanged(Service service) { // merge some change events to reduce the push frequency: if (futureMap .containsKey(UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName()))) { return; } //发送服务变更事件 this.applicationContext.publishEvent(new ServiceChangeEvent(this, service)); } }PushService.onApplicationEvent监听ServiceChangeEvent事件
@Component public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { @Autowired private SwitchDomain switchDomain; private static ConcurrentMap<String, Future> futureMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static volatile ConcurrentMap<String, Receiver.AckEntry> ackMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, PushClient>> clientMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ServiceChangeEvent event) { Service service = event.getService(); String serviceName = service.getName(); String namespaceId = service.getNamespaceId(); //nacos服务端给每个客户端实例推送udp包时,该实例就是一个udp客户端, //clientMap中存放的就是这些udp客户端信息 Future future = GlobalExecutor.scheduleUdpSender(() -> { try { Loggers.PUSH.info(serviceName + " is changed, add it to push queue."); ConcurrentMap<String, PushClient> clients = clientMap .get(UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(namespaceId, serviceName)); if (MapUtils.isEmpty(clients)) { return; } Map<String, Object> cache = new HashMap<>(16); long lastRefTime = System.nanoTime(); for (PushClient client : clients.values()) { if (client.zombie()) { Loggers.PUSH.debug("client is zombie: " + client.toString()); clients.remove(client.toString()); Loggers.PUSH.debug("client is zombie: " + client.toString()); continue; } Receiver.AckEntry ackEntry; Loggers.PUSH.debug("push serviceName: {} to client: {}", serviceName, client.toString()); String key = getPushCacheKey(serviceName, client.getIp(), client.getAgent()); byte[] compressData = null; Map<String, Object> data = null; //switchDomain.getDefaultPushCacheMillis()默认是10秒, //即10000毫秒,不会进入这个分支,所以compressData=null if (switchDomain.getDefaultPushCacheMillis() >= 20000 && cache.containsKey(key)) { org.javatuples.Pair pair = (org.javatuples.Pair) cache.get(key); compressData = (byte[]) (pair.getValue0()); data = (Map<String, Object>) pair.getValue1(); Loggers.PUSH.debug("[PUSH-CACHE] cache hit: {}:{}", serviceName, client.getAddrStr()); } if (compressData != null) { ackEntry = prepareAckEntry(client, compressData, data, lastRefTime); } else { //compressData=null,所以会进入这个分支, //关注prepareHostsData(client)方法 ackEntry = prepareAckEntry(client, prepareHostsData(client), lastRefTime); if (ackEntry != null) { cache.put(key, new org.javatuples.Pair<>(ackEntry.origin.getData(), ackEntry.data)); } } Loggers.PUSH.info("serviceName: {} changed, schedule push for: {}, agent: {}, key: {}", client.getServiceName(), client.getAddrStr(), client.getAgent(), (ackEntry == null ? null : ackEntry.key)); //通过udp协议向nacos 消费者客户端推送数据 udpPush(ackEntry); } } catch (Exception e) { Loggers.PUSH.error("[NACOS-PUSH] failed to push serviceName: {} to client, error: {}", serviceName, e); } finally { futureMap.remove(UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(namespaceId, serviceName)); } }, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); futureMap.put(UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(namespaceId, serviceName), future); } }咋一看这个方法很复杂,首先看一下这个方法的主体结构,其实主要就是开启了一个一次性延迟任务(注意不是定时任务,只会执行一次),它的职责就是通过udp协议向nacos客户端推送数据,对应方法:udpPush(ackEntry)
