Resource
-
Spring的Resource接口位于包org.springframework.core.io中;
-
Spring定义Resource接口是为了提供更强的访问底层资源能力的抽象;
-
对spring来说Resource接口代表着物理存在的任何资源。
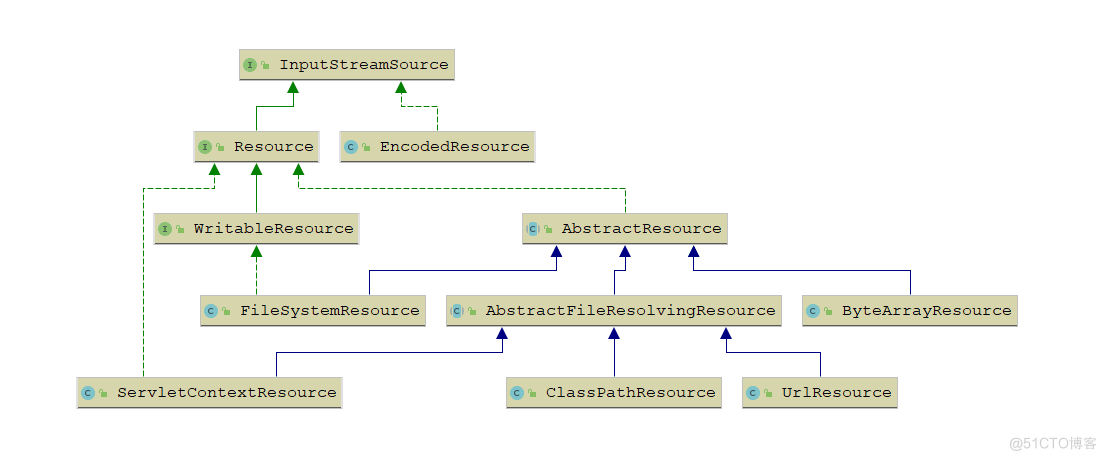
其中,最常用的有四个:
- ClassPathResource:通过 ClassPathResource 以类路径的方式进行访问。
- FileSystemResource:通过 FileSystemResource 以文件系统绝对路径的方式进行访问。
- ServletContextResource:通过 ServletContextResource 以相对于Web应用根目录的方式进行访问。
- UrlResource:通过java.net.URL来访问资源,当然它也支持File格式,如“file:”。
Resource接口
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { //判断资源是否存在 boolean exists(); //判断资源的内容是否可读 default boolean isReadable() { return exists(); } //判断当前Resource代表的底层资源是否已经打开 default boolean isOpen() { return false; } //判断是否是文件系统的文件 default boolean isFile() { return false; } //返回当前资源对应的URL URL getURL() throws IOException; //返回当前资源对应的URI URI getURI() throws IOException; //返回当前资源对应的File File getFile() throws IOException; default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException { return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream()); } //返回当前资源的长度 long contentLength() throws IOException; //返回当前Resource代表的底层资源的最后修改时间 long lastModified() throws IOException; //根据资源的相对路径创建新资源 Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; //获取资源的文件名 @Nullable String getFilename(); //返回当前资源的底层资源的描述符 String getDescription(); //获取当前资源代表的输入流 InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException; }它是spring访问资源最基本的接口。实际访问的时候直接用Resource接口就可以,不必使用其子类。其实经常用到的(resource的真正目的)方法是public InputStream getInputStream()。
FileSystemResource
public class FileSystemResource extends AbstractResource implements WritableResource { private final String path; @Nullable private final File file; private final Path filePath; public FileSystemResource(String path) { Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null"); this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path); this.file = new File(path); this.filePath = this.file.toPath(); } @Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { try { return Files.newInputStream(this.filePath); } catch (NoSuchFileException ex) { throw new FileNotFoundException(ex.getMessage()); } } }这里的path一般要给出绝对路径,当然也可以是相对路径,如果是相对路径要注意其根目录。
ClassPathResource
public class ClassPathResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource { private final String path; @Nullable private ClassLoader classLoader; @Nullable private Class<?> clazz; public ClassPathResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null"); String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path); if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) { pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1); } this.path = pathToUse; this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); } @Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { InputStream is; if (this.clazz != null) { is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path); } else if (this.classLoader != null) { is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path); } else { is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path); } if (is == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist"); } return is; } }这里是通过Class或者ClassLoader的getResourceAsStream()方法来获得InputStream的。其path一般都是以“classpath:”开头,如果以“classpath*:”开头表示所有与给定名称匹配的classpath资源都应该被获取。
ServletContextResource