udpPush(ackEntry)
@Component public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { private static volatile ConcurrentMap<String, Receiver.AckEntry> ackMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static volatile ConcurrentMap<String, Receiver.AckEntry> ackMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private static DatagramSocket udpSocket; private static Receiver.AckEntry udpPush(Receiver.AckEntry ackEntry) { if (ackEntry == null) { Loggers.PUSH.error("[NACOS-PUSH] ackEntry is null."); return null; } //如果重试次数大于MAX_RETRY_TIMES=1次,就不再发送udp包了 if (ackEntry.getRetryTimes() > MAX_RETRY_TIMES) { Loggers.PUSH.warn("max re-push times reached, retry times {}, key: {}", ackEntry.retryTimes, ackEntry.key); ackMap.remove(ackEntry.key); udpSendTimeMap.remove(ackEntry.key); failedPush += 1; return ackEntry; } try { if (!ackMap.containsKey(ackEntry.key)) { totalPush++; } //结合Receiver.run()可知,ackMap存放的是已发送udp但是还没收到ACK响应的数据包 ackMap.put(ackEntry.key, ackEntry); //udpSendTimeMap存放每个udp数据包开始发送的事件 udpSendTimeMap.put(ackEntry.key, System.currentTimeMillis()); Loggers.PUSH.info("send udp packet: " + ackEntry.key); //发送udp数据包 udpSocket.send(ackEntry.origin); ackEntry.increaseRetryTime(); //又提交了一个延迟任务(延迟10秒),其实这个任务的作用就是重试, //实现的效果就是当前发送完udp之后,如果没有收到ACK响应,就隔10秒重发一次,并且只重试一次 GlobalExecutor.scheduleRetransmitter(new Retransmitter(ackEntry), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(ACK_TIMEOUT_NANOS), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); return ackEntry; } catch (Exception e) { Loggers.PUSH.error("[NACOS-PUSH] failed to push data: {} to client: {}, error: {}", ackEntry.data, ackEntry.origin.getAddress().getHostAddress(), e); ackMap.remove(ackEntry.key); udpSendTimeMap.remove(ackEntry.key); failedPush += 1; return null; } } //实现重发的任务Retransmitter public static class Retransmitter implements Runnable { Receiver.AckEntry ackEntry; public Retransmitter(Receiver.AckEntry ackEntry) { this.ackEntry = ackEntry; } @Override public void run() { //如果ackMap中包含该数据包,就重发一次,ackMap存放的都是没有收到ACK响应的包 //如果接受到ACK响应,会移除(参考Receiver线程) if (ackMap.containsKey(ackEntry.key)) { Loggers.PUSH.info("retry to push data, key: " + ackEntry.key); udpPush(ackEntry); } } } }上面这段代码其实就一个作用:向nacos客户端发送udp包,如果隔了10秒还没收到ACK响应,就重发一次(通过另一个延迟任务实现)。
PushService类结构
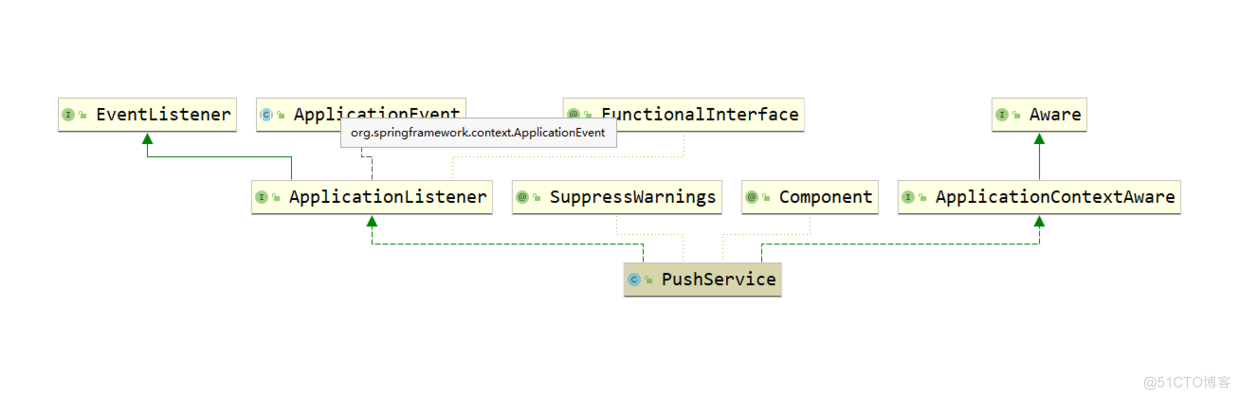
第一眼就会看到一个关键接口:ApplicationListener,没错,PushService这个类就是一个事件监听类,它所监听的事件正是ServiceChangeEvent,onApplicationEvent方法已经在上面讲过了。
static代码块
PushService中有一个static代码块,static代码块在类被主动引用的时候会首先执行一次。
@Component @SuppressWarnings("PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule") public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { static { try { udpSocket = new DatagramSocket(); Receiver receiver = new Receiver(); Thread inThread = new Thread(receiver); inThread.setDaemon(true); inThread.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.naming.push.receiver"); inThread.start(); GlobalExecutor.scheduleRetransmitter(() -> { try { removeClientIfZombie(); } catch (Throwable e) { Loggers.PUSH.warn("[NACOS-PUSH] failed to remove client zombie"); } }, 0, 20, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (SocketException e) { Loggers.SRV_LOG.error("[NACOS-PUSH] failed to init push service"); } } }这个代码块里先是开启了一个线程:Receiver,然后又开启了一个定时任务(20秒执行一次),对应的逻辑代码:removeClientIfZombie(),对他们分别简单讲解下。