public class ServletContextResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource implements ContextResource { private final ServletContext servletContext; private final String path; public ServletContextResource(ServletContext servletContext, String path) { // check ServletContext Assert.notNull(servletContext, "Cannot resolve ServletContextResource without ServletContext"); this.servletContext = servletContext; // check path Assert.notNull(path, "Path is required"); String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path); if (!pathToUse.startsWith("/")) { pathToUse = "/" + pathToUse; } this.path = pathToUse; } @Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { InputStream is = this.servletContext.getResourceAsStream(this.path); if (is == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException("Could not open " + getDescription()); } return is; } }ServletContextResource通过ServletContext的getResourceAsStream()来取得InputStream,这里path必须以“/”开头,并且相对于当前上下文的根目录。如常用的path="/WEB-INF/web.xml"。
UrlResource
public class UrlResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource { @Nullable private final URI uri; private final URL url; private final URL cleanedUrl; public UrlResource(URI uri) throws MalformedURLException { Assert.notNull(uri, "URI must not be null"); this.uri = uri; this.url = uri.toURL(); this.cleanedUrl = getCleanedUrl(this.url, uri.toString()); } @Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { URLConnection con = this.url.openConnection(); ResourceUtils.useCachesIfNecessary(con); try { return con.getInputStream(); } catch (IOException ex) { // Close the HTTP connection (if applicable). if (con instanceof HttpURLConnection) { ((HttpURLConnection) con).disconnect(); } throw ex; } } }UrlResource 封装了java.net.URL,它能够被用来访问任何通过URL可以获得的对象,例如:文件、HTTP对象、FTP对象等。
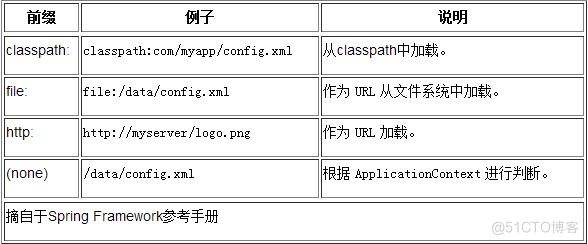
所有的URL都有个标准的 String表示,这些标准前缀可以标识不同的URL类型,包括file:访问文件系统路径,http: 通过HTTP协议访问的资源,ftp: 通过FTP访问的资源等等。
在Spring配置文件中,我们只需要给出字符串类型的path即可,Spring会通过ResourceEditor(java.beans.PropertyEditor的子类)和ResourceLoader把给定的path转换为相应的Resource。
转换规则如下:
ResourceLoader
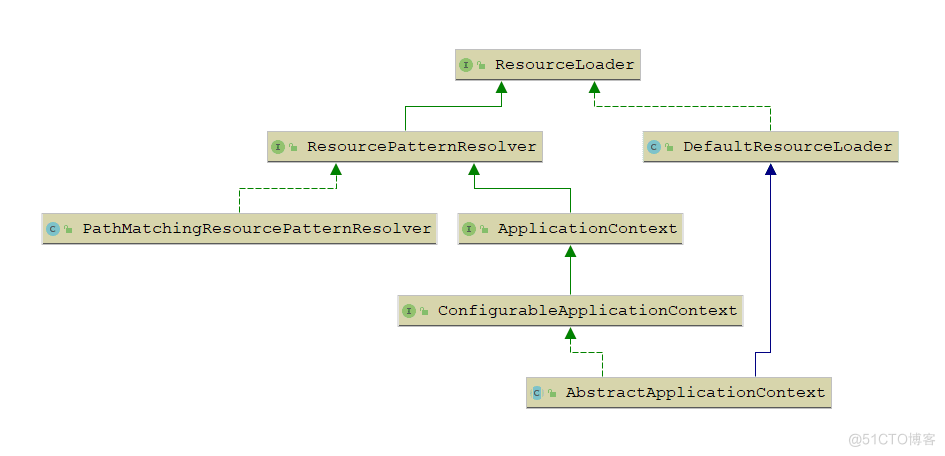
Resource接口有很多实现类,我们当然可以使用各自的构造函数创建符合需求的Resource实例,然而Spring提供了ResourceLoader接口用于实现不同的Resource加载策略,即将不同Resource实例的创建交给ResourceLoader来计算。
在ResourceLoader接口中,主要定义了一个方法:getResource(),它通过提供的资源location参数获取Resource实例,该实例可以是ClasPathResource、FileSystemResource、UrlResource等,但是该方法返回的Resource实例并不保证该Resource一定是存在的,需要调用exists方法判断。该方法需要支持以下模式的资源加载:
- 1、URL位置资源,如”file:C:/test.dat”
- 2、ClassPath位置资源,如”classpath:test.dat”
- 3、相对路径资源,如”WEB-INF/test.dat”,此时返回的Resource实例根据实现不同而不同。
ResourceLoader接口还提供了getClassLoader()方法,在加载classpath下的资源时作为参数传入ClassPathResource。将ClassLoader暴露出来,对于想要获取ResourceLoader和使用ClassLoader的用户来说,可以直接调用getClassLoader()方法获得,而不是依赖ThreadContextClassLoader,因为有些时候ResourceLoader内部使用自定义的ClassLoader。
在实际开发中经常会遇到需要通过某种匹配方式查找资源,而且可能有多个资源匹配这种模式,在Spring中提供了ResourcePatternResolver接口用于实现这种需求,该接口继承自ResourceLoader接口,定义了自己的模式匹配接口:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader { String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:"; //支持路径匹配模式返回多个Resource实例 Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException; }ResourcePatternResolver定义了getResources()方法用于根据传入的locationPattern查找和其匹配的Resource实例,并以数组的形式返回,在返回的数组中不可以存在相同的Resource实例。ResourcePatternResolver中还定义了”classpath*:”模式,用于表示查找classpath下所有的匹配Resource。
在Spring中,对ResourceLoader提供了DefaultResourceLoader、FileSystemResourceLoader和ServletContextResourceLoader等单独实现,对ResourcePatternResolver接口则提供了PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver实现。并且ApplicationContext接口继承了ResourcePatternResolver,在实现中,ApplicationContext的实现类会将逻辑代理给相关的单独实现类,如PathMatchingResourceLoader等。在ApplicationContext中ResourceLoaderAware接口,可以将ResourceLoader(自身)注入到实现该接口的Bean中,在Bean中可以将其强制转换成ResourcePatternResolver接口使用(为了安全,强转前需要判断)。
DefaultResourceLoader类