Receiver线程
@Component @SuppressWarnings("PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule") public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { public static class Receiver implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (true) { byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 64]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length); try { udpSocket.receive(packet); String json = new String(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8).trim(); AckPacket ackPacket = JacksonUtils.toObj(json, AckPacket.class); InetSocketAddress socketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) packet.getSocketAddress(); String ip = socketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress(); int port = socketAddress.getPort(); //接受到ACK响应的时间距离上次接受到的时间之差如果大于10秒 //ACK_TIMEOUT_NANOS = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(10L) if (System.nanoTime() - ackPacket.lastRefTime > ACK_TIMEOUT_NANOS) { Loggers.PUSH.warn("ack takes too long from {} ack json: {}", packet.getSocketAddress(), json); } String ackKey = getAckKey(ip, port, ackPacket.lastRefTime); AckEntry ackEntry = ackMap.remove(ackKey); if (ackEntry == null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "unable to find ackEntry for key: " + ackKey + ", ack json: " + json); } long pushCost = System.currentTimeMillis() - udpSendTimeMap.get(ackKey); Loggers.PUSH .info("received ack: {} from: {}:{}, cost: {} ms, unacked: {}, total push: {}", json, ip, port, pushCost, ackMap.size(), totalPush); //pushCostMap存放每个数据包的耗时 pushCostMap.put(ackKey, pushCost); udpSendTimeMap.remove(ackKey); } catch (Throwable e) { Loggers.PUSH.error("[NACOS-PUSH] error while receiving ack data", e); } } } } }这个线程一直轮询接受UDP协议的响应,接受到ACK响应包后没干其它事,主要就是维护一些属性:ackMap、pushCostMap、udpSendTimeMap,至于这些属性干嘛用的(其中pushCostMap已经知道,见上面注释),可以往下看,后面会有用到。
定时任务:removeClientIfZombie()
@Component @SuppressWarnings("PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule") public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { //根据方法命名,可以隐约猜到,应该是移除僵尸客户端的 private static void removeClientIfZombie() { int size = 0; for (Map.Entry<String, ConcurrentMap<String, PushClient>> entry : clientMap.entrySet()) { ConcurrentMap<String, PushClient> clientConcurrentMap = entry.getValue(); for (Map.Entry<String, PushClient> entry1 : clientConcurrentMap.entrySet()) { PushClient client = entry1.getValue(); //如果是僵尸client,则从clientMap中移除 if (client.zombie()) { clientConcurrentMap.remove(entry1.getKey()); } } size += clientConcurrentMap.size(); } if (Loggers.PUSH.isDebugEnabled()) { Loggers.PUSH.debug("[NACOS-PUSH] clientMap size: {}", size); } } public class PushClient { public boolean zombie() { return System.currentTimeMillis() - lastRefTime > switchDomain.getPushCacheMillis(serviceName); } } }该方法就是维护了clientMap(见onApplicationEvent方法中注释),在client.zombie()判断规则中有个很关键的属性:lastRefTime(位于PushClient中),要知道这个属性的意思,就需要知道clientMap是如何初始化的(clientMap中存放的就是PushClient)?
到这里,Receiver线程中维护的那几个属性的作用也已经很清楚了:
- ackMap:存放所有已经发送了udp但还没收到客户端的ACK响应的数据包;
- pushCostMap:存放每个数据包的耗时;
- udpSendTimeMap:存放每个数据包开始发送的时间; Receiver线程就是用来接收ACK响应的,所以每接受到一个响应包,就会从ackMap和udpSendTimeMap中移除,所以Receiver线程的作用也很清楚了。
UDP客户端的初始化
clientMap中存放的是所有的udp客户端,nacos服务端需要往客户端通过udp协议推送数据,所以需要将所有客户端进行初始化。
不知道大家有没有注意到上面onApplicationEvent方法的代码中我加了两个注释,在构建Receiver.AckEntry对象的时候,会执行到这行代码:ackEntry = prepareAckEntry(client, prepareHostsData(client), lastRefTime),然后重点关注下prepareHostsData(client)方法:
@Component @SuppressWarnings("PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule") public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { private static Map<String, Object> prepareHostsData(PushClient client) throws Exception { Map<String, Object> cmd = new HashMap<String, Object>(2); cmd.put("type", "dom"); //初始化udp客户端 cmd.put("data", client.getDataSource().getData(client)); return cmd; } } //InstanceController类中pushDataSource初始化代码 @RestController @RequestMapping(UtilsAndCommons.NACOS_NAMING_CONTEXT + "/instance") public class InstanceController { private DataSource pushDataSource = new DataSource() { @Override public String getData(PushService.PushClient client) { ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode(); try { //默认传入的udp的端口为0,即不开启nacos服务端udp推送功能 result = doSrvIpxt(client.getNamespaceId(), client.getServiceName(), client.getAgent(), client.getClusters(), client.getSocketAddr().getAddress().getHostAddress(), 0, StringUtils.EMPTY, false, StringUtils.EMPTY, StringUtils.EMPTY, false); } catch (Exception e) { String serviceNameField = "name"; String lastRefTimeField = "lastRefTime"; if (result.get(serviceNameField) == null) { String serviceName = client.getServiceName(); if (serviceName == null) { serviceName = StringUtils.trimToEmpty(serviceName); } result.put(serviceNameField, serviceName); result.put(lastRefTimeField, System.currentTimeMillis()); } Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("PUSH-SERVICE: service is not modified", e); } // overdrive the cache millis to push mode result.put("cacheMillis", switchDomain.getPushCacheMillis(client.getServiceName())); return result.toString(); } }; //继续看doSrvIpxt方法,方法很长,这里只贴片段 public ObjectNode doSrvIpxt(String namespaceId, String serviceName, String agent, String clusters, String clientIP, int udpPort, String env, boolean isCheck, String app, String tid, boolean healthyOnly) throws Exception { ClientInfo clientInfo = new ClientInfo(agent); ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode(); Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName); long cacheMillis = switchDomain.getDefaultCacheMillis(); // now try to enable the push try { //udpPort是服务发现时指定的 if (udpPort > 0 && pushService.canEnablePush(agent)) { pushService .addClient(namespaceId, serviceName, clusters, agent, new InetSocketAddress(clientIP, udpPort), pushDataSource, tid, app); cacheMillis = switchDomain.getPushCacheMillis(serviceName); } } catch (Exception e) { Loggers.SRV_LOG .error("[NACOS-API] failed to added push client {}, {}:{}", clientInfo, clientIP, udpPort, e); cacheMillis = switchDomain.getDefaultCacheMillis(); } //代码略…… } }doSrvIpxt方法会调用PushService类的addClient方法,而clientMap就是在addClient方法中初始化的:
@Component public class PushService implements ApplicationContextAware, ApplicationListener<ServiceChangeEvent> { public void addClient(String namespaceId, String serviceName, String clusters, String agent, InetSocketAddress socketAddr, DataSource dataSource, String tenant, String app) { PushClient client = new PushClient(namespaceId, serviceName, clusters, agent, socketAddr, dataSource, tenant, app); addClient(client); } public void addClient(PushClient client) { // client is stored by key 'serviceName' because notify event is driven by serviceName change String serviceKey = UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(client.getNamespaceId(), client.getServiceName()); ConcurrentMap<String, PushClient> clients = clientMap.get(serviceKey); if (clients == null) { clientMap.putIfAbsent(serviceKey, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(1024)); clients = clientMap.get(serviceKey); } PushClient oldClient = clients.get(client.toString()); if (oldClient != null) { oldClient.refresh(); } else { PushClient res = clients.putIfAbsent(client.toString(), client); if (res != null) { Loggers.PUSH.warn("client: {} already associated with key {}", res.getAddrStr(), res.toString()); } Loggers.PUSH.debug("client: {} added for serviceName: {}", client.getAddrStr(), client.getServiceName()); } } }看到这我们已经清楚clientMap初始化的来龙去脉了,现在再回看一下僵尸client的判断规则:
public boolean zombie() { //客户端从初始化到响应ack,超过了10秒,就认为是僵尸client //lastRefTime是PushClient类中的属性,默认是当前时间,可以代表PushClient初始化的时间 //这句代码就可以理解为:如果一个客户端长时间没有进行ack响应,就认识它是僵尸client return System.currentTimeMillis() - lastRefTime > switchDomain.getPushCacheMillis(serviceName); }当任务某个客户端是僵尸client时,就从客户端集合(clientMap)中移除,下次就不会向它推送udp数据包了。
Nacos心跳机制总结
PushService类的主要功能基本上讲的差不多了,可能有人会觉得一脸懵,nacos源码想说明白确实不容易,里面有太多的异步任务,跳来跳去,很容易晕,我这里做一个总结吧。
udp推送
- 当服务端注册表中实例发送了变更时,就会发布ServiceChangeEvent事件,就会被PushService监听到,监听到之后就会以服务维度向客户端通过udp协议推送通知,从clientMap中找出需要推送的客户端进行能推送;
- 如果发送失败或者超过10秒没收到ack响应,就会隔10秒进行重试(从ackMap中找出需要重试的包,ackMap由Receiver线程维护),最大重试次数默认为1次,超过1次就不再发送;
ack接收
- PushService类的static代码块中开启了守护线程Receiver,用于循环接收来自客户端的ack响应,使用ackMap维护所有已发送udp包但还没有进行ack响应的包,如果接收到ack响应,就从ackMap中移除;
udp客户端集合维护
- PushService类的static代码块中开启了一个定时任务(20秒一次)专门用来维护clientMap(存放了所有需要进行udp推送的客户端),如果发现哪个客户端从初始化到响应ack的时间间隔超过了10秒,就从clientMap中移除,那么下次就不会再往这个客户端推送udp了。
Nacos服务的健康检查
Nacos Server会开启一个定时任务来检查注册服务的健康情况,对于超过15秒没收到客户端的心跳实例会将它的 healthy属性置为false,此时当客户端不会将该实例的信息发现,如果某个服务的实例超过30秒没收到心跳,则剔除该实例,如果剔除的实例恢复,发送心跳则会恢复。
当有实例注册的时候,我们会看到有个service.init()的方法,该方法的实现主要是将ClientBeatCheckTask加入到线程池当中:
@Component public class ServiceManager implements RecordListener<Service> { @Resource(name = "consistencyDelegate") private ConsistencyService consistencyService; private void putServiceAndInit(Service service) throws NacosException { putService(service); service = getService(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName()); //启动服务检查 service.init(); consistencyService .listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), true), service); consistencyService .listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), false), service); Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[NEW-SERVICE] {}", service.toJson()); } }ClientBeatCheckTask中的run方法主要做两件事心跳时间超过15秒则设置该实例信息为不健康状况和心跳时间超过30秒则删除该实例信息,如下代码:
public class ClientBeatCheckTask implements Runnable { private Service service; @Override public void run() { try { if (!getDistroMapper().responsible(service.getName())) { return; } if (!getSwitchDomain().isHealthCheckEnabled()) { return; } //获取服务所有实例信息 List<Instance> instances = service.allIPs(true); // first set health status of instances: for (Instance instance : instances) { //如果心跳时间超过15秒则设置该实例信息为不健康状况 if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getInstanceHeartBeatTimeOut()) { if (!instance.isMarked()) { if (instance.isHealthy()) { //设置该实例信息为不健康状况 instance.setHealthy(false); Loggers.EVT_LOG .info("{POS} {IP-DISABLED} valid: {}:{}@{}@{}, region: {}, msg: client timeout after {}, last beat: {}", instance.getIp(), instance.getPort(), instance.getClusterName(), service.getName(), UtilsAndCommons.LOCALHOST_SITE, instance.getInstanceHeartBeatTimeOut(), instance.getLastBeat()); getPushService().serviceChanged(service); ApplicationUtils.publishEvent(new InstanceHeartbeatTimeoutEvent(this, instance)); } } } } if (!getGlobalConfig().isExpireInstance()) { return; } // then remove obsolete instances: for (Instance instance : instances) { if (instance.isMarked()) { continue; } //如果心跳时间超过30秒则删除该实例信息 if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getIpDeleteTimeout()) { // delete instance Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[AUTO-DELETE-IP] service: {}, ip: {}", service.getName(), JacksonUtils.toJson(instance)); deleteIp(instance); } } } catch (Exception e) { Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("Exception while processing client beat time out.", e); } } } public static final long DEFAULT_HEART_BEAT_TIMEOUT = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(15); public static final long DEFAULT_IP_DELETE_TIMEOUT = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(30);首先我们来看一下deleteIp方法,该方法内部主要通过构建删除请求,发送删除请求:
public class ClientBeatCheckTask implements Runnable { private void deleteIp(Instance instance) { try { NamingProxy.Request request = NamingProxy.Request.newRequest(); request.appendParam("ip", instance.getIp()).appendParam("port", String.valueOf(instance.getPort())) .appendParam("ephemeral", "true").appendParam("clusterName", instance.getClusterName()) .appendParam("serviceName", service.getName()).appendParam("namespaceId", service.getNamespaceId()); //构建Url String url = "http://" + IPUtil.localHostIP() + IPUtil.IP_PORT_SPLITER + EnvUtil.getPort() + EnvUtil.getContextPath() + UtilsAndCommons.NACOS_NAMING_CONTEXT + "/instance?" + request.toUrl(); //发送Http删除请求 // delete instance asynchronously: HttpClient.asyncHttpDelete(url, null, null, new Callback<String>() { @Override public void onReceive(RestResult<String> result) { if (!result.ok()) { Loggers.SRV_LOG .error("[IP-DEAD] failed to delete ip automatically, ip: {}, caused {}, resp code: {}", instance.toJson(), result.getMessage(), result.getCode()); } } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) { Loggers.SRV_LOG .error("[IP-DEAD] failed to delete ip automatically, ip: {}, error: {}", instance.toJson(), throwable); } @Override public void onCancel() { } }); } catch (Exception e) { Loggers.SRV_LOG .error("[IP-DEAD] failed to delete ip automatically, ip: {}, error: {}", instance.toJson(), e); } } }删除实例的接口
@RestController @RequestMapping(UtilsAndCommons.NACOS_NAMING_CONTEXT + "/instance") public class InstanceController { @CanDistro @DeleteMapping @Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE) public String deregister(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Instance instance = getIpAddress(request); String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID); String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME); NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName); Service service = serviceManager.getService(namespaceId, serviceName); if (service == null) { Loggers.SRV_LOG.warn("remove instance from non-exist service: {}", serviceName); return "ok"; } //删除方法 serviceManager.removeInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral(), instance); return "ok"; } }内部通过调用ServiceManager的removeInstance方法