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader { @Nullable private ClassLoader classLoader; private final Set<ProtocolResolver> protocolResolvers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4); private final Map<Class<?>, Map<Resource, ?>> resourceCaches = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(4); //获取Resource的具体实现类实例 @Override public Resource getResource(String location) { Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); //ProtocolResolver ,用户自定义协议资源解决策略 for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : getProtocolResolvers()) { Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this); if (resource != null) { return resource; } } //如果是以/开头,则构造ClassPathContextResource返回 if (location.startsWith("/")) { return getResourceByPath(location); } //若以classpath:开头,则构造 ClassPathResource 类型资源并返回,在构造该资源时, // 通过 getClassLoader()获取当前的 ClassLoader else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); } else { //构造 URL ,尝试通过它进行资源定位,若没有抛出 MalformedURLException 异常, // 则判断是否为 FileURL , 如果是则构造 FileUrlResource 类型资源,否则构造 UrlResource。 // 若在加载过程中抛出 MalformedURLException 异常, // 则委派 getResourceByPath() 实现资源定位加载 try { // Try to parse the location as a URL... URL url = new URL(location); return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url)); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { // No URL -> resolve as resource path. return getResourceByPath(location); } } } protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader()); } }DefaultResourceLoader是ResourceLoader的默认实现,AbstractApplicationContext继承该类。它接收ClassLoader作为构造函数的参数,或使用不带参数的构造函数,此时ClassLoader使用默认的ClassLoader(一般为ThreadContextClassLoader),ClassLoader也可以通过set方法后继设置。
其最主要的逻辑实现在getResource方法中,该方法首先判断传入的location是否以”classpath:”开头,如果是,则创建ClassPathResource(移除”classpath:”前缀),否则尝试创建UrlResource,如果当前location没有定义URL的协议(即以”file:”、”zip:”等开头,比如使用相对路径”resources/META-INF/MENIFEST.MF),创建UrlResource会抛出MalformedURLException,此时调用getResourceByPath()方法获取Resource实例。getResourceByPath()方法默认返回ClassPathContextResource实例。在FileSystemResourceLoader中有不同实现。
FileSystemResourceLoader类
FileSystemResourceLoader继承自DefaultResourceLoader,它的getResource方法的实现逻辑和DefaultResourceLoader相同,不同的是它实现了自己的getResourceByPath方法,即当UrlResource创建失败时,它会使用FileSystemContextResource实例而不是ClassPathContextResource:
public class FileSystemResourceLoader extends DefaultResourceLoader { @Override protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } return new FileSystemContextResource(path); } private static class FileSystemContextResource extends FileSystemResource implements ContextResource { public FileSystemContextResource(String path) { super(path); } @Override public String getPathWithinContext() { return getPath(); } } }使用该类时要特别注意的一点:即使location以”/”开头,资源的查找还是相对于VM启动时的相对路径而不是绝对路径(从以上代码片段也可以看出,它会先截去开头的”/”),这个和Servlet Container保持一致。如果需要使用绝对路径,需要添加”file:”前缀。
ServletContextResourceLoader类
ServletContextResourceLoader类继承自DefaultResourceLoader,和FileSystemResourceLoader一样,它的getResource方法的实现逻辑和DefaultResourceLoader相同,不同的是它实现了自己的getResourceByPath方法,即当UrlResource创建失败时,它会使用ServletContextResource实例:
public class ServletContextResourceLoader extends DefaultResourceLoader { private final ServletContext servletContext; public ServletContextResourceLoader(ServletContext servletContext) { this.servletContext = servletContext; } //此实现支持web应用程序根目录下的文件路径。 @Override protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, path); } }这里的path即使以”/”开头,也是相对ServletContext的路径,而不是绝对路径,要使用绝对路径,需要添加”file:”前缀。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver类
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver类实现了ResourcePatternResolver接口,它包含了对ResourceLoader接口的引用,在对继承自ResourceLoader接口的方法的实现会代理给该引用, 同时在getResources()方法实现中,当找到一个匹配的资源location时,可以使用该引用解析成Resource实例。默认使用DefaultResourceLoader类,用户可以使用构造函数传入自定义的ResourceLoader。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver还包含了一个对PathMatcher接口的引用,该接口基于路径字符串实现匹配处理,如判断一个路径字符串是否包含通配符(’*’、’?’),判断给定的path是否匹配给定的pattern等。Spring提供了AntPathMatcher对PathMatcher的默认实现,表达该PathMatcher是采用Ant风格的实现。其中PathMatcher的接口定义如下:
public interface PathMatcher { boolean isPattern(String path); boolean match(String pattern, String path); boolean matchStart(String pattern, String path); String extractPathWithinPattern(String pattern, String path); Map<String, String> extractUriTemplateVariables(String pattern, String path); Comparator<String> getPatternComparator(String path); String combine(String pattern1, String pattern2); }isPattern(String path):
判断path是否是一个pattern,即判断path是否包含通配符:
@Override public boolean isPattern(@Nullable String path) { if (path == null) { return false; } boolean uriVar = false; for (int i = 0; i < path.length(); i++) { char c = path.charAt(i); if (c == '*' || c == '?') { return true; } if (c == '{') { uriVar = true; continue; } if (c == '}' && uriVar) { return true; } } return false; }match(String pattern, String path):
判断给定path是否可以匹配给定pattern:
@Override public boolean match(String pattern, String path) { return doMatch(pattern, path, true, null); }matchStart(String pattern, String path):
判断给定path是否可以匹配给定pattern,该方法不同于match,它只是做部分匹配,即当发现给定path匹配给定path的可能性比较大时,即返回true。在PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver中,可以先使用它确定需要全面搜索的范围,然后在这个比较小的范围内再找出所有的资源文件全路径做匹配运算。
在AntPathMatcher中,都使用doMatch方法实现,match方法的fullMatch为true,而matchStart的fullMatch为false:
@Override public boolean matchStart(String pattern, String path) { return doMatch(pattern, path, false, null); }ServletContextResourcePatternResolver类
ServletContextResourcePatternResolver类继承自PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver类,它重写了父类的文件查找逻辑,即对ServletContextResource资源使用ServletContext.getResourcePaths()方法来查找参数目录下的文件,而不是File.listFiles()方法:
AbstractApplicationContext对ResourcePatternResolver接口的实现
ApplicationContext接口继承了ResourcePatternResolver接口,也就实现了ResourcePatternResolver这个接口,所以任何的ApplicationContext实现都可以看成是一个ResourceLoader或ResourcePatternResolver的实例。
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver { }在AbstractApplicationContext中,对ResourcePatternResolver的实现只是简单的将getResources()方法的实现代理给resourcePatternResolver字段,而该字段默认在AbstractApplicationContext创建时新建一个PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver实例:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext { public AbstractApplicationContext() { this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver(); } public AbstractApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { this(); setParent(parent); } @Override public void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { this.parent = parent; if (parent != null) { Environment parentEnvironment = parent.getEnvironment(); if (parentEnvironment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { getEnvironment().merge((ConfigurableEnvironment) parentEnvironment); } } } /** * 返回此 ResourcePatternResolver资源模式解析器, * 用于将多个资源的位置按照模式解析到资源实例中。 * 默认是org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver。 * 支持ant风格的位置模式。 * 可以在子类中重写,用于扩展解析策略,例如在web环境中。在需要解决位置模式时不要调用此函数。 * 相反,调用上下文的getResources方法,它将委托给ResourcePatternResolver。 * @return 此应用上下文的 ResourcePatternResolver 资源模式解析器 * @see #getResources * @see org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver */ protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() { return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this); } @Override public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern); } } public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null"); this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; }这就意味着整个ApplicationContext的实现类完全可以支持ResourceLoader以及ResourcePatternResolver,这也是高级容器支持统一资源加载的原因,在容器读取配置的时候便委派给了PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver以及DefaultResourceLoader来执行。
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/shadow_zed/article/details/72540927
https://www.cnblogs.com/jixp/articles/10702486.html