@Component public class ServiceManager implements RecordListener<Service> { public void removeInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips) throws NacosException { Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName); synchronized (service) { removeInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral, service, ips); } } private void removeInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral, Service service, Instance... ips) throws NacosException { String key = KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral); //排除要删除的实例信息 List<Instance> instanceList = substractIpAddresses(service, ephemeral, ips); Instances instances = new Instances(); instances.setInstanceList(instanceList); //更新实例信息 consistencyService.put(key, instances); } }重点看下substractIpAddresses内部通过调用updateIpAddresses,该方法内部主要就是移除到超过30秒的实例信息
@Component public class ServiceManager implements RecordListener<Service> { private List<Instance> substractIpAddresses(Service service, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips) throws NacosException { return updateIpAddresses(service, UtilsAndCommons.UPDATE_INSTANCE_ACTION_REMOVE, ephemeral, ips); } public List<Instance> updateIpAddresses(Service service, String action, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips) throws NacosException { Datum datum = consistencyService .get(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), ephemeral)); //获取所有实例信息 List<Instance> currentIPs = service.allIPs(ephemeral); Map<String, Instance> currentInstances = new HashMap<>(currentIPs.size()); Set<String> currentInstanceIds = Sets.newHashSet(); for (Instance instance : currentIPs) { currentInstances.put(instance.toIpAddr(), instance); currentInstanceIds.add(instance.getInstanceId()); } //初始化Map Map<String, Instance> instanceMap; if (datum != null && null != datum.value) { instanceMap = setValid(((Instances) datum.value).getInstanceList(), currentInstances); } else { instanceMap = new HashMap<>(ips.length); } for (Instance instance : ips) { if (!service.getClusterMap().containsKey(instance.getClusterName())) { Cluster cluster = new Cluster(instance.getClusterName(), service); cluster.init(); service.getClusterMap().put(instance.getClusterName(), cluster); Loggers.SRV_LOG .warn("cluster: {} not found, ip: {}, will create new cluster with default configuration.", instance.getClusterName(), instance.toJson()); } //移除超过30秒的实例信息 if (UtilsAndCommons.UPDATE_INSTANCE_ACTION_REMOVE.equals(action)) { instanceMap.remove(instance.getDatumKey()); } else { Instance oldInstance = instanceMap.get(instance.getDatumKey()); if (oldInstance != null) { instance.setInstanceId(oldInstance.getInstanceId()); } else { instance.setInstanceId(instance.generateInstanceId(currentInstanceIds)); } instanceMap.put(instance.getDatumKey(), instance); } } if (instanceMap.size() <= 0 && UtilsAndCommons.UPDATE_INSTANCE_ACTION_ADD.equals(action)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "ip list can not be empty, service: " + service.getName() + ", ip list: " + JacksonUtils .toJson(instanceMap.values())); } return new ArrayList<>(instanceMap.values()); } }心跳机制简单图

参考: https://blog.csdn.net/jb84006/article/details/117634375
https://www.cnblogs.com/wtzbk/p/14366240.html
